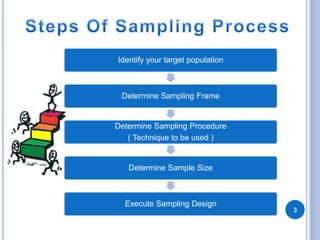
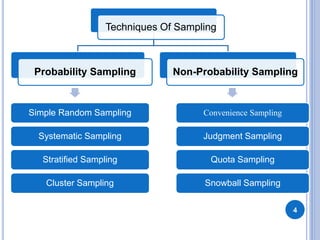
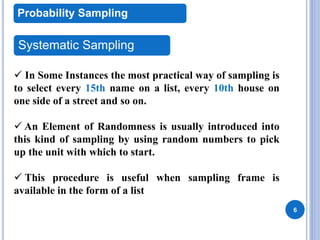
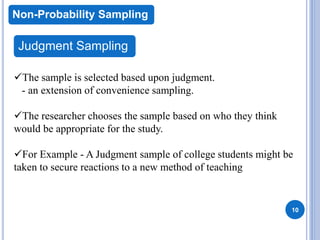
This document discusses sampling and different sampling techniques. It defines sampling as selecting a subset of individuals from a population to gather data and make conclusions about the larger population. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling, where every member of the population has a chance of being selected, and non-probability sampling, where not every member has a known chance of selection. Some common sampling techniques discussed are simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, convenience sampling, judgment sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling. The document also distinguishes between random sampling error and non-sampling error.