This presentation discusses document analysis and character recognition. It begins with an introduction that motivates DAR and CR research. It then describes the fields of off-line and on-line document analysis and CR. Key aspects covered include preprocessing, feature extraction, segmentation, learning and classification. The objective is to achieve high character recognition accuracy for isolated and cursive Arabic characters using rule-based algorithms. The presentation describes the database collection and a rule-based algorithm for isolated offline handwritten character recognition.















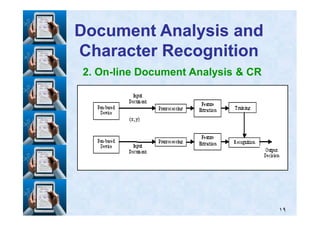




































![Classically [Classically [1111], on], on--line recognizers consist of:line recognizers consist of:
11. A preprocessor. A preprocessor
22. A classifier which provides estimates of. A classifier which provides estimates of
probabilities for the different categories ofprobabilities for the different categories of
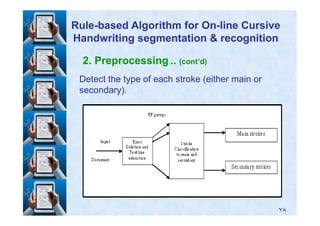
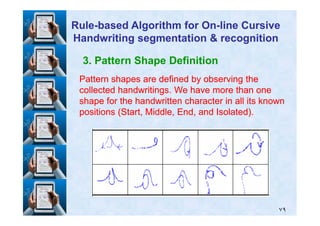
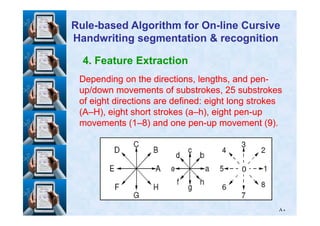
RuleRule--based Algorithm for Onbased Algorithm for On--line Cursiveline Cursive
Handwriting segmentation & recognitionHandwriting segmentation & recognition
٦٠
probabilities for the different categories ofprobabilities for the different categories of
characters andcharacters and
33. A postprocessor, which eventually incorporates. A postprocessor, which eventually incorporates
a language modela language model
We propose a ruleWe propose a rule--based algorithm for the two earlybased algorithm for the two early
stages of an onstages of an on--line recognizer cursive Arabicline recognizer cursive Arabic
handwritinghandwriting](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masterdefense-150201032744-conversion-gate01/85/Rule-based-algorithm-for-handwritten-characters-recognition-60-320.jpg)
















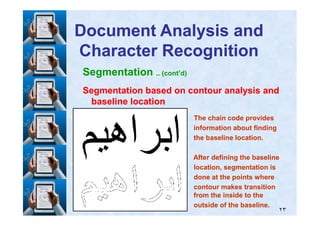
![5. Training .. (cont’d)
S. ElS. El--Dabi [Dabi [33,, 99] used to extract sequentially a set of features] used to extract sequentially a set of features
and accumulating the values while moving along the wordand accumulating the values while moving along the word
image (column by column) then checked against the featureimage (column by column) then checked against the feature
space of a given font until a character is recognized or the endspace of a given font until a character is recognized or the end
RuleRule--based Algorithm for Onbased Algorithm for On--line Cursiveline Cursive
Handwriting segmentation & recognitionHandwriting segmentation & recognition
٨٣
space of a given font until a character is recognized or the endspace of a given font until a character is recognized or the end
of the word is reached.of the word is reached.
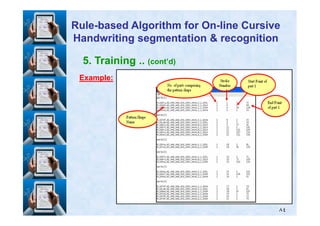
We need to build a registry comprising all skeleton patternsWe need to build a registry comprising all skeleton patterns
(feature space) of all pattern shapes.(feature space) of all pattern shapes.
We made transcription files of the training data to describeWe made transcription files of the training data to describe
the content of each training file. These files stand forthe content of each training file. These files stand for
manual segmentation of the word strokesmanual segmentation of the word strokes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masterdefense-150201032744-conversion-gate01/85/Rule-based-algorithm-for-handwritten-characters-recognition-83-320.jpg)



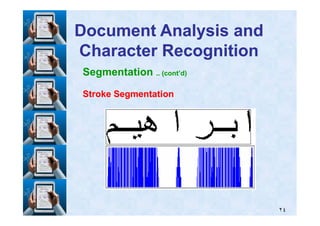
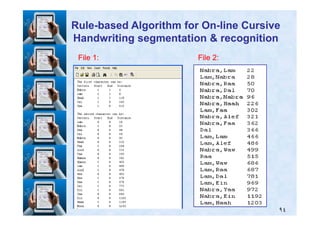
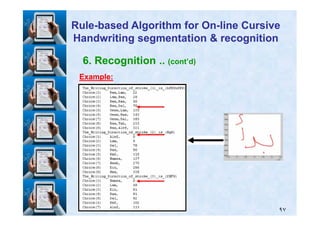
![6. Recognition .. (cont’d)
GroupGroup11 = ['A' 'B' 'C' 'D' 'E' 'F' 'G' 'H'], Group= ['A' 'B' 'C' 'D' 'E' 'F' 'G' 'H'], Group22 = ['a' 'b' 'c' 'd' 'e' 'f' 'g' 'h']= ['a' 'b' 'c' 'd' 'e' 'f' 'g' 'h']
& Group& Group33 = ['= ['11' '' '22' '' '33' '' '44' '' '55' '' '66' '' '77' '' '88'];'];
The penalties are decided as follows:The penalties are decided as follows:
RuleRule--based Algorithm for Onbased Algorithm for On--line Cursiveline Cursive
Handwriting segmentation & recognitionHandwriting segmentation & recognition
٨٩](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masterdefense-150201032744-conversion-gate01/85/Rule-based-algorithm-for-handwritten-characters-recognition-89-320.jpg)





