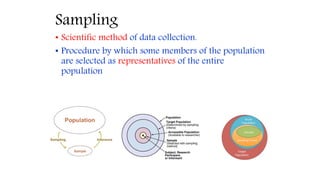
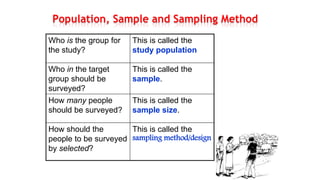
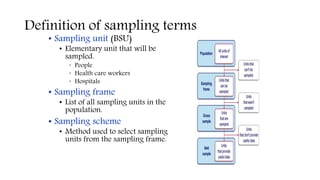
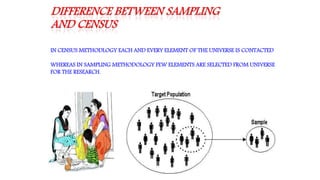
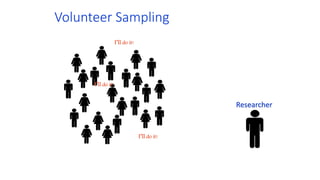
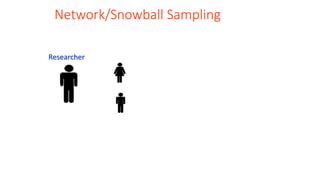
This document discusses sampling techniques used in scientific studies. It defines sampling as selecting a representative subset of a population to make inferences about the entire population. The key points are:
1) Sampling can save time and money compared to a census by studying a representative sample rather than the entire population.
2) Important principles of sampling include choosing samples systematically and objectively, clearly defining sample units, ensuring sample units are independent, and using consistent sampling methods.
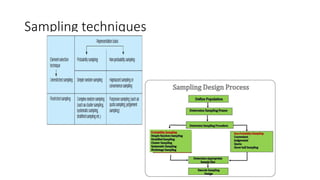
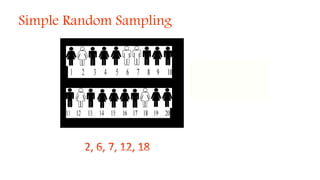
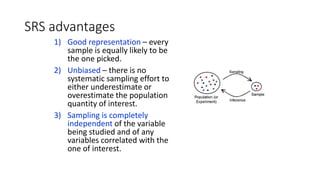
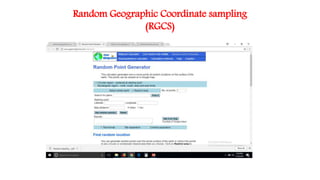
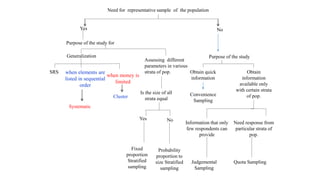
3) There are various sampling techniques including simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, cluster sampling, and systematic random sampling. Each technique has advantages and limitations depending on the characteristics of the population and goals of the study.