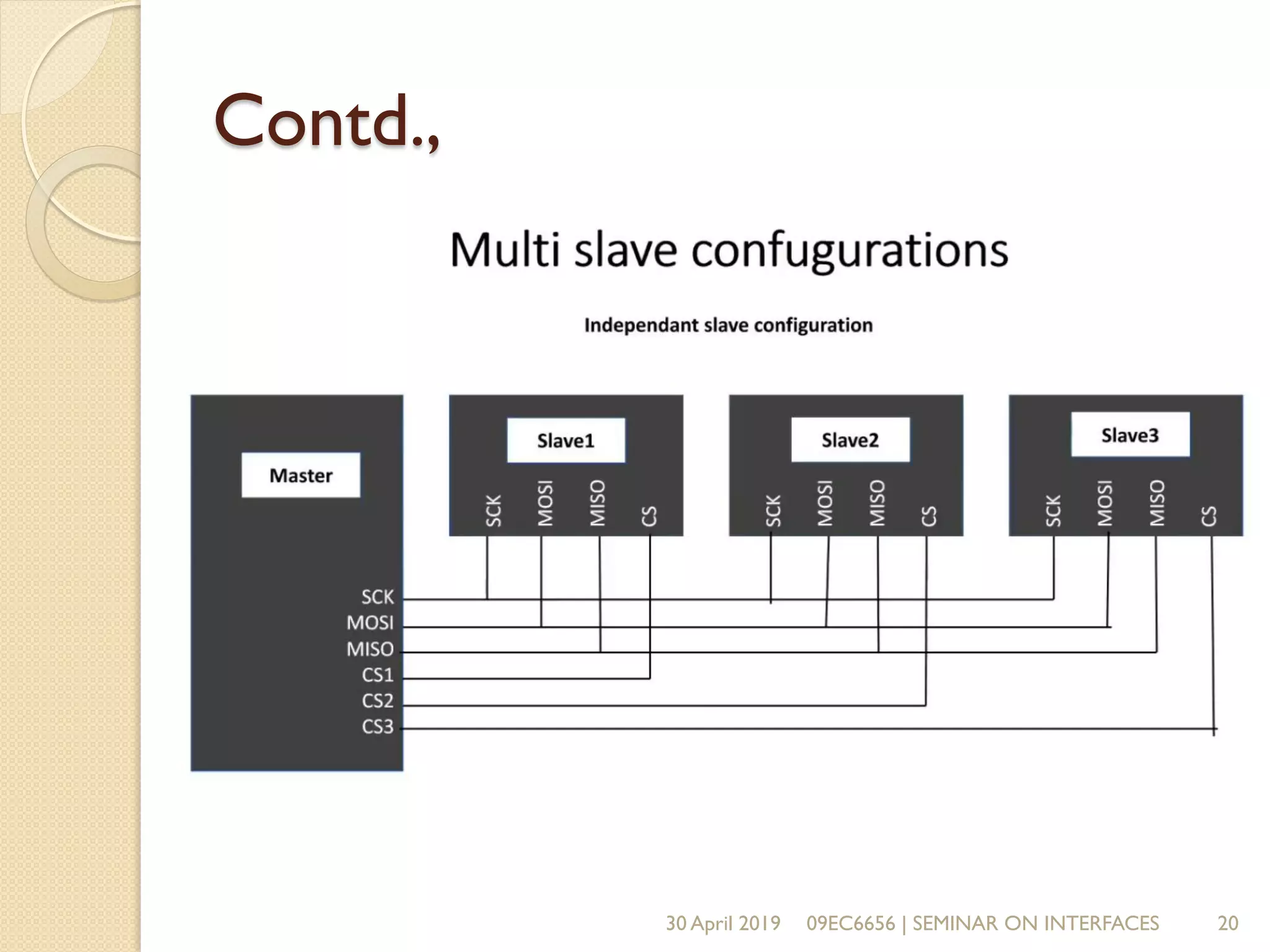
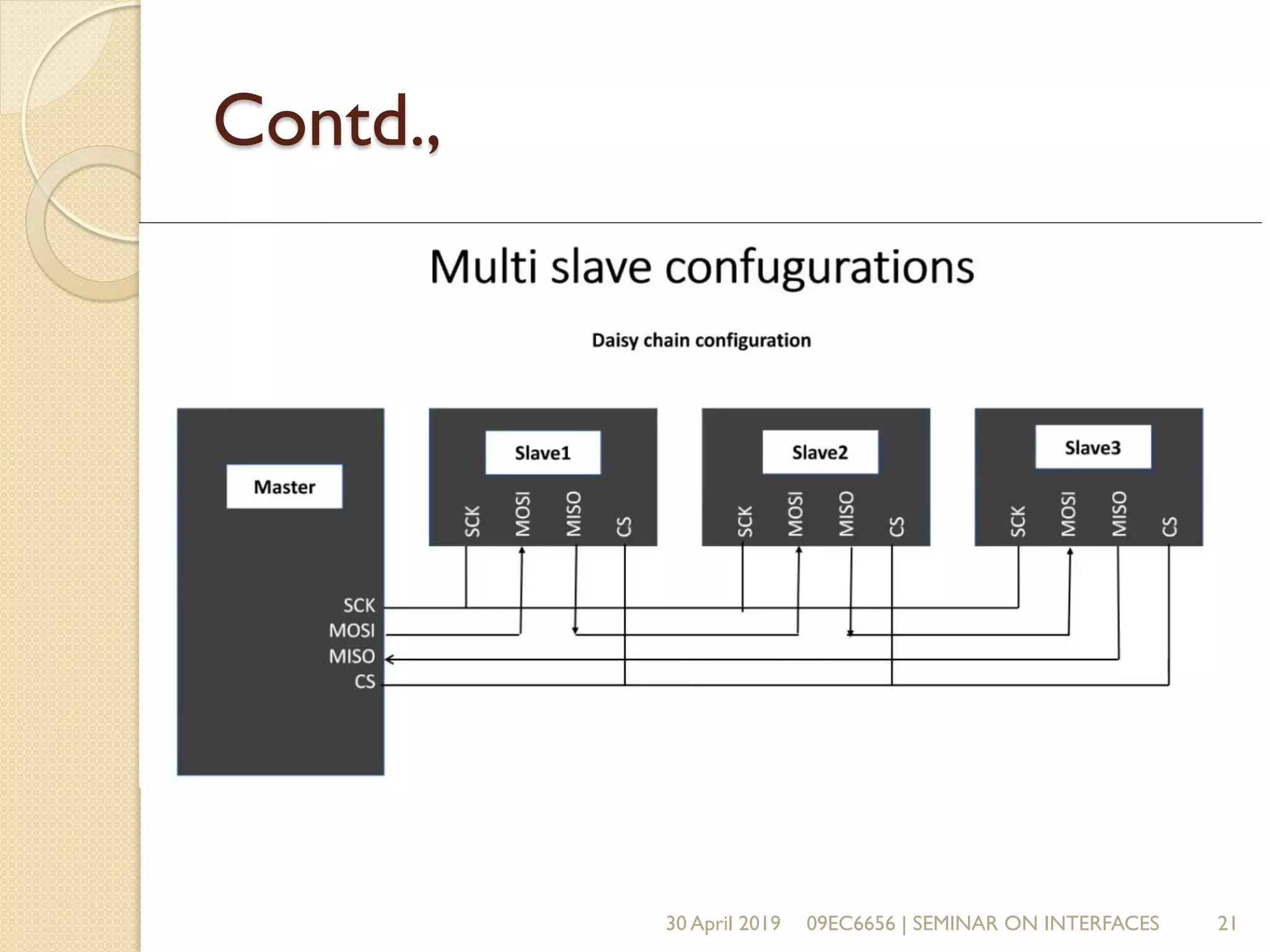
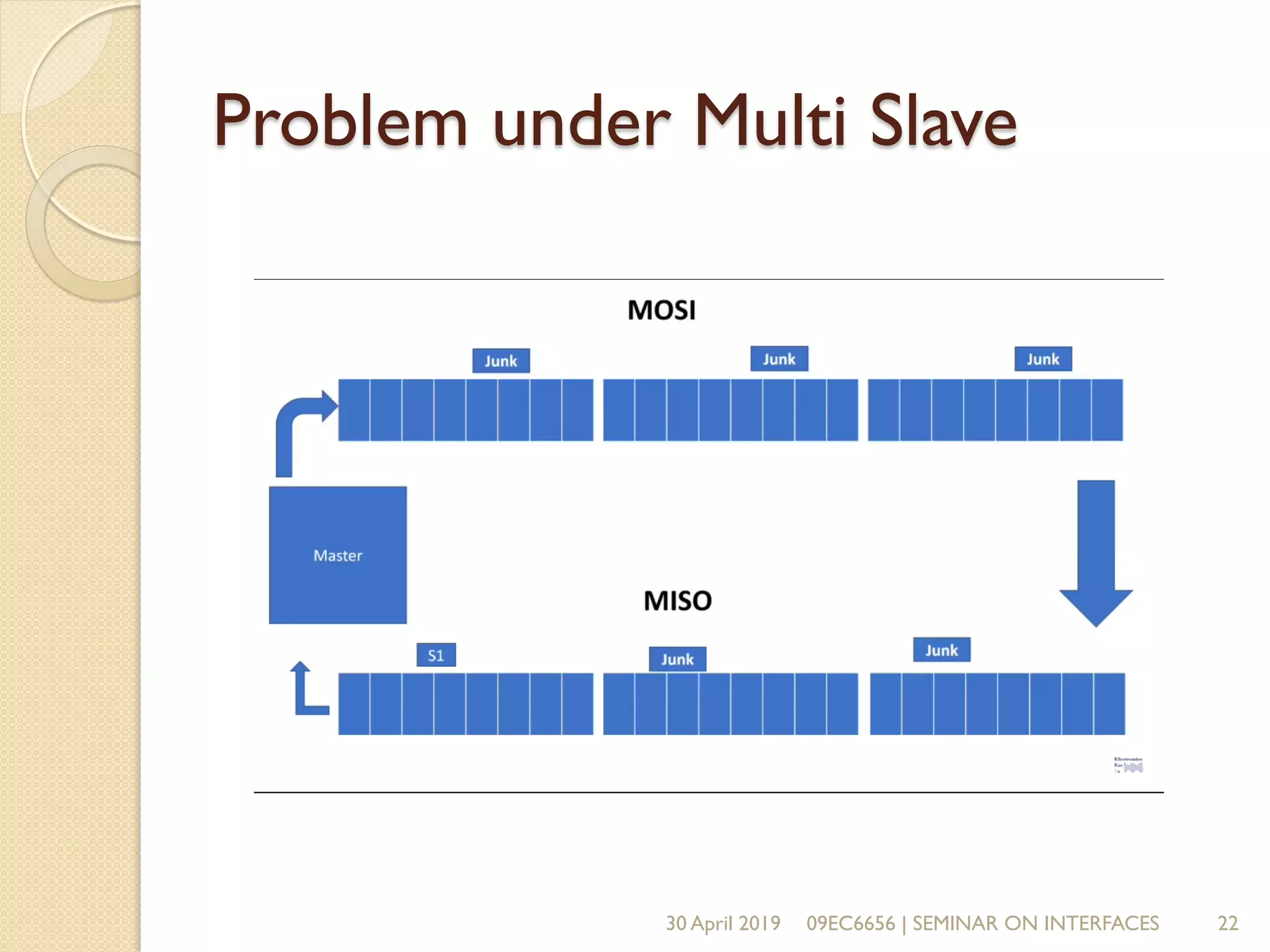