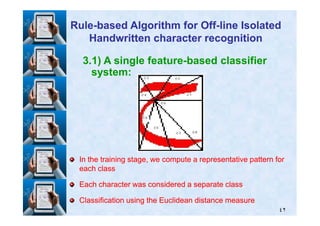
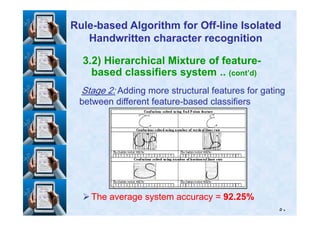
![Results and Discussion
RuleRule--based Algorithm for Onbased Algorithm for On--line Cursiveline Cursive
Handwriting segmentation & recognitionHandwriting segmentation & recognition
TestTraining
44No. of writers
94317No. of words
4351814No. of char.
٩٨
Results representation:Results representation:
Neskovic and Cooper [Neskovic and Cooper [1414], have developed an on], have developed an on--lineline
segmentationsegmentation--byby--recognition system for English using HMMsrecognition system for English using HMMs
together with Dynamic programming technique (Viterbi). Thetogether with Dynamic programming technique (Viterbi). The
output of the system is a ranked set of words. The system'soutput of the system is a ranked set of words. The system's
performance depends on the writer, on his style and the clarityperformance depends on the writer, on his style and the clarity
of his writing: For good writers the correct word is in the topof his writing: For good writers the correct word is in the top 55
words overwords over 9797% of the time. For bad writers the correct word is% of the time. For bad writers the correct word is
in the topin the top 55 words overwords over 9090% of the time.% of the time.
4351814No. of char.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masterdefense-150201032744-conversion-gate01/85/Rule-based-algorithm-for-handwritten-characters-recognition-98-320.jpg)
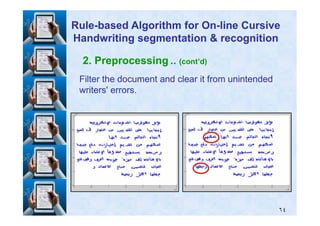
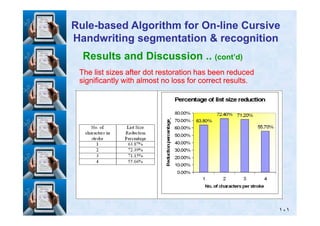
![Results and Discussion .. (cont’d)
Using the same terminology in [Using the same terminology in [1414], we can represent our], we can represent our
results as follows:results as follows:
Before dot restoration, the correct segmentationBefore dot restoration, the correct segmentation--
recognition results of the test strokes exist within the toprecognition results of the test strokes exist within the top
list memberslist members 9393%% of the time (of the time (9696%% of the time for the testof the time for the test
RuleRule--based Algorithm for Onbased Algorithm for On--line Cursiveline Cursive
Handwriting segmentation & recognitionHandwriting segmentation & recognition
٩٩
list memberslist members 9393%% of the time (of the time (9696%% of the time for the testof the time for the test
characters).characters).
After dot restoration, the correct segmentationAfter dot restoration, the correct segmentation--recognitionrecognition
results of the test strokes exist within the top list membersresults of the test strokes exist within the top list members
9292%% of the time (of the time (9595%% of the time for the test characters).of the time for the test characters).
Recognition
Probability
Correctly
Recognized
Total Number
.95٤١٥٤٣٥Characters
.92٢٧٩٣٠٥Strokes
.74٧٠٩٤Words](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masterdefense-150201032744-conversion-gate01/85/Rule-based-algorithm-for-handwritten-characters-recognition-99-320.jpg)






![Following the pen trajectory causes the loss ofFollowing the pen trajectory causes the loss of
the global pattern shape information which thethe global pattern shape information which the
offoff--line image provides (e.g., confusions betweenline image provides (e.g., confusions between
{{وو,, رر} and {} and {ـھـ,ـھـ, ـمفـ.)}ـمفـ}).
On the other hand, converting the onOn the other hand, converting the on--line data toline data to
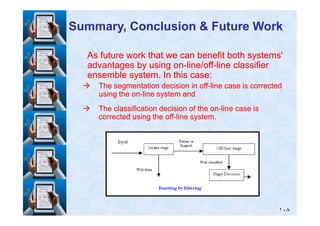
Summary, Conclusion & Future WorkSummary, Conclusion & Future Work
١٠٧
On the other hand, converting the onOn the other hand, converting the on--line data toline data to
bitmaps and trying to solve it as offbitmaps and trying to solve it as off--line is a veryline is a very
hard task, still under research and is not yethard task, still under research and is not yet
achieving reliable results [achieving reliable results [4040,, 4141,, 4242].].
Besides, the segmentation task is quite harder inBesides, the segmentation task is quite harder in
case of offcase of off--line than online than on--line.line.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masterdefense-150201032744-conversion-gate01/85/Rule-based-algorithm-for-handwritten-characters-recognition-107-320.jpg)