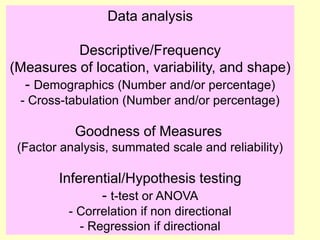
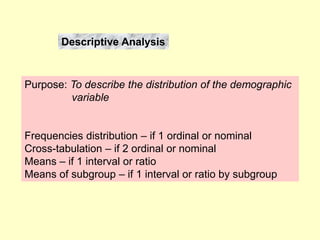
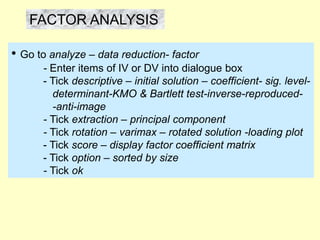
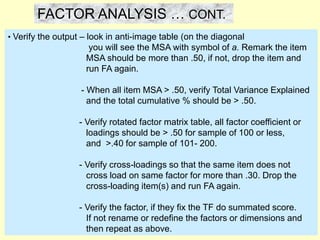
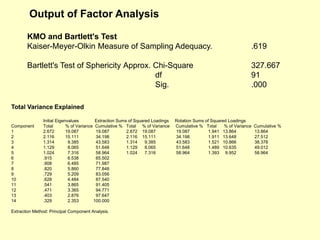
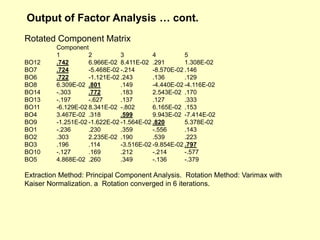
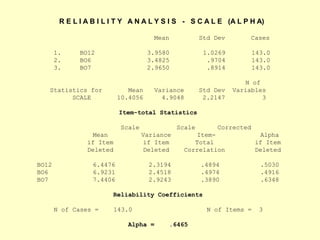
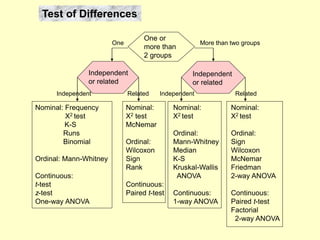
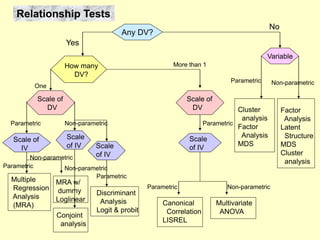
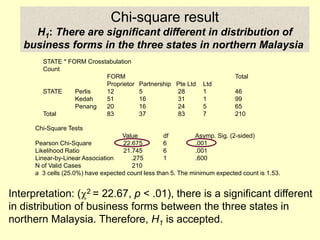
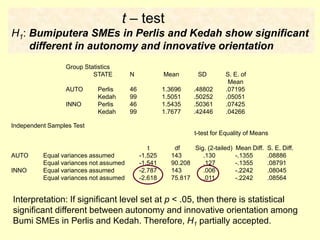
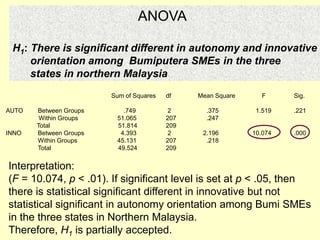
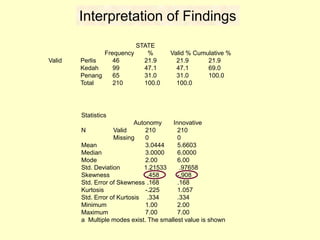
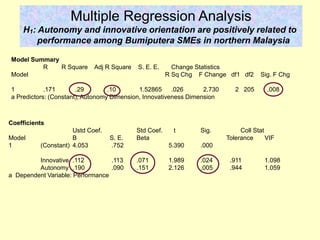
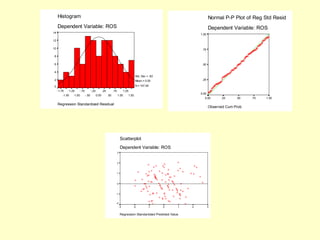
This document provides information on analyzing data using SPSS 13.0. It discusses objectives of data analysis, an overview of SPSS, data management, entry, analysis techniques including descriptive analysis, reliability analysis, factor analysis, tests of differences and relationships. Descriptive analysis is used to describe distributions. Reliability analysis and factor analysis are used to assess validity and reliability. Appropriate techniques for comparing groups and analyzing relationships depend on measurement levels and number of variables. Examples of outputs from SPSS are also included.