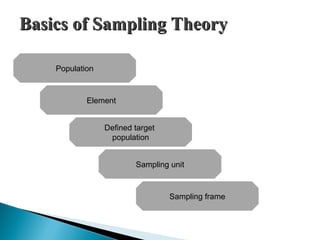
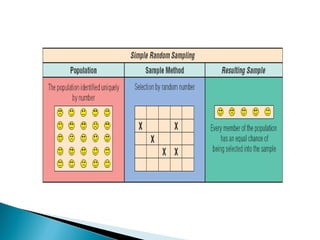
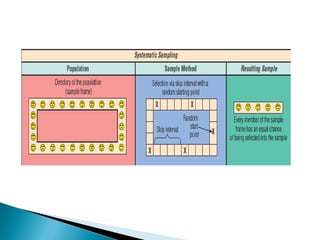
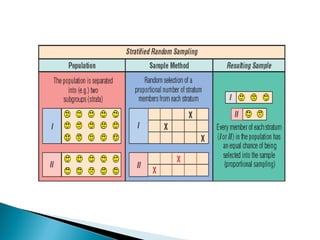
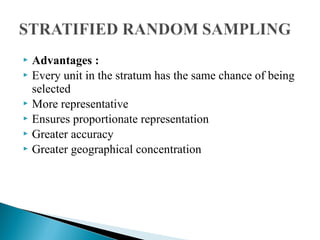
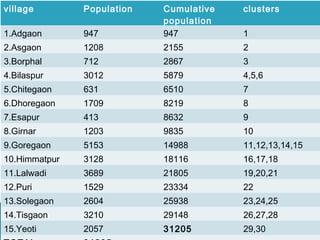
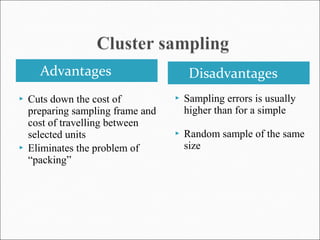
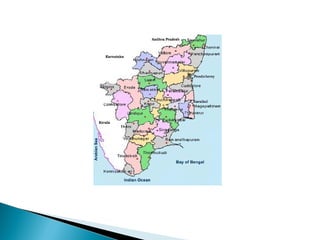
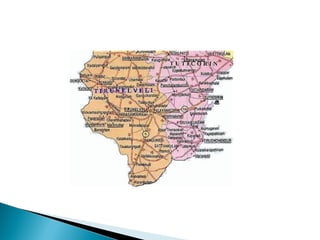
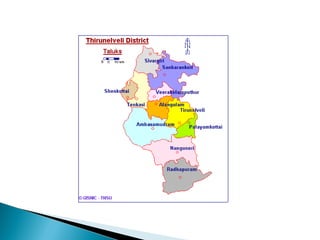
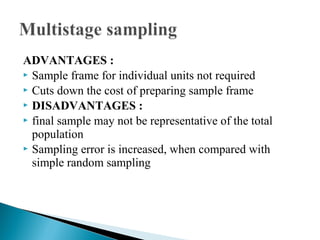
This document discusses various sampling methods used in research. It begins by defining key sampling terms like population, sample, sampling unit, and sampling frame. It then describes the main types of sampling: probability sampling methods which use random selection and allow statistical inference about the population, and non-probability sampling methods which do not use random selection. Specific probability methods discussed include simple random sampling, systematic random sampling, stratified random sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling. Common non-probability methods mentioned are convenience sampling, purposive sampling, and snowball sampling. The document provides details on how to implement several of these sampling techniques and notes their relative advantages and limitations.