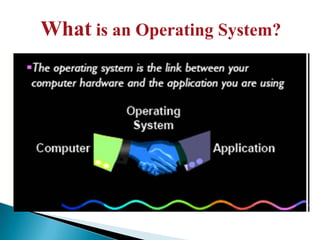
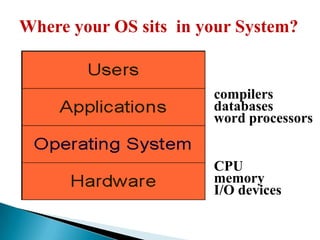
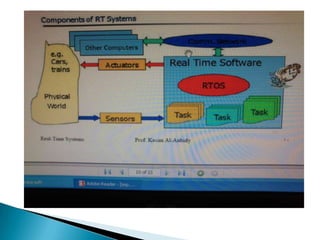
An operating system is software that manages computer resources and provides services to application programs. It sits between the computer hardware and application software. There are three main types of operating systems: stand-alone, network, and embedded. Real-time operating systems (RTOS) are designed for applications with time-critical deadlines like process control. Key features of an RTOS include short and predictable context switching, interrupt handling times, and inter-process communication. Popular RTOS include VxWorks, QNX, and RTLinux.