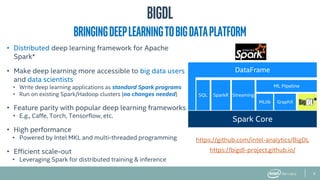
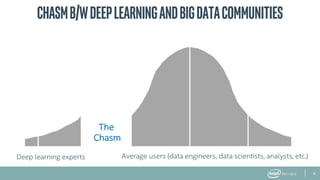
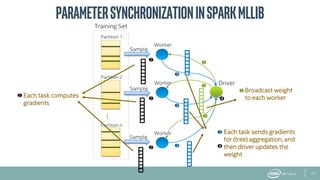
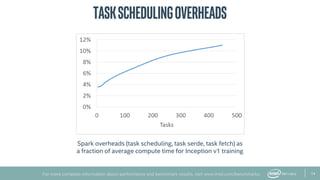
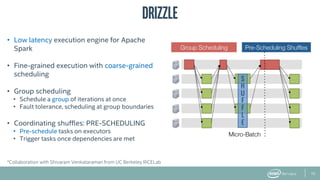
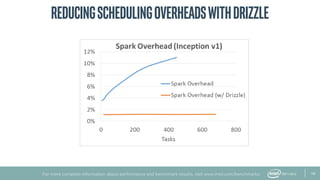
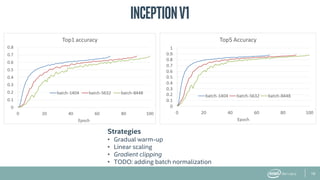
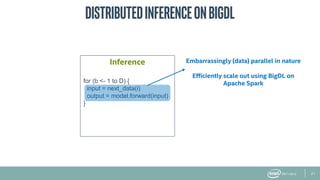
The document provides an overview of BigDL, a distributed deep learning framework that integrates seamlessly with Apache Spark, allowing data scientists to build and run deep learning applications without needing to alter existing Spark or Hadoop clusters. It highlights the framework's performance features, such as optimizing parameter synchronization and scalable batch size, and outlines its application in various domains, including fraud detection and image processing. Additionally, BigDL supports pre-trained models and offers capabilities for efficient inference and image augmentation.