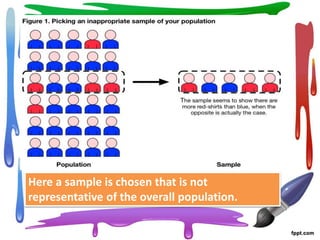
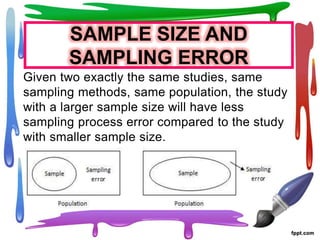
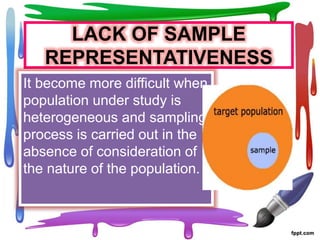
Sampling errors occur when a sample is not truly representative of the overall population being studied. Sampling errors are more likely when samples are small, heterogeneous populations are studied without accounting for differences, or the sampling process is not well planned or executed. Factors that can contribute to sampling errors include a lack of knowledge about appropriate sampling methods, insufficient resources, lack of participation from subjects, and not having existing sampling frames for large populations. Researchers should take care to select samples that are representative of populations and employ sampling techniques appropriately based on the phenomenon being studied.