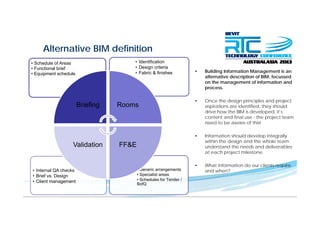
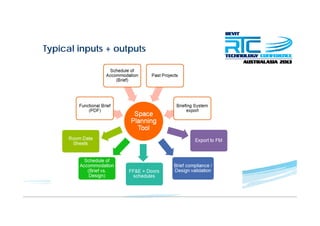
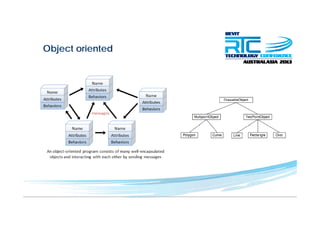
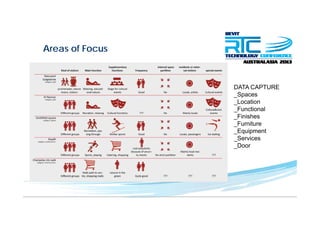
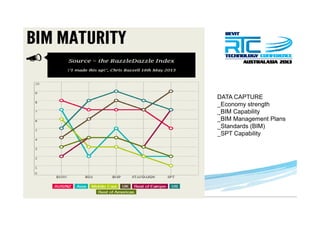
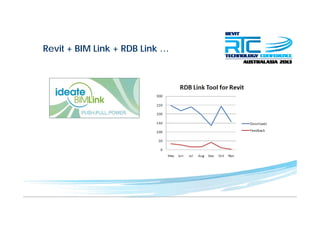
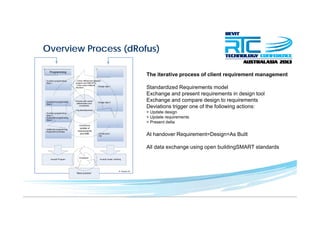
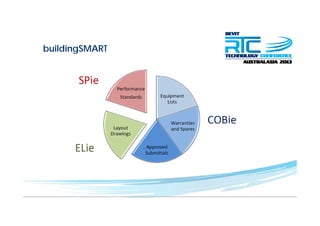
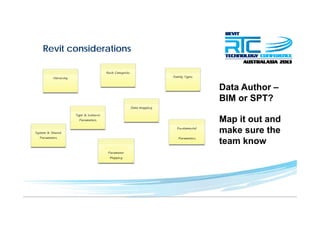
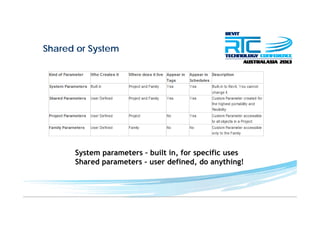
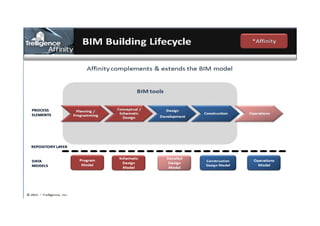
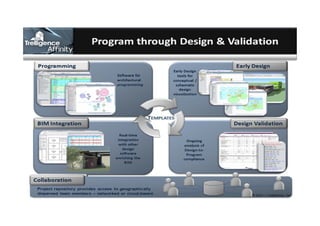
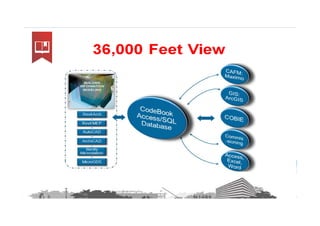
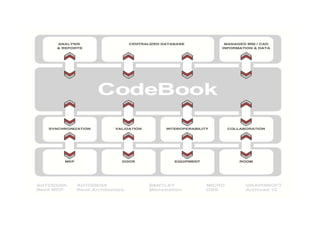
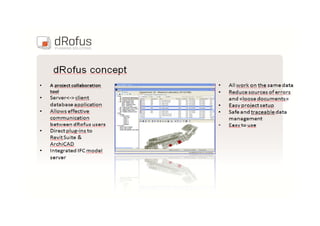
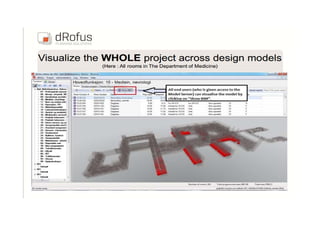
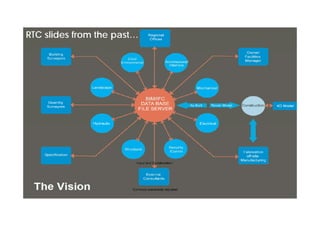
This document discusses space planning technologies (SPT) and their integration with building information modeling (BIM). It describes SPT as software that enables briefing of facilities, integrates briefing data with BIM models, generates reports, analyzes brief vs. design, and exports data downstream. The document outlines typical SPT inputs like spaces, location, functions, and furniture, as well as common outputs like area schedules and room data sheets. It also discusses integrating SPTs like Affinity, BuildingOne, CodeBook, and dRofus with BIM tools like Revit through open standards. The document provides advice on implementation including defining roles and deliverables, designating data authors, and getting training to ensure proper integration of