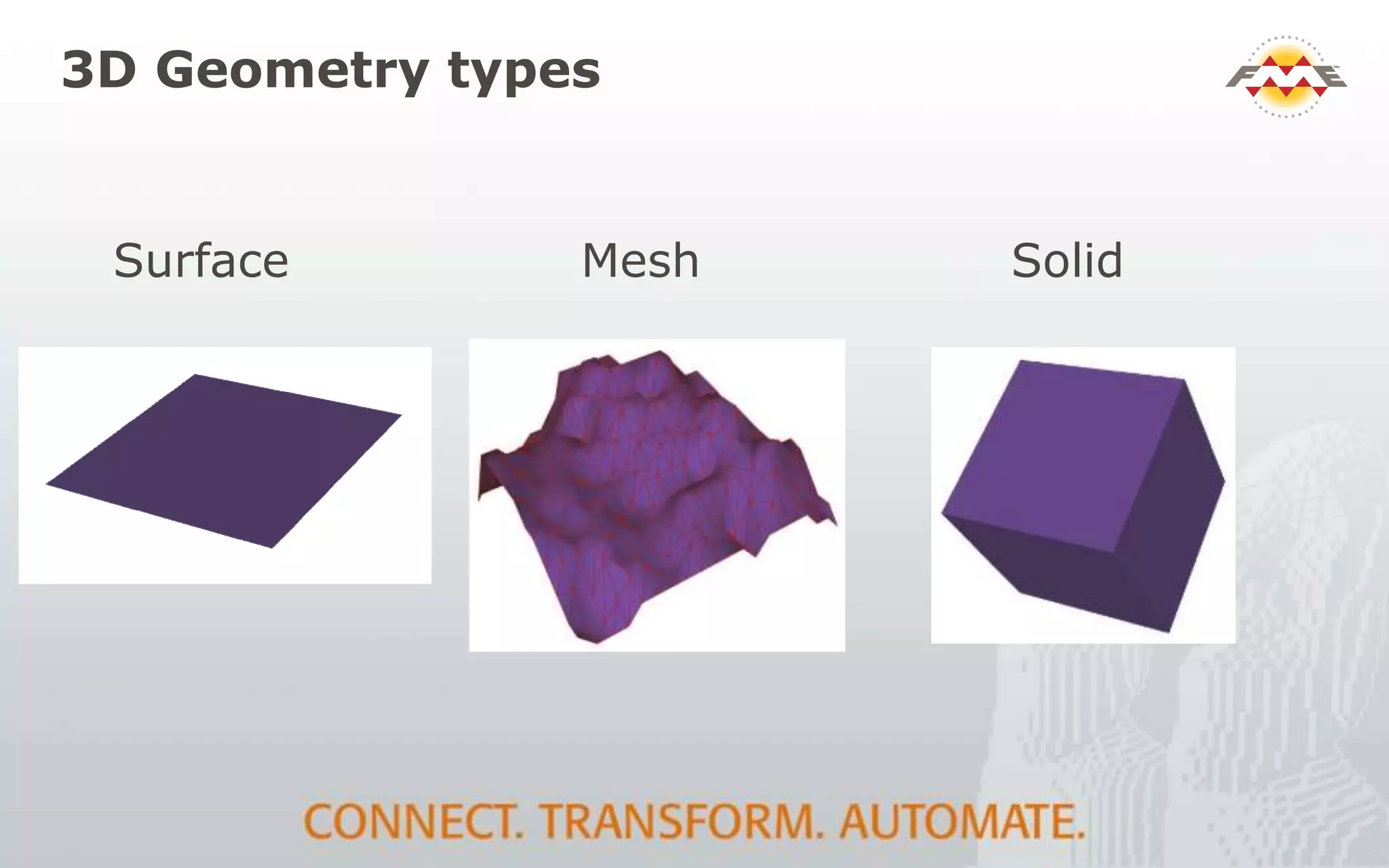
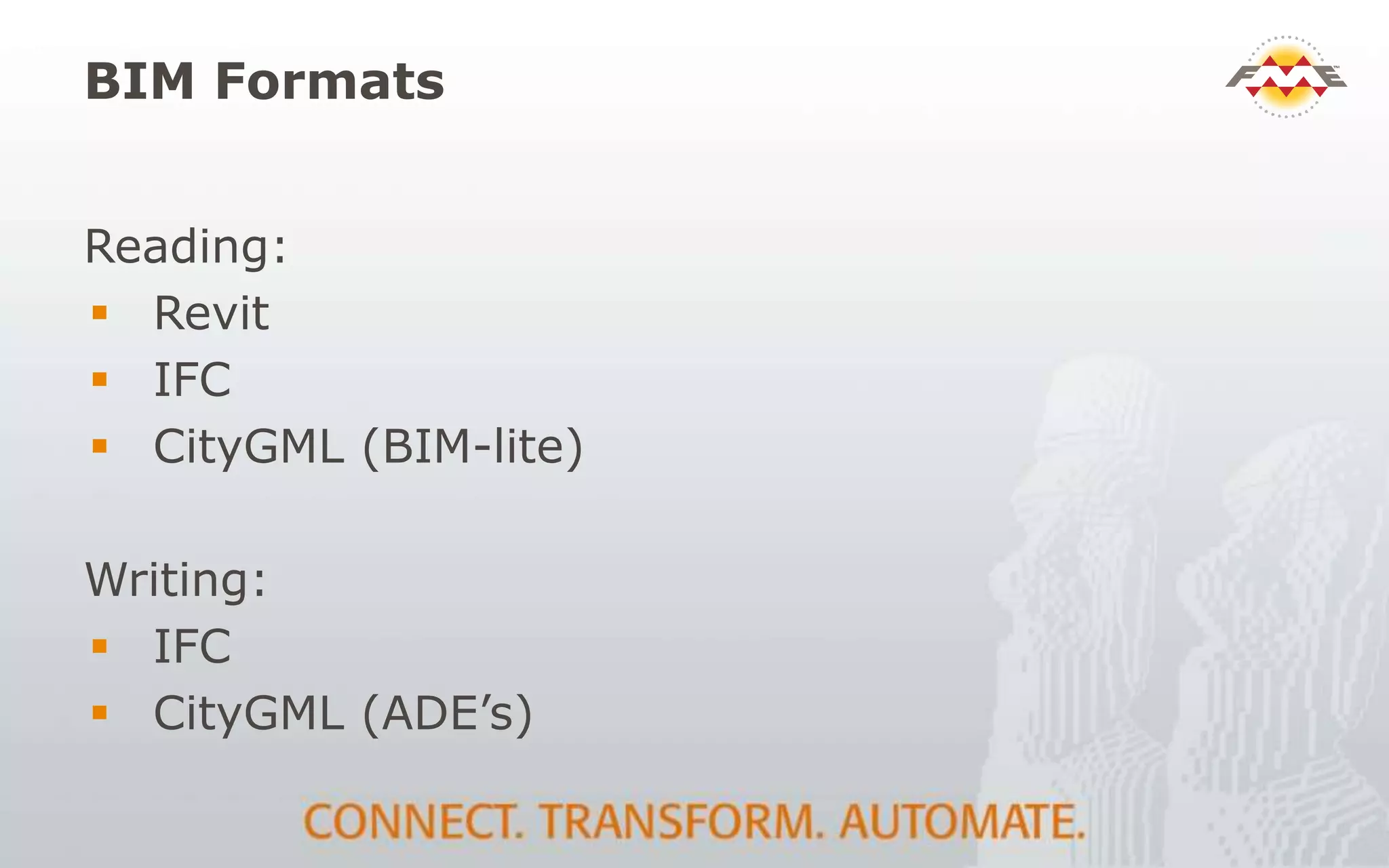
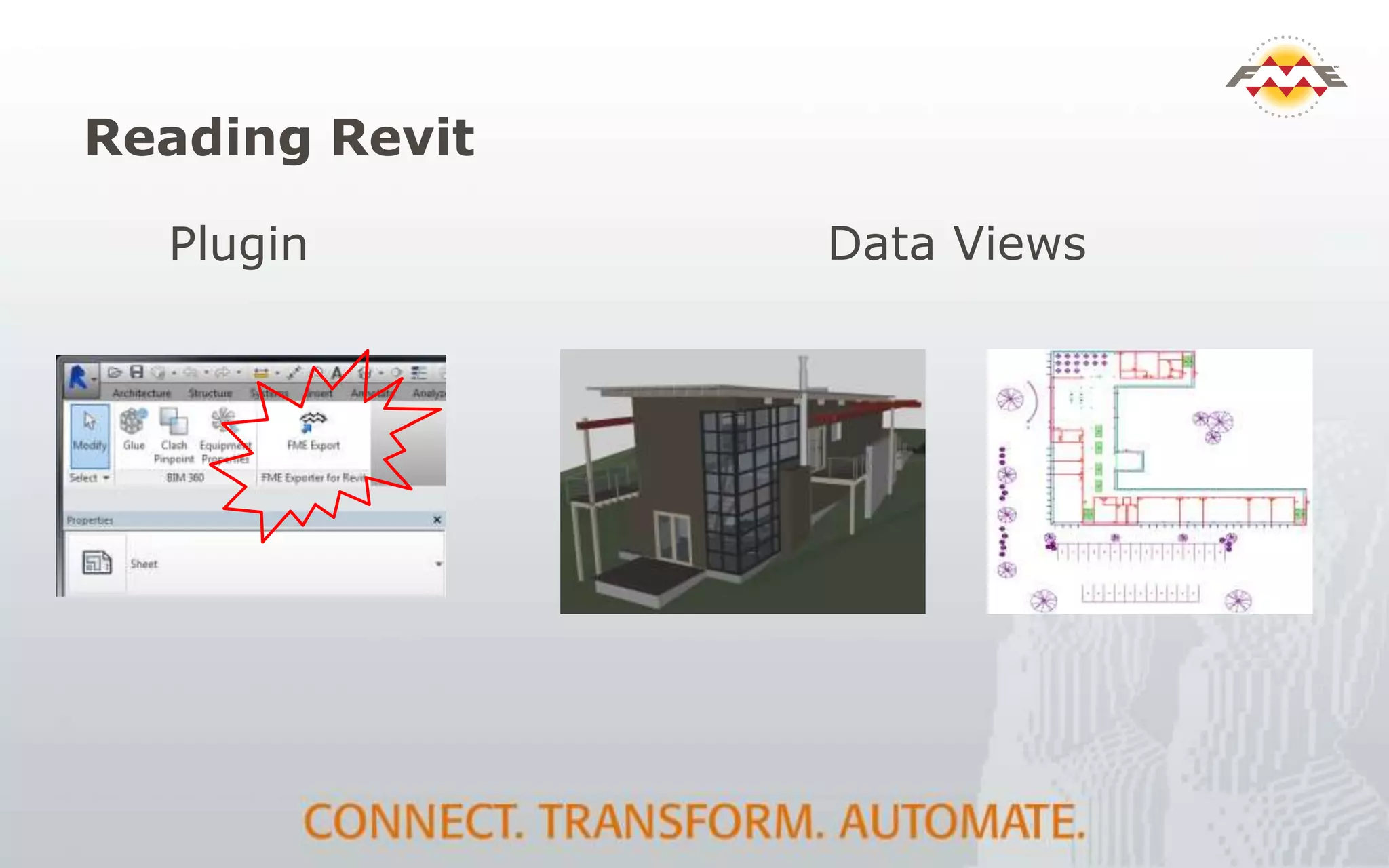
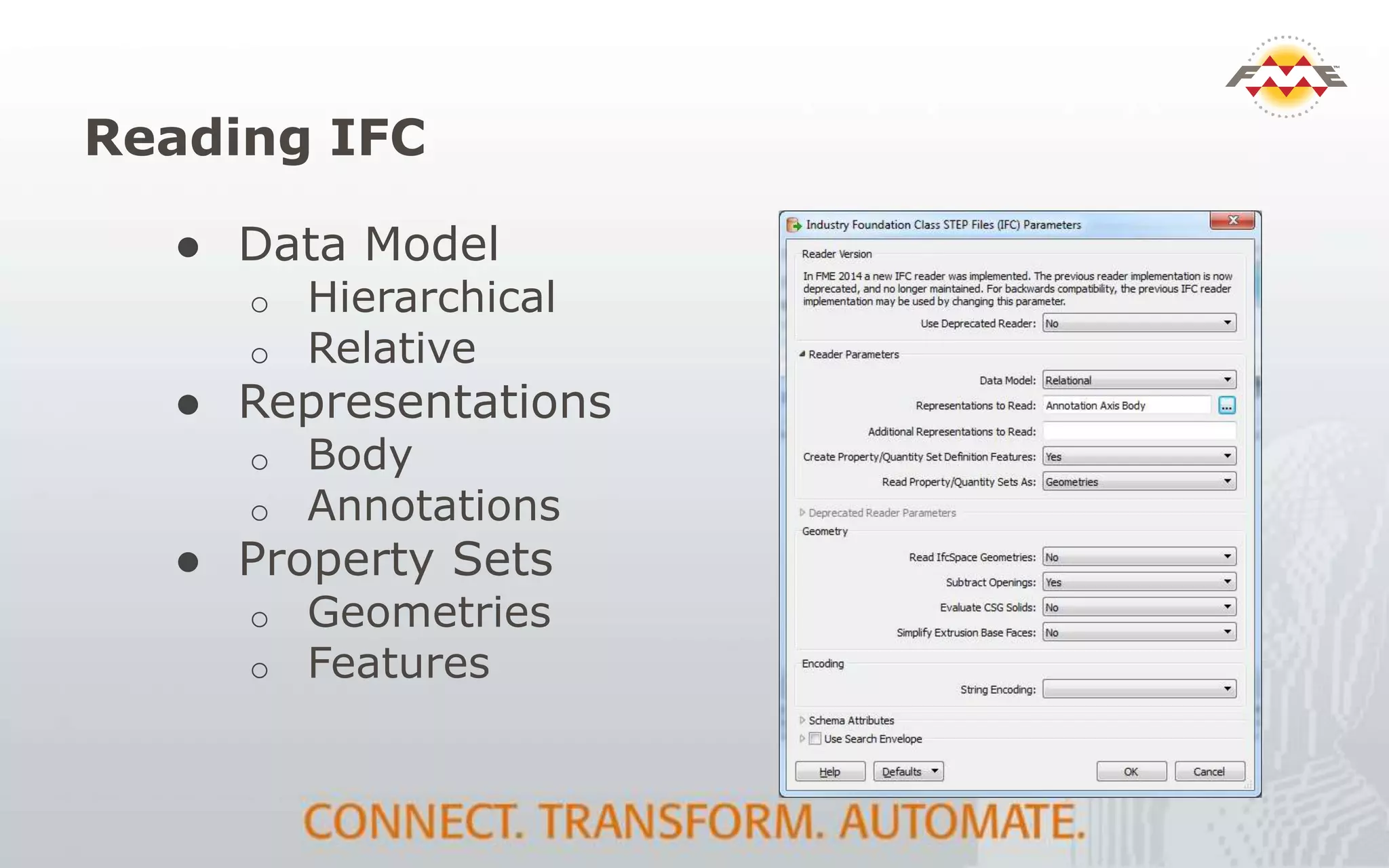
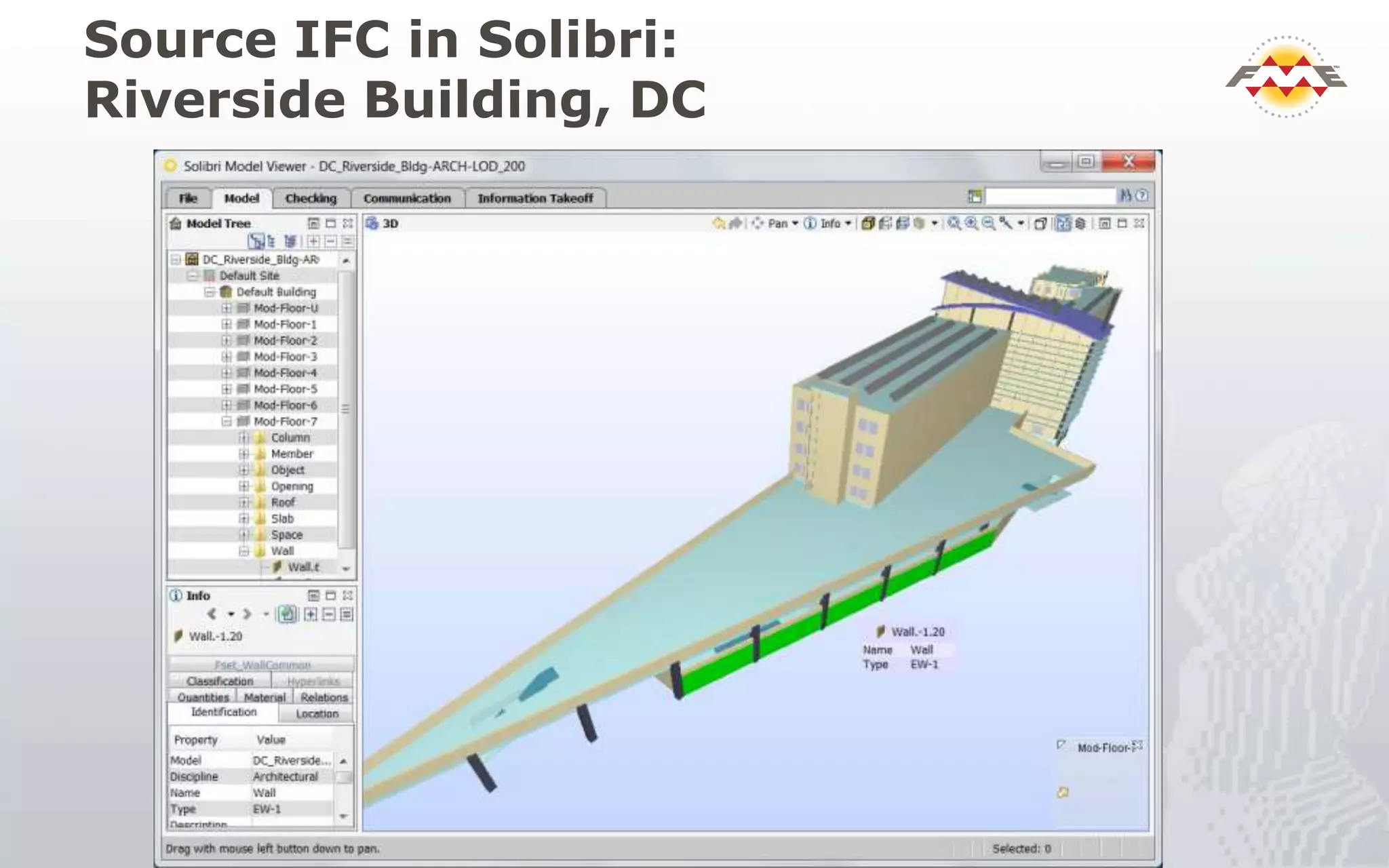
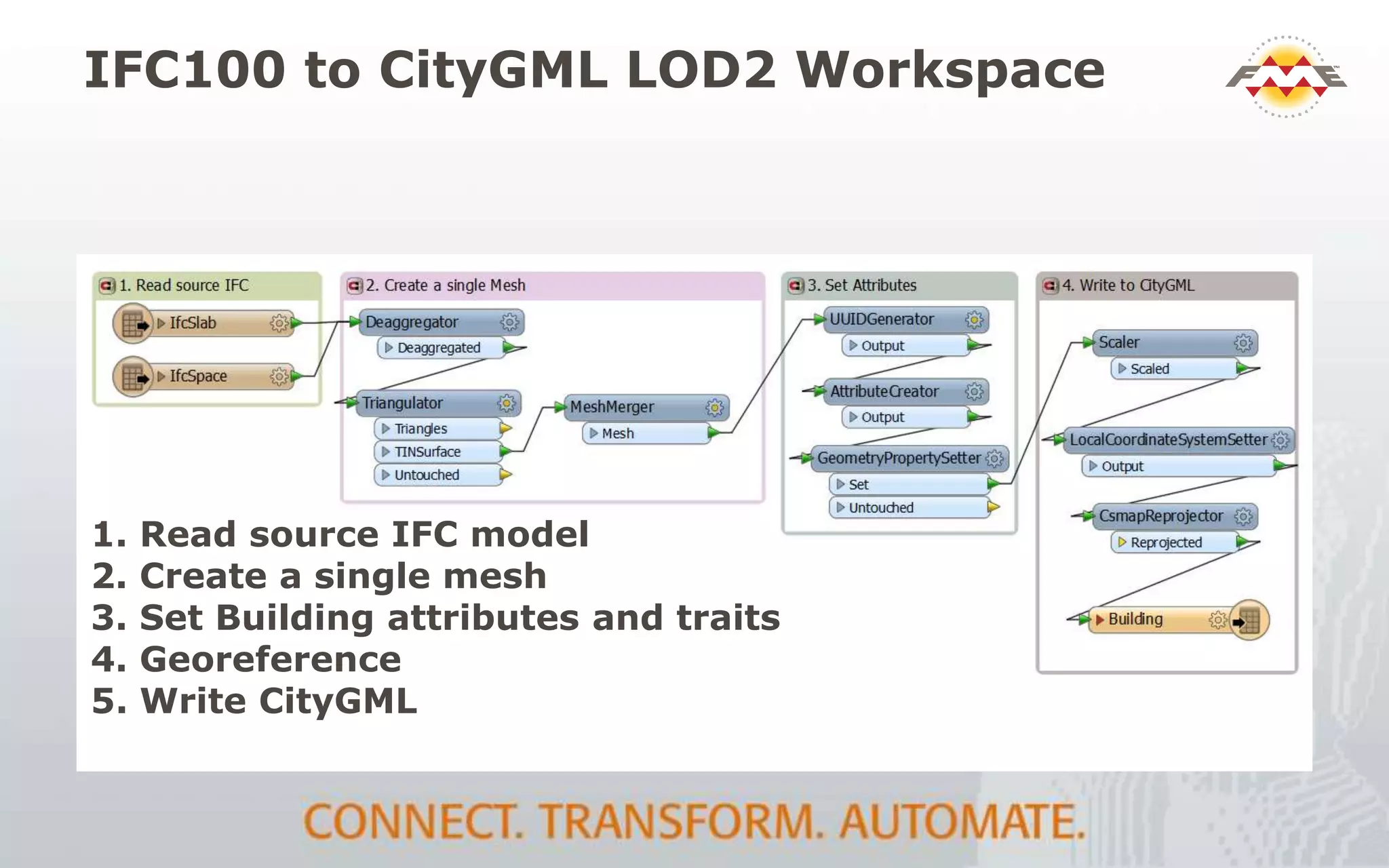
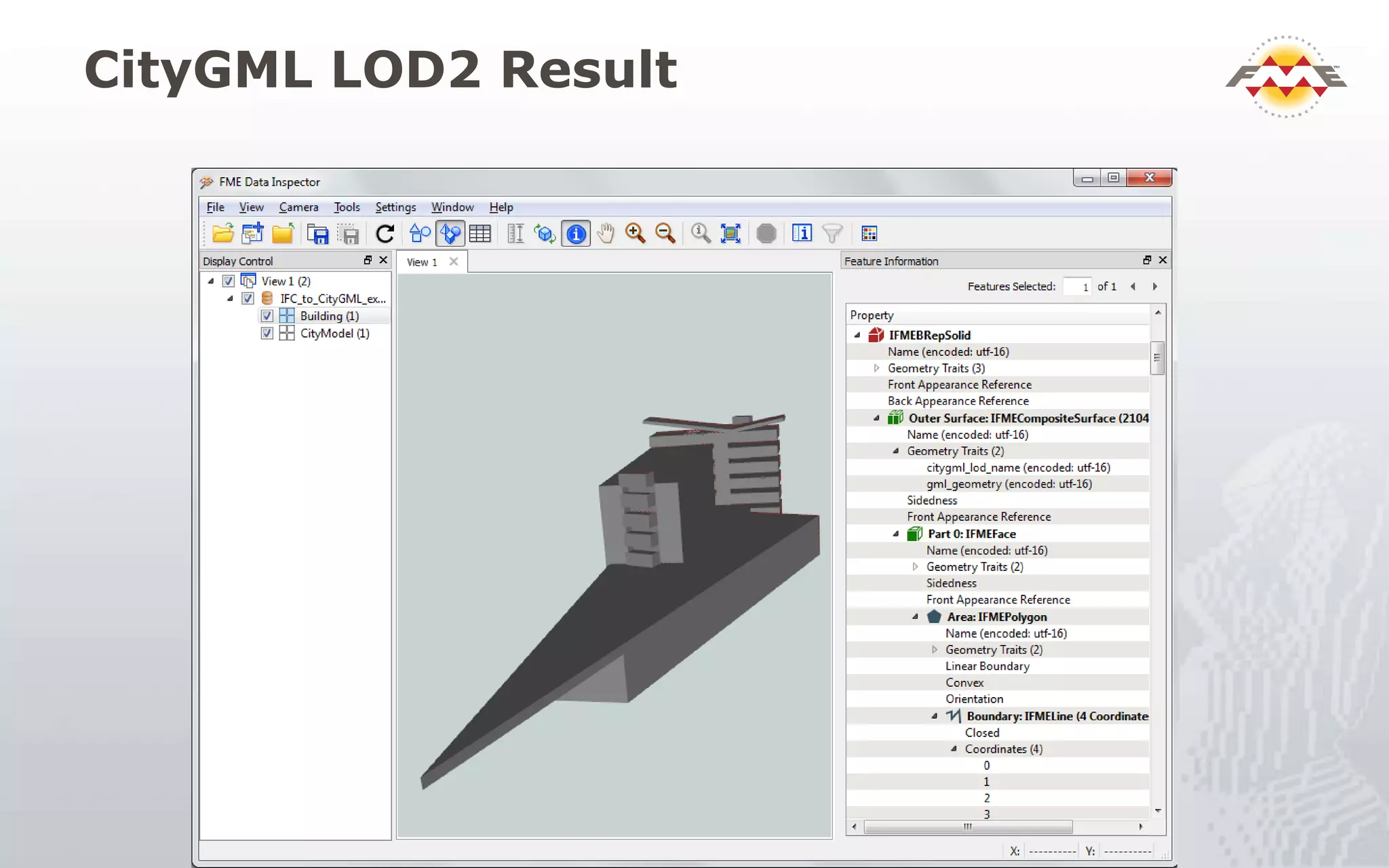
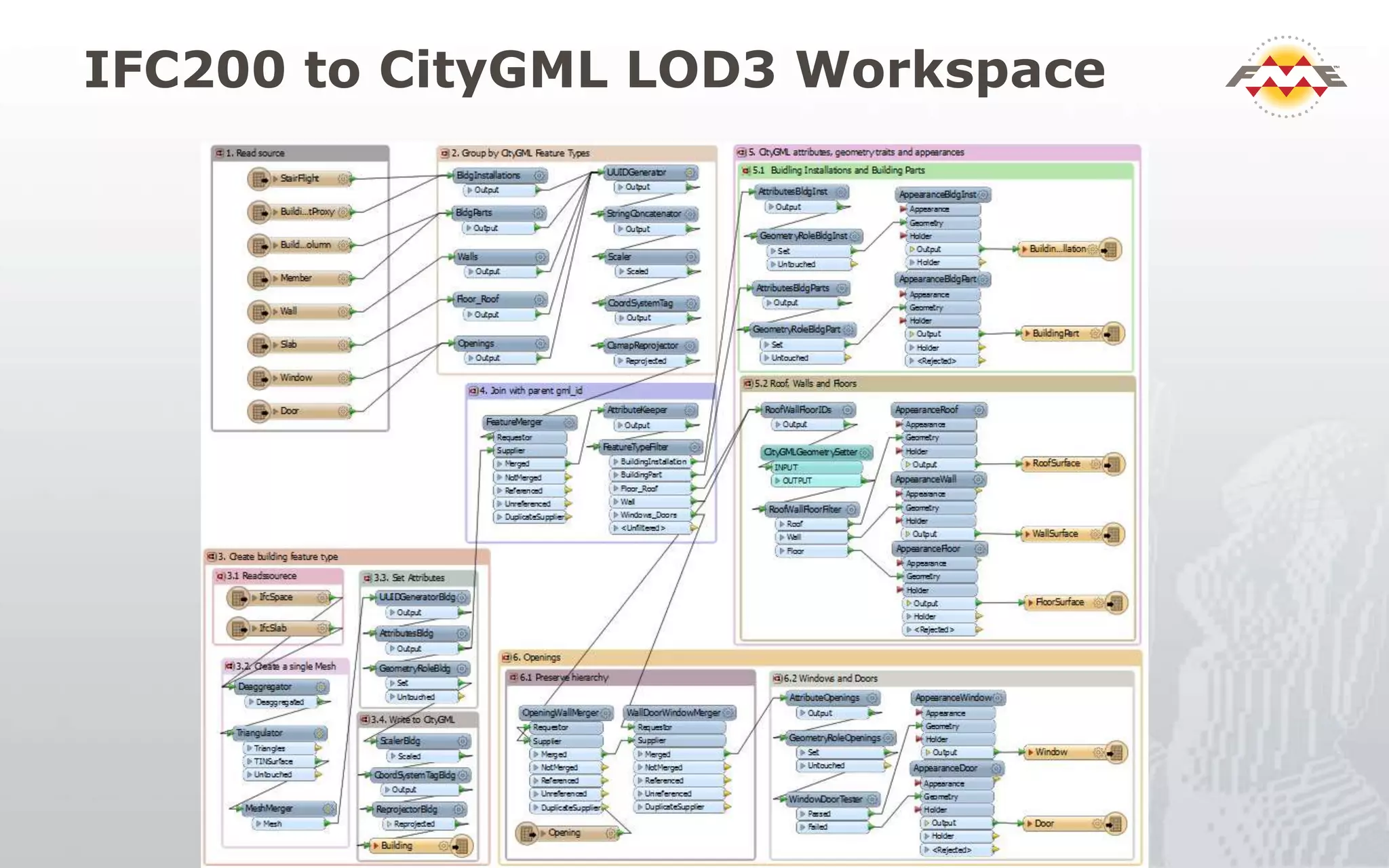
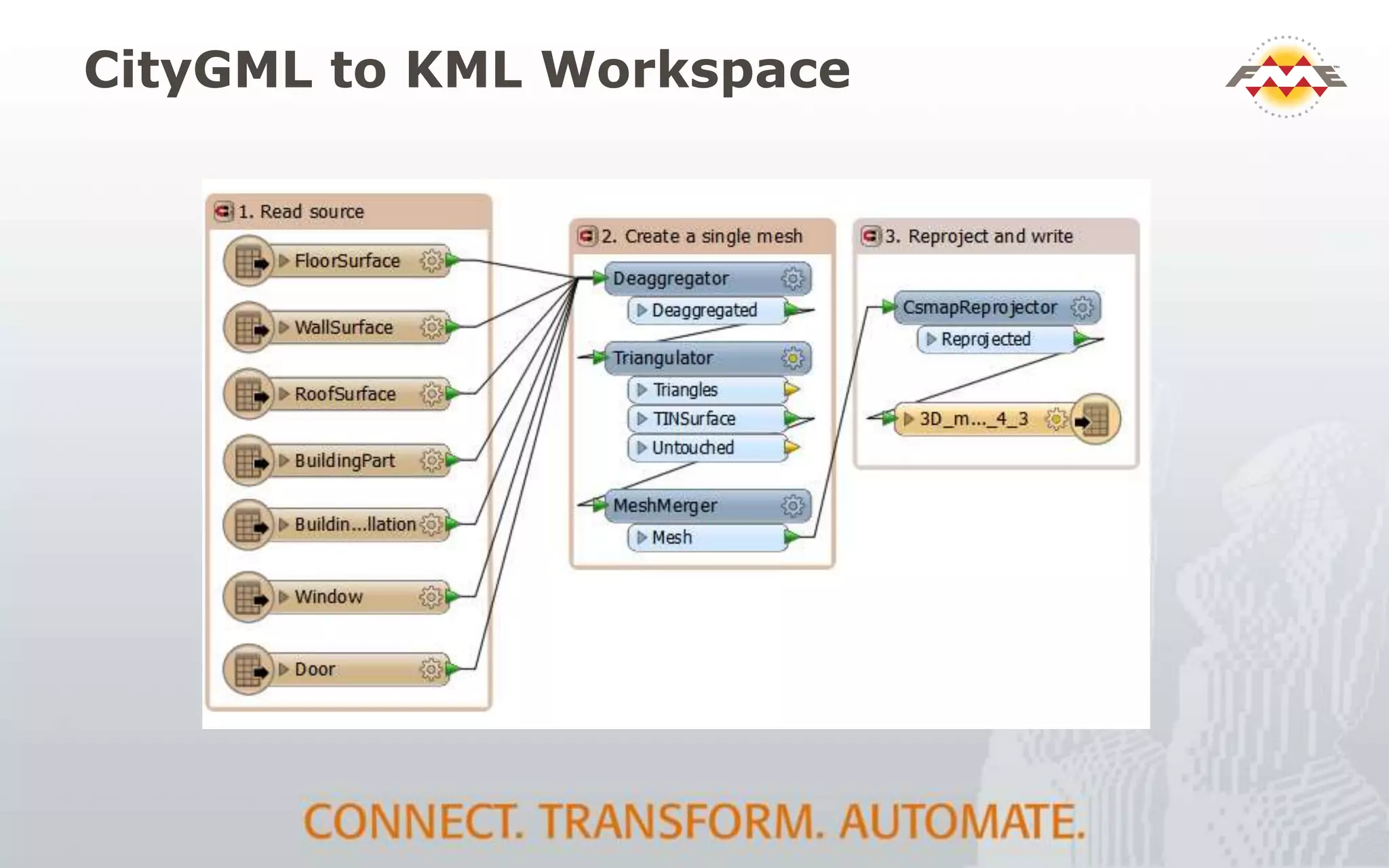
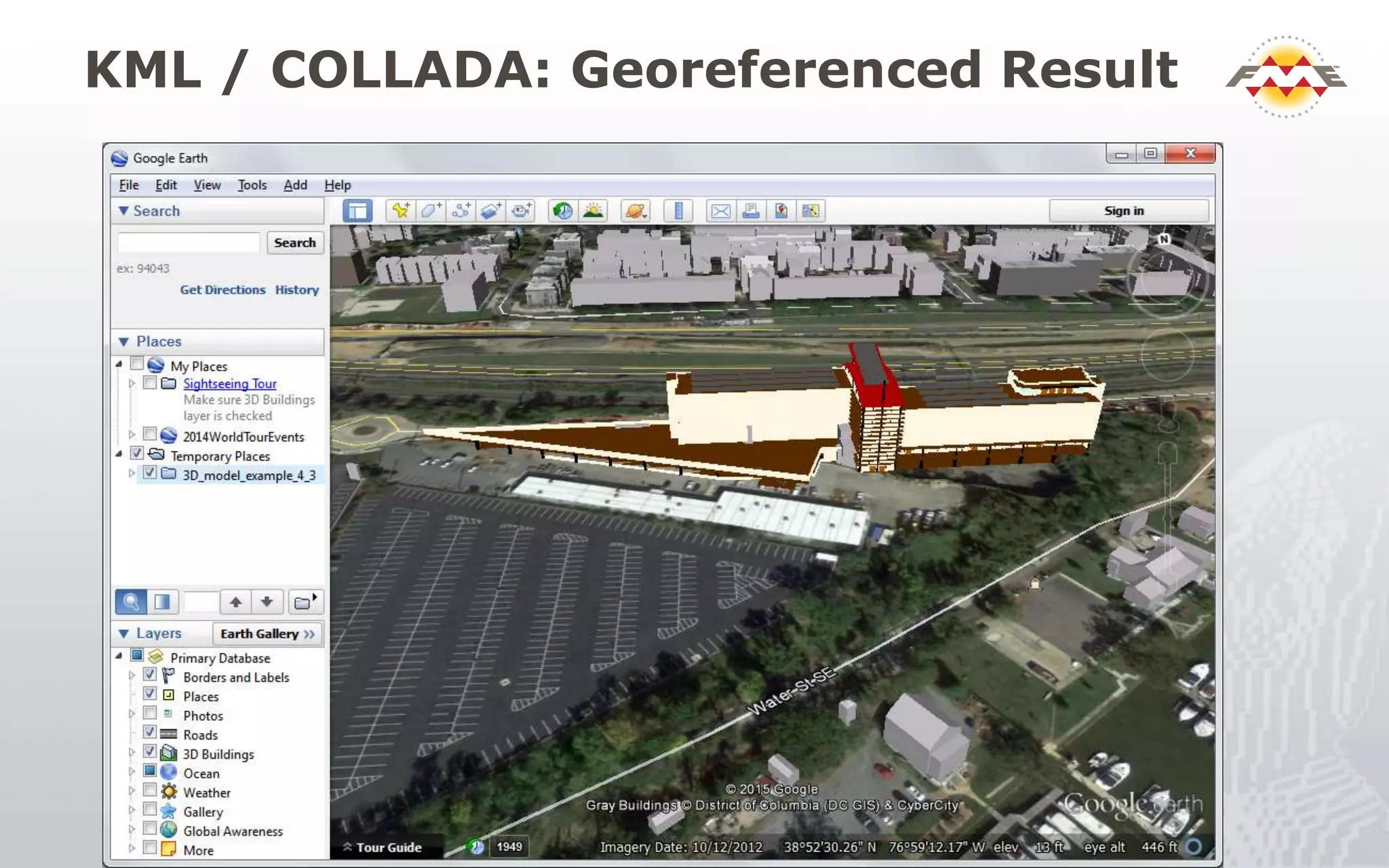
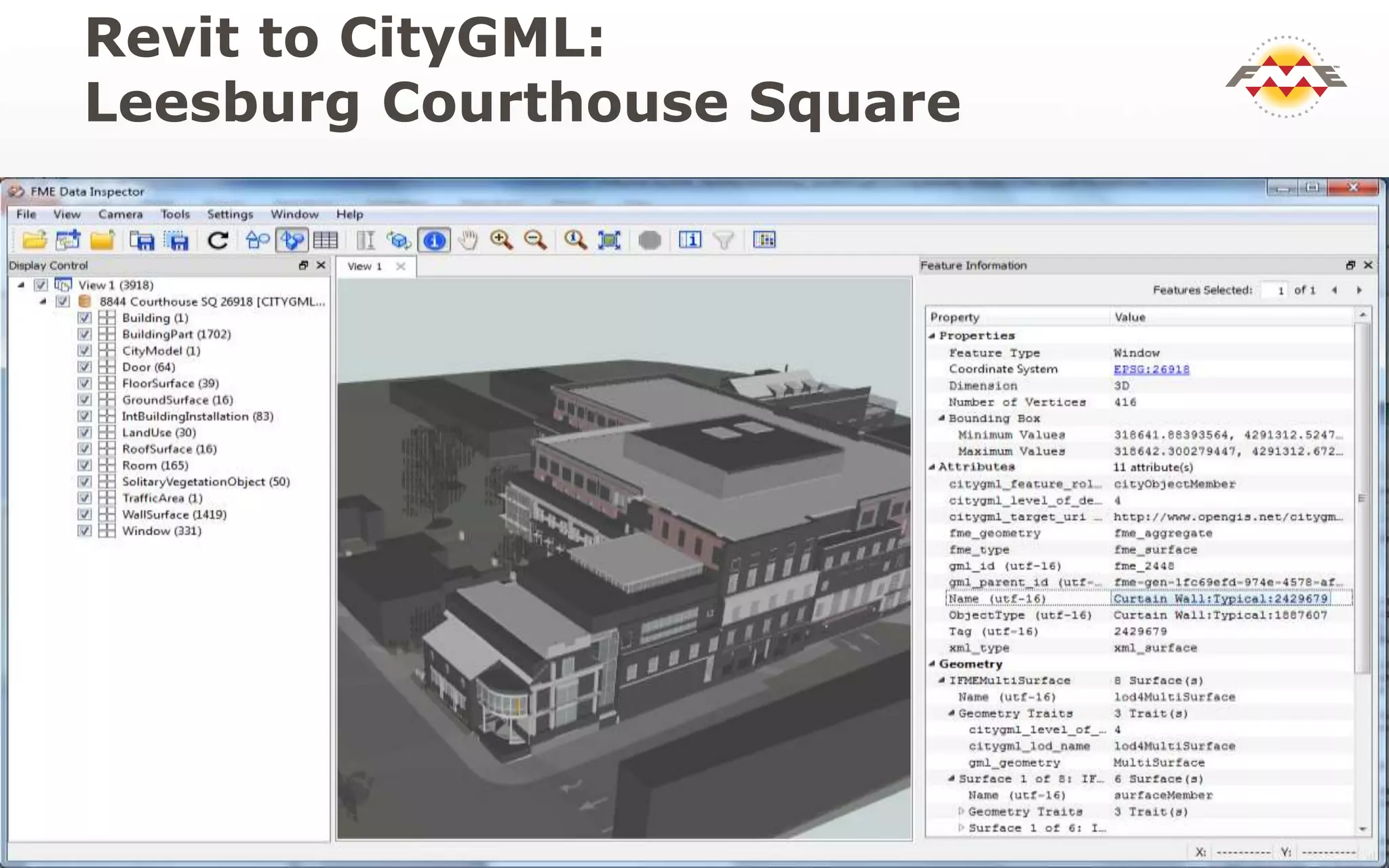
