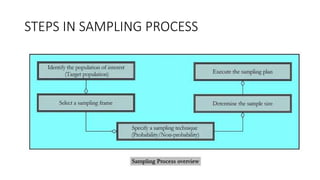
The document outlines the 5 main steps in the sampling process:
1. Identify the target population that researchers want to generalize findings to.
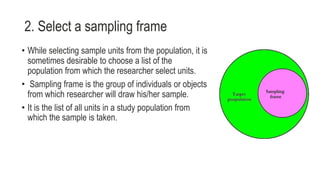
2. Select a sampling frame which is a list of the population units to sample from.
3. Specify the sampling technique as either probability/random or non-probability/non-random.
4. Determine an appropriate sample size based on factors like time, cost and desired accuracy.
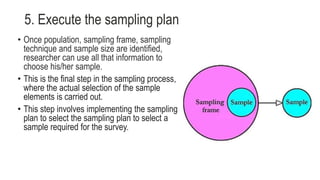
5. Execute the sampling plan by implementing the selection of the specific sample units.