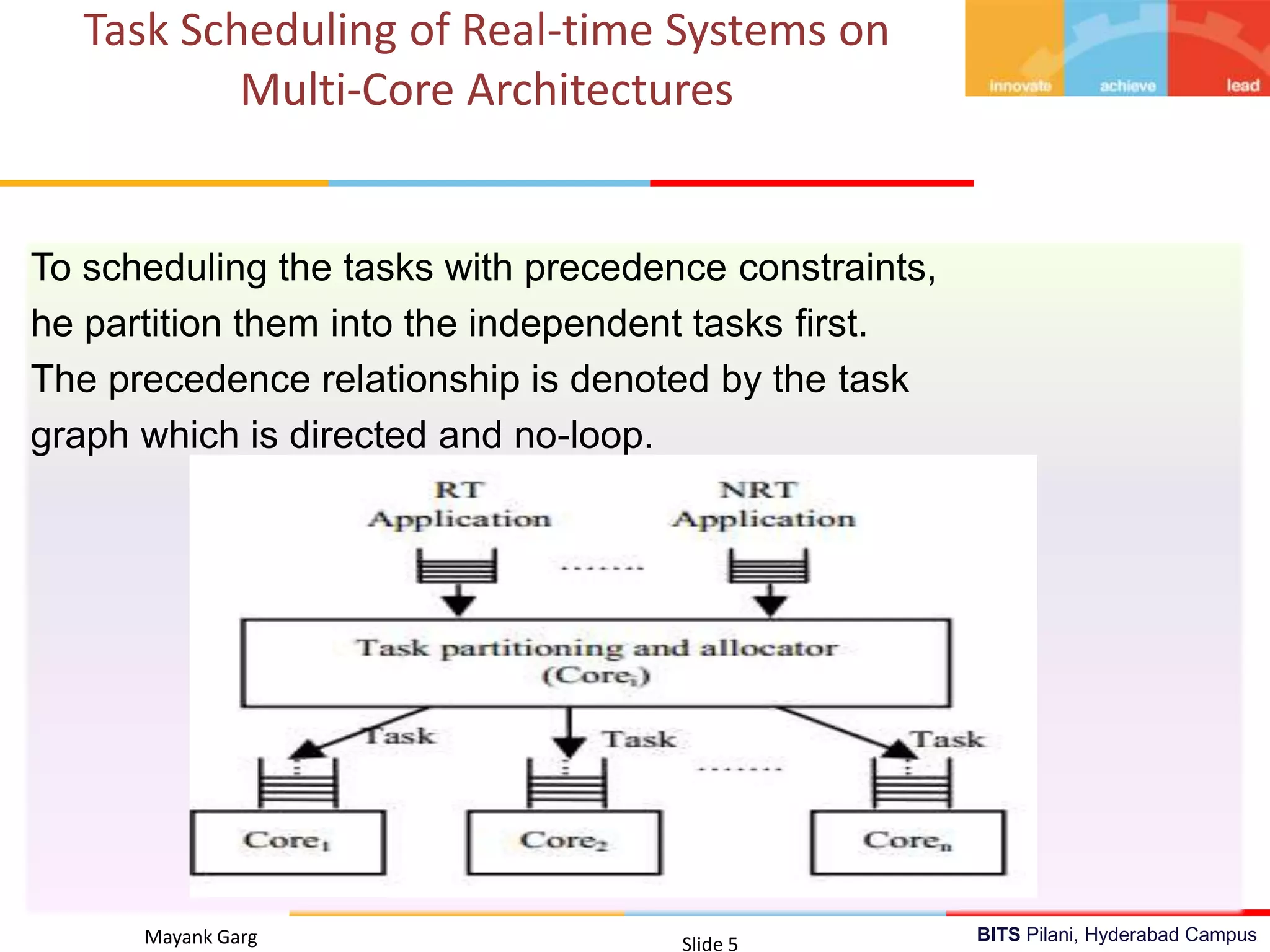
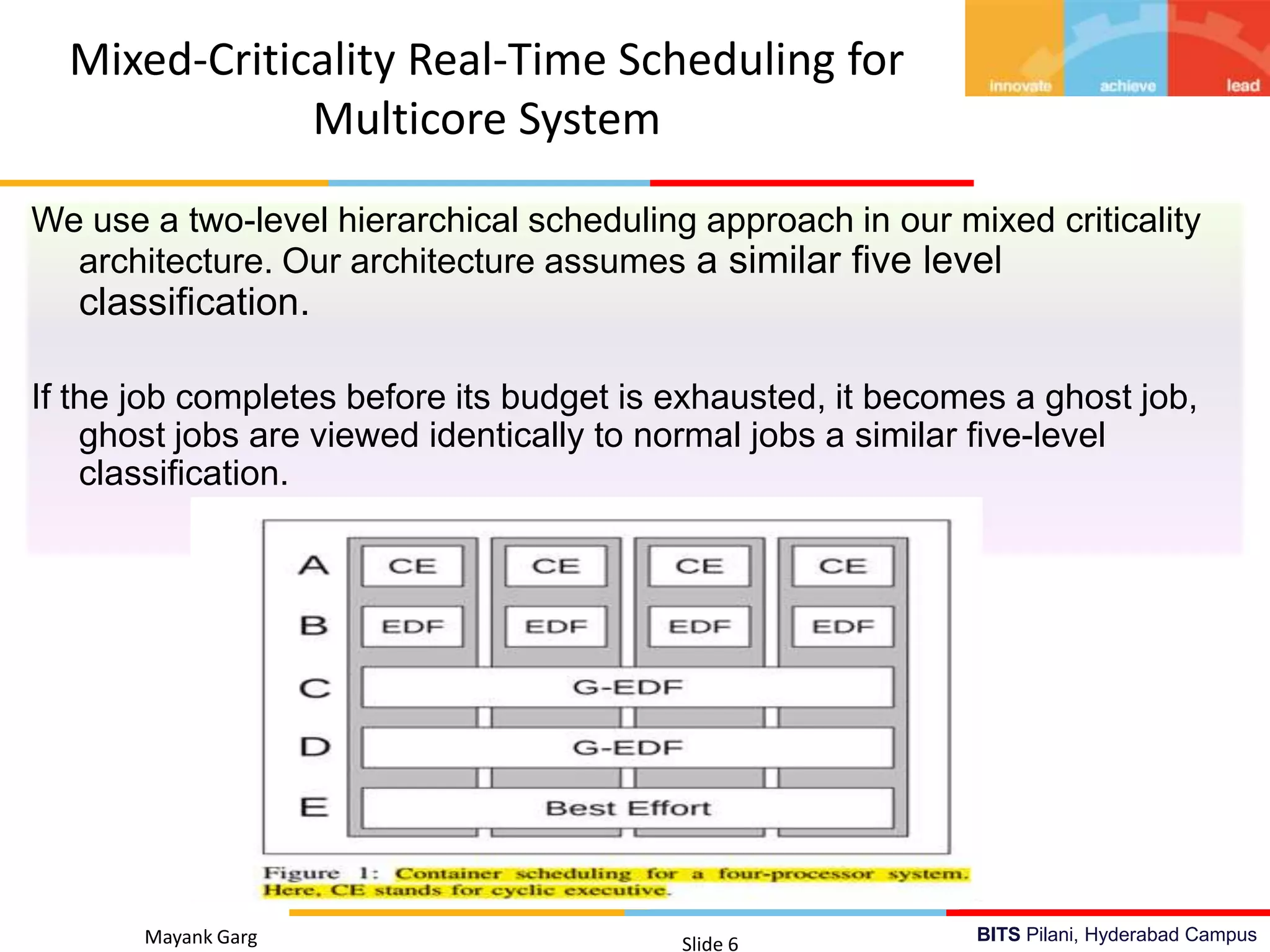
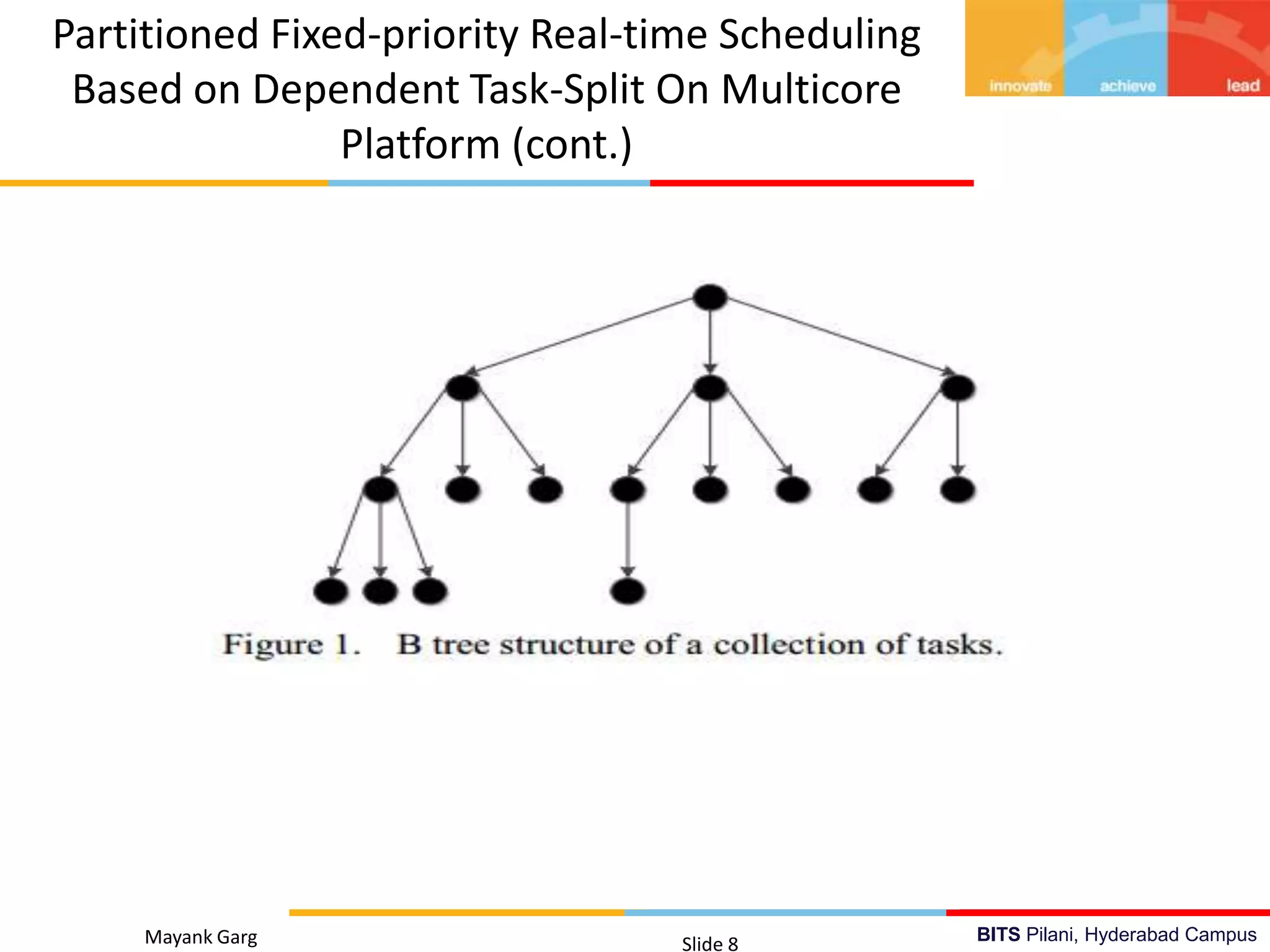
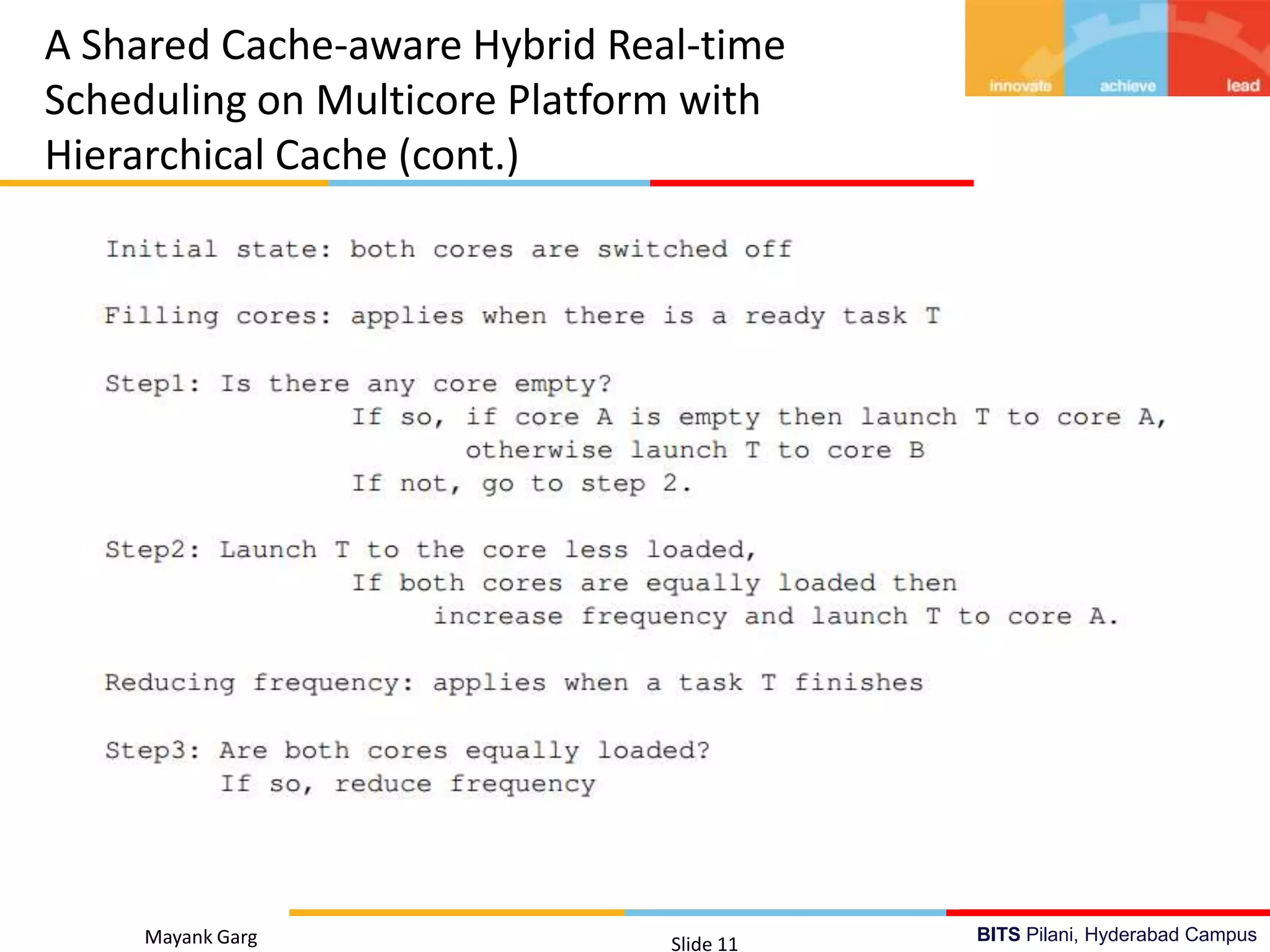
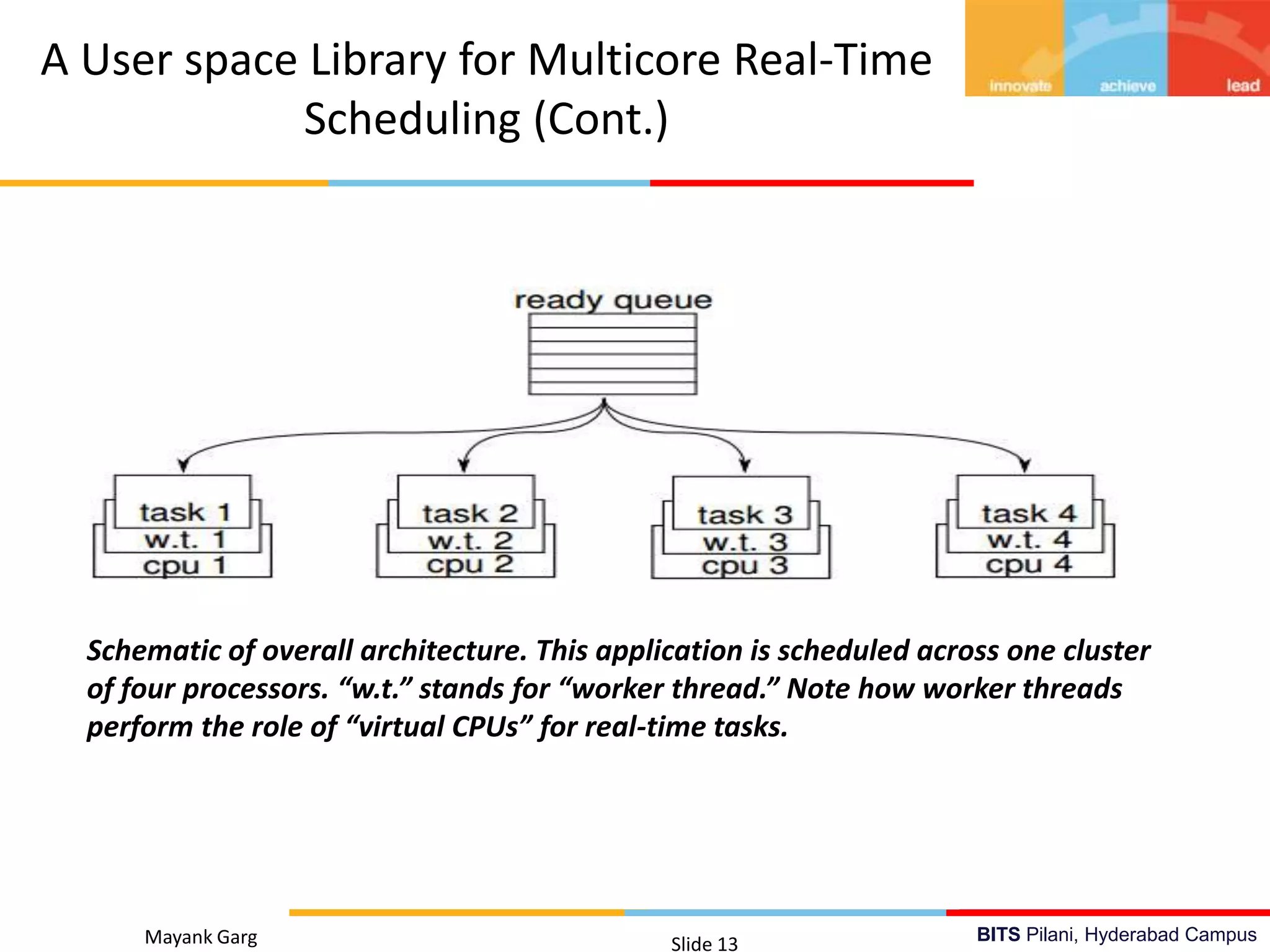
The document presents research by Mayank Garg on real-time scheduling in multi-core systems at the BITS Pilani Hyderabad campus. It discusses various scheduling methodologies including partitioned fixed-priority, mixed-criticality, and power-aware scheduling, along with the design of a user space library for real-time applications. The goal is to develop an optimal scheduling algorithm that enhances the performance of multi-core real-time systems.