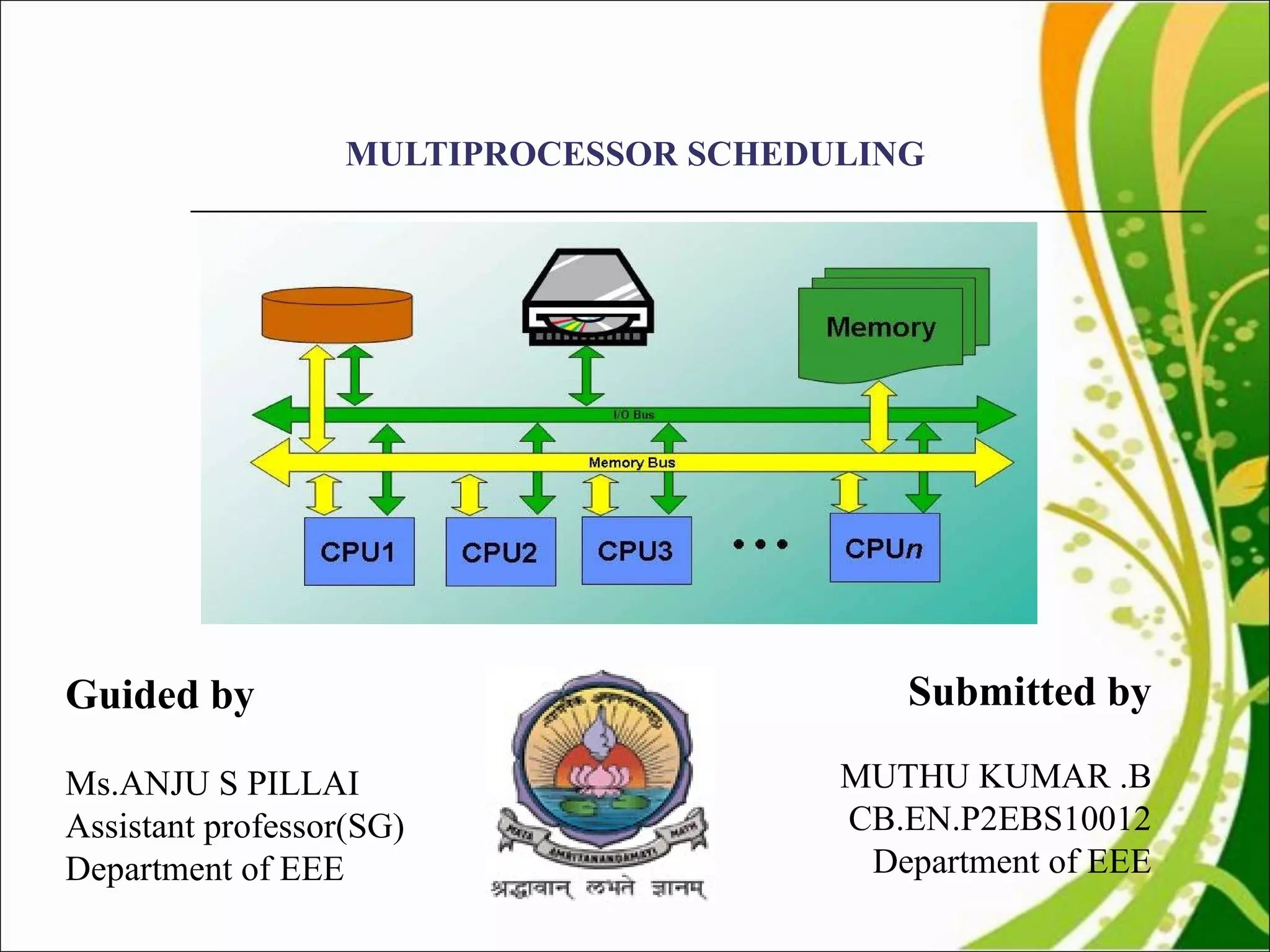
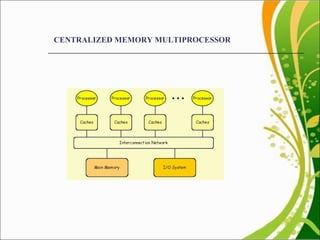
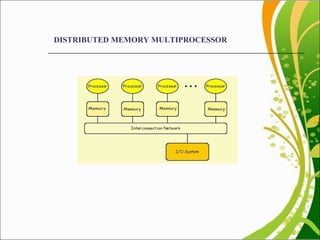
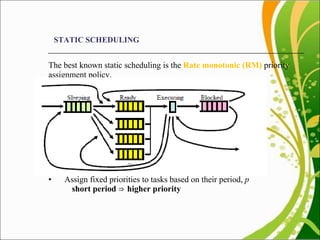
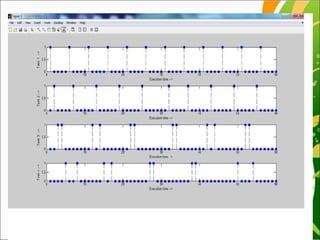
This document discusses multiprocessor scheduling. It describes generating synthetic tasks, assigning priorities using static and dynamic methods like Rate Monotonic and Earliest Deadline First algorithms, and allocating tasks to processors using static and dynamic allocation strategies. Real-time scheduling is important for applications like patient monitoring, smart environments, and mobile devices. The work aims to find better processor utilization by evaluating different task-processor assignment policies and scheduling tasks dynamically.