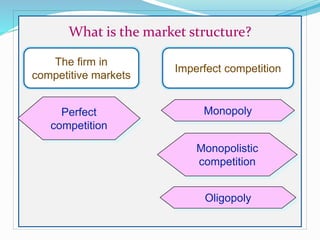
This document defines different types of market structures:
- Perfect competition has many small firms, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, and firms that are price-takers.
- Monopoly has a single seller of a unique product without close substitutes that can influence price.
- Monopolistic competition features many small differentiated product sellers with some product differentiation and freedom of entry and exit.
- Oligopoly has a market dominated by a small number of interdependent firms that closely watch each other's actions.