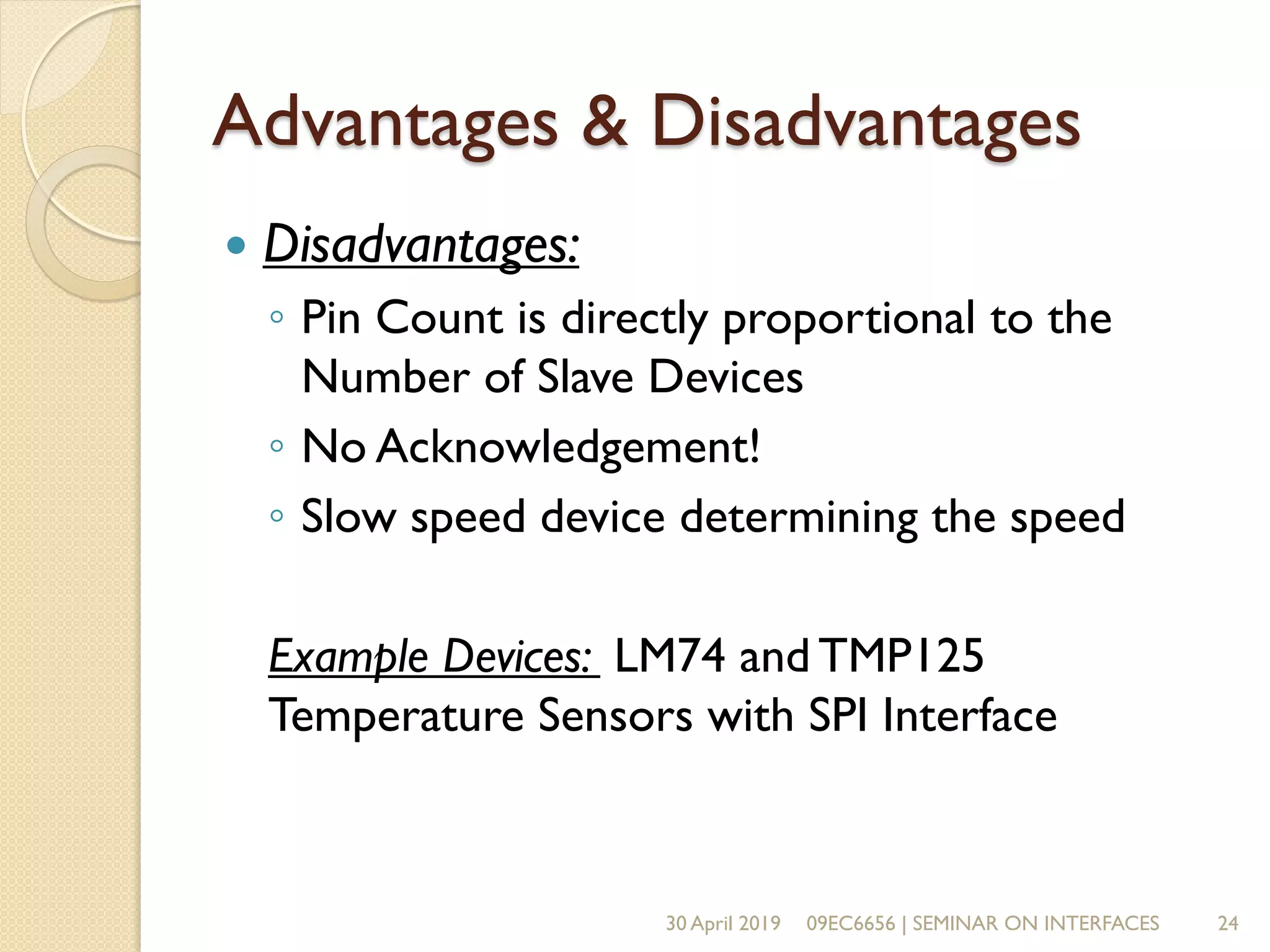
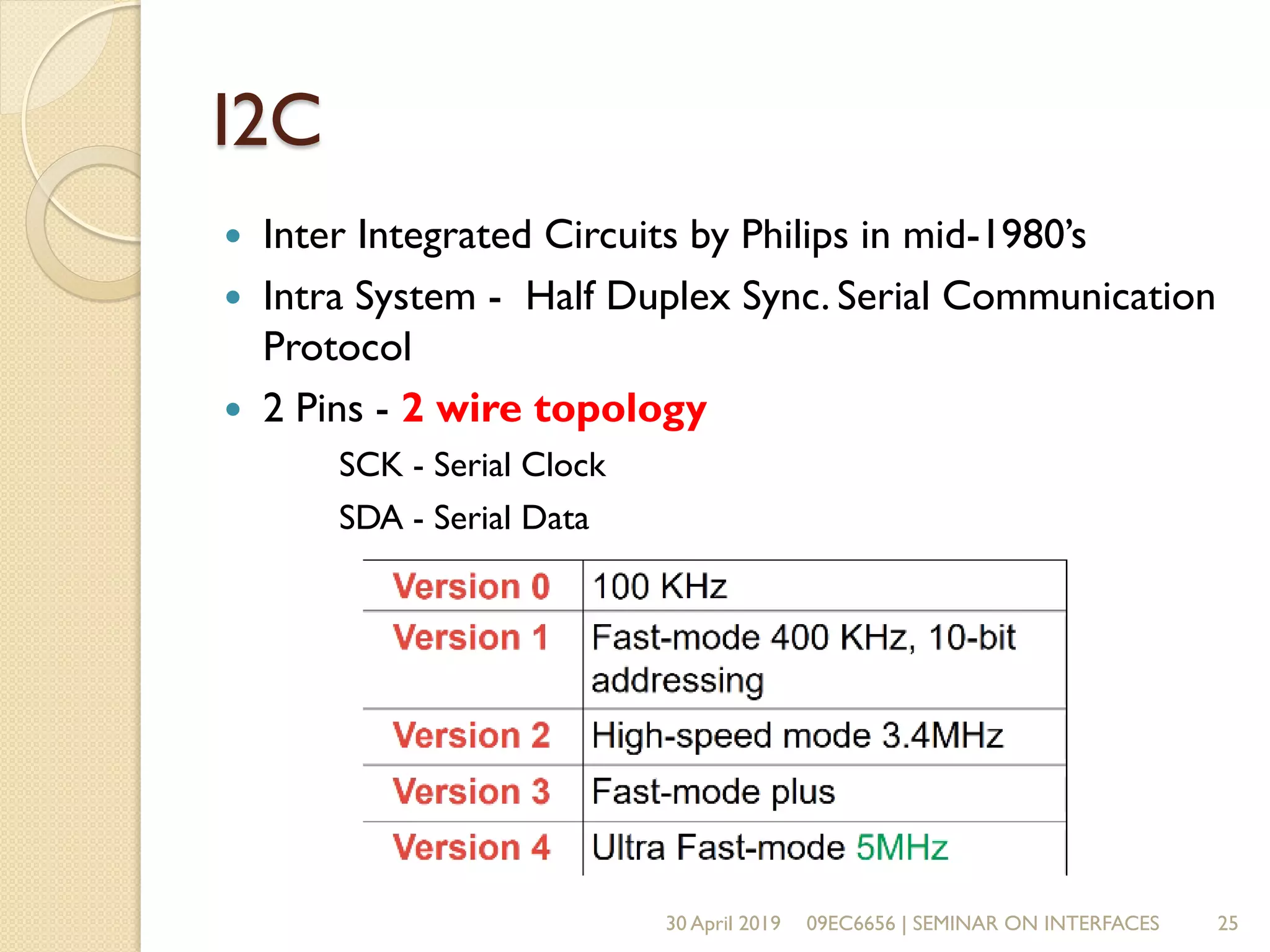
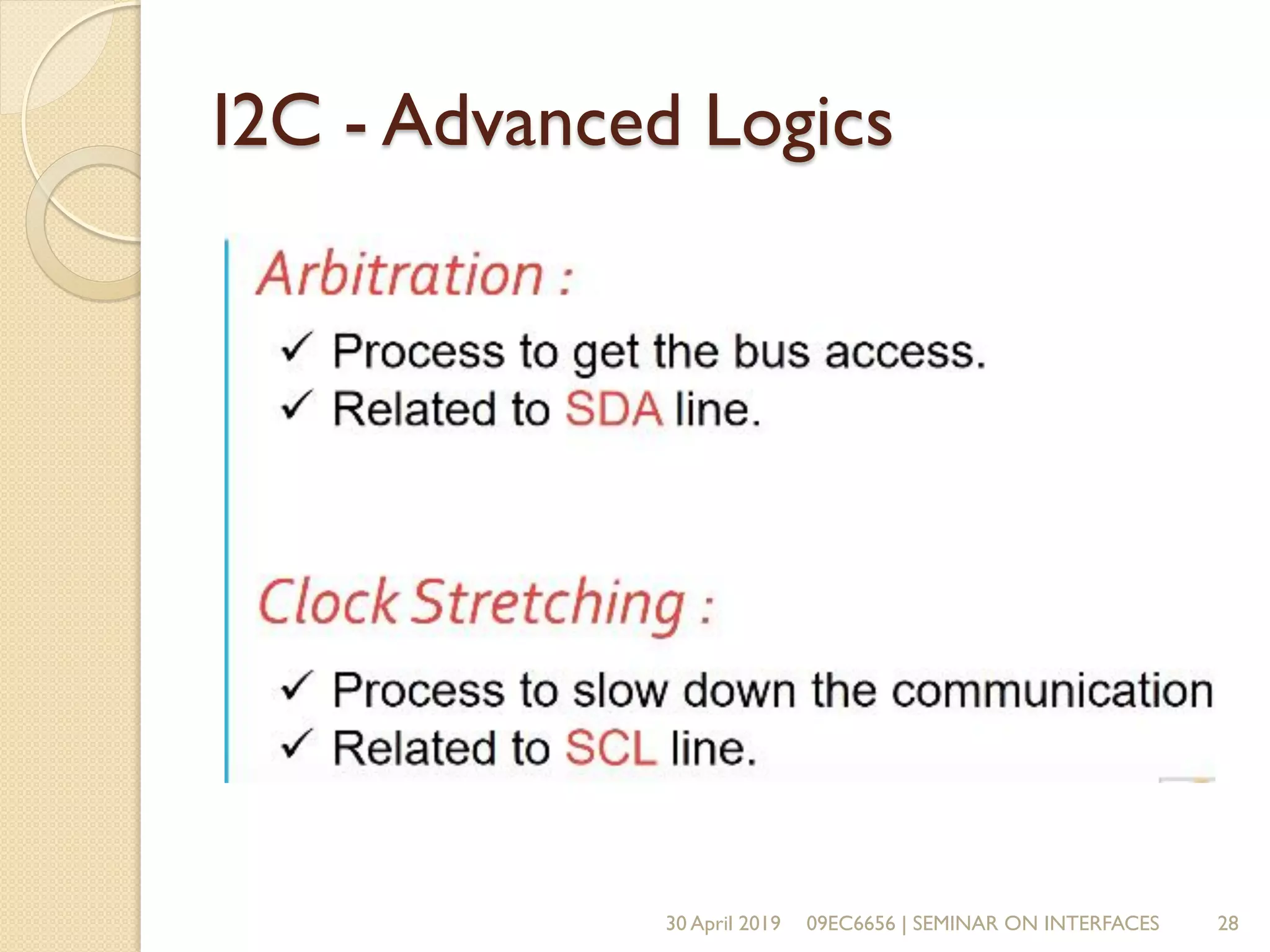
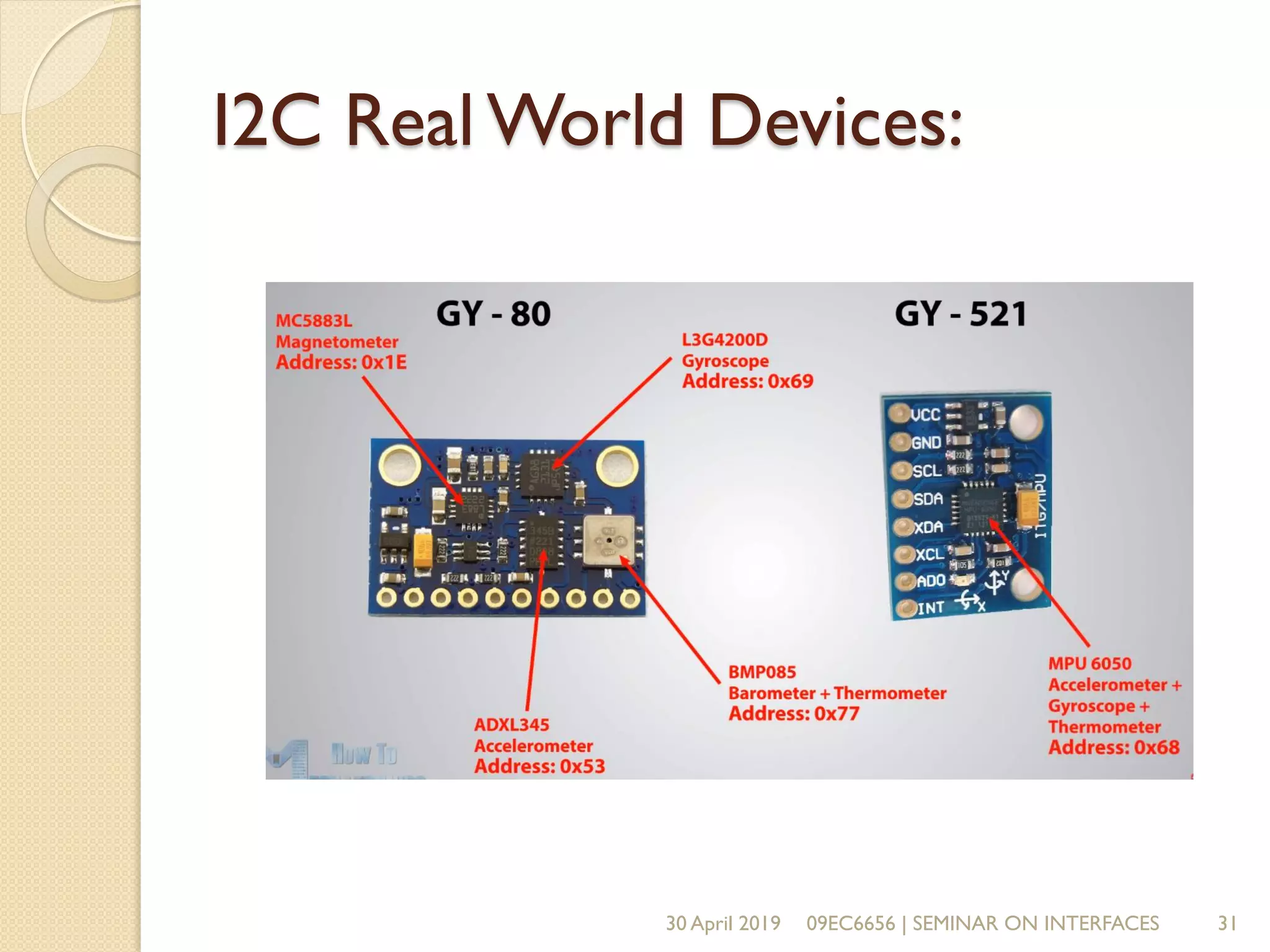
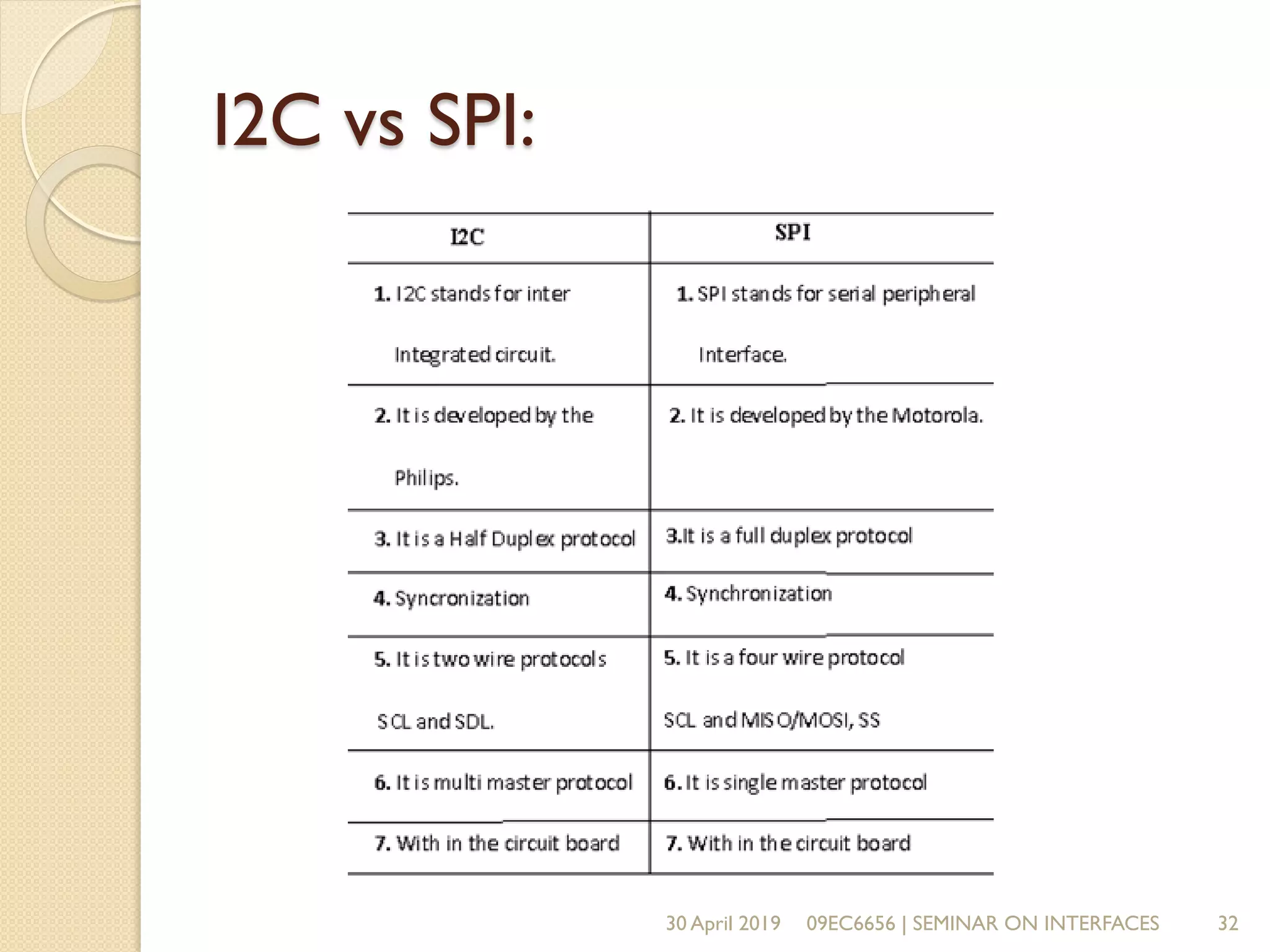
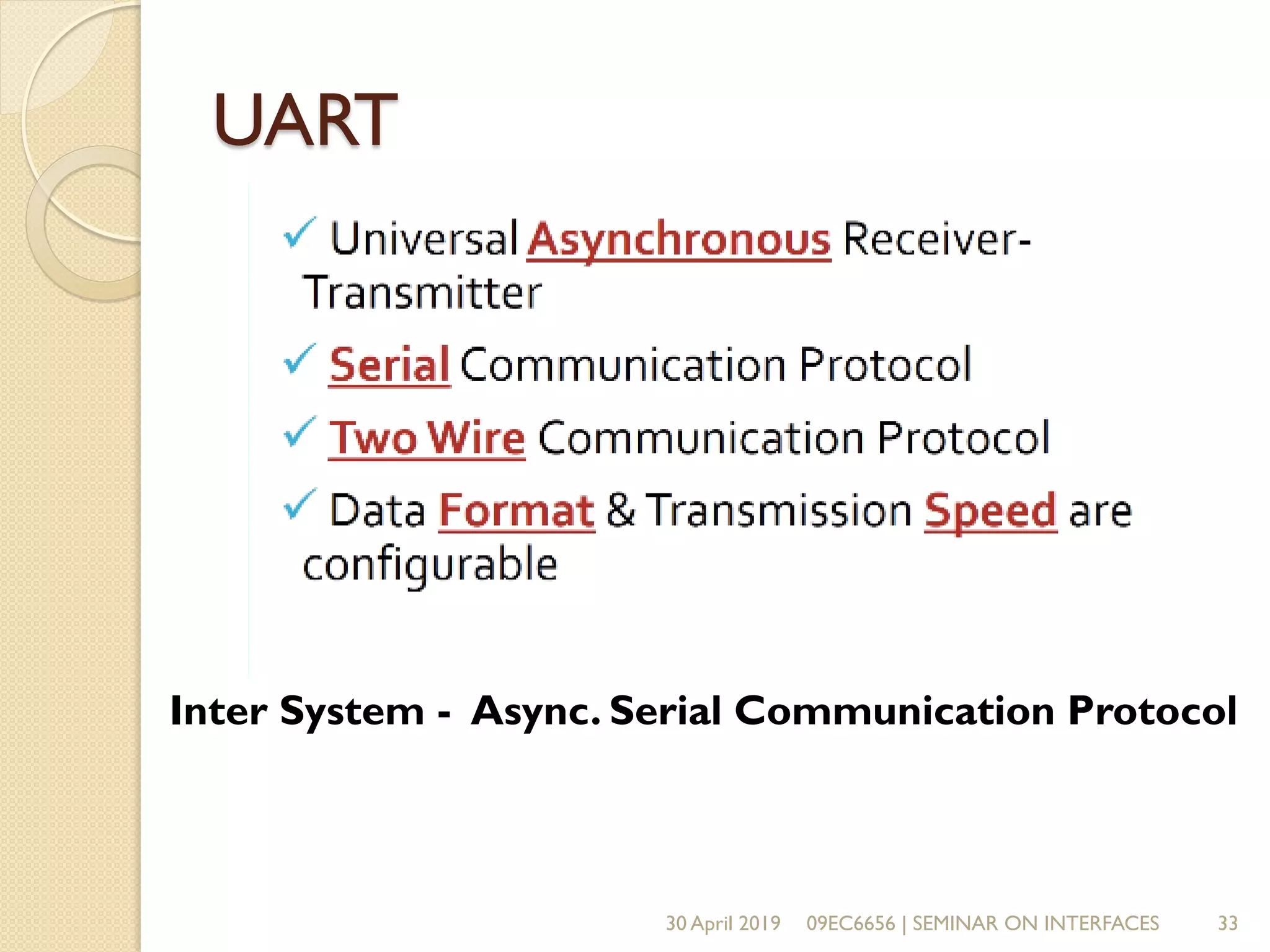
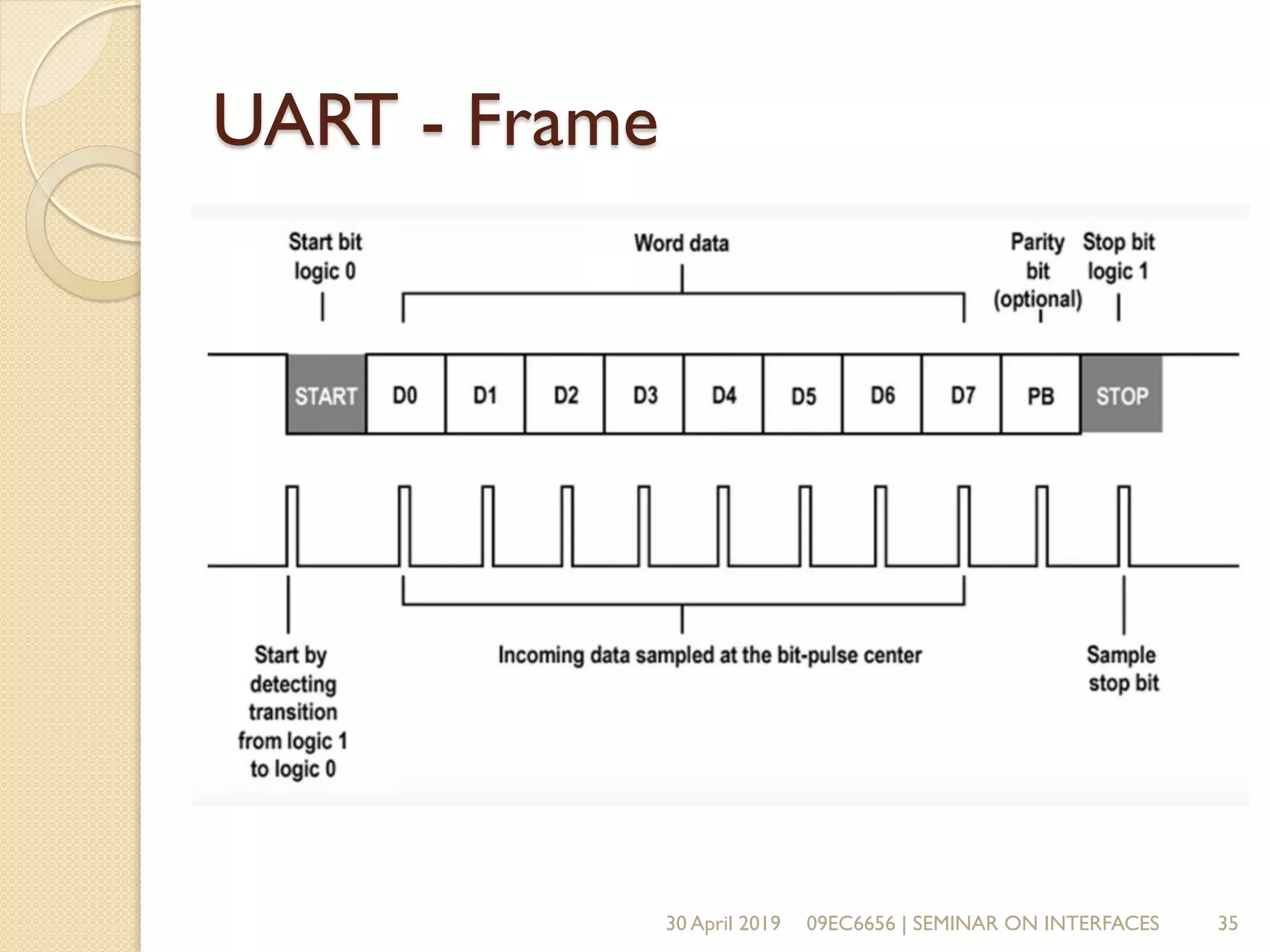
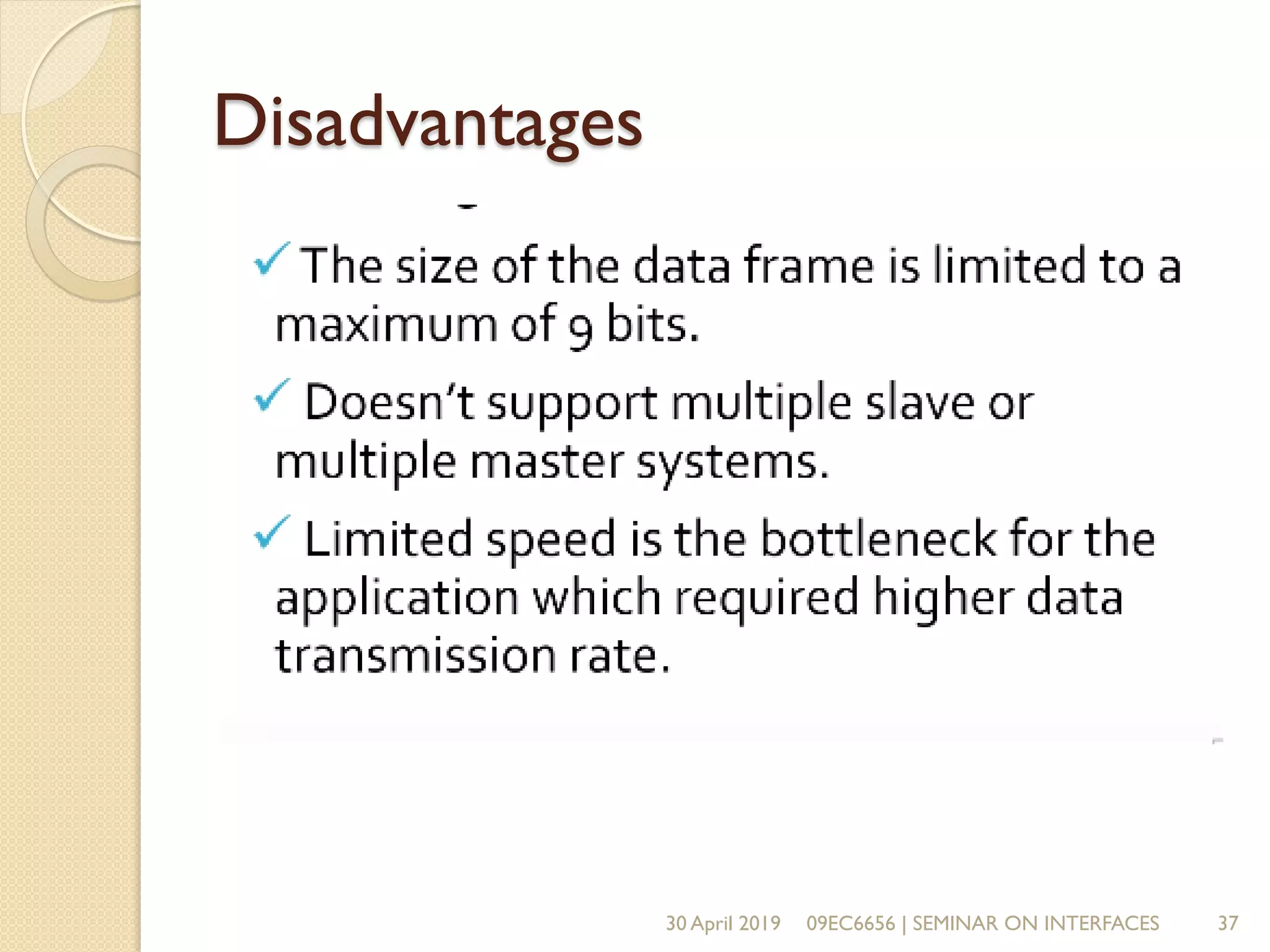
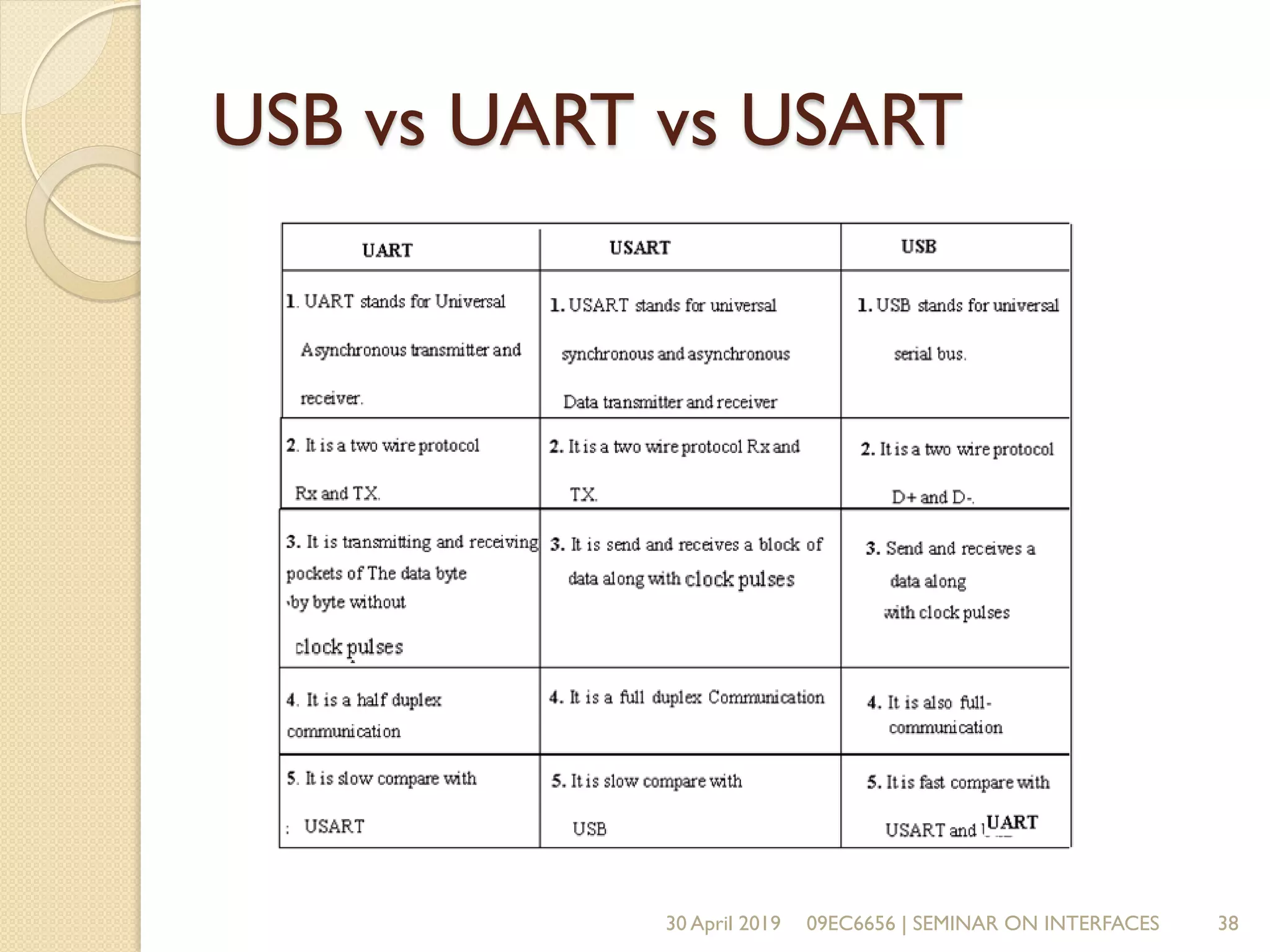
The document presents a seminar on electronic communication protocols including SPI, I2C, and UART, focusing on their roles in embedded systems for data exchange. It outlines the types of communication, their advantages and disadvantages, and specifics of each protocol, such as pin configurations and synchronization methods. The seminar highlights the importance of understanding these protocols for practical applications in real-world devices.