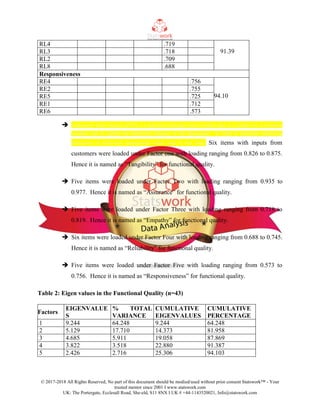
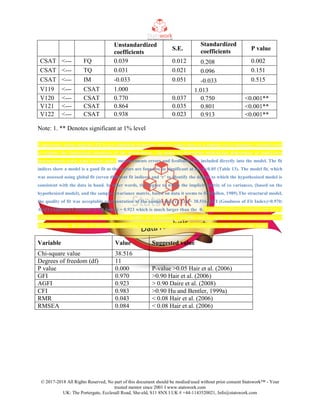
The document discusses exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and its application for analyzing multi-item measurement scales in the context of customer service quality, identifying five key dimensions: tangibility, assurance, empathy, reliability, and responsiveness. It details the statistical methods used, including principal components analysis with varimax rotation, and confirms the findings through confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) on data gathered from wind turbine customers. The fit indices indicate that the proposed models are consistent with the data and sufficiently represent the underlying quality dimensions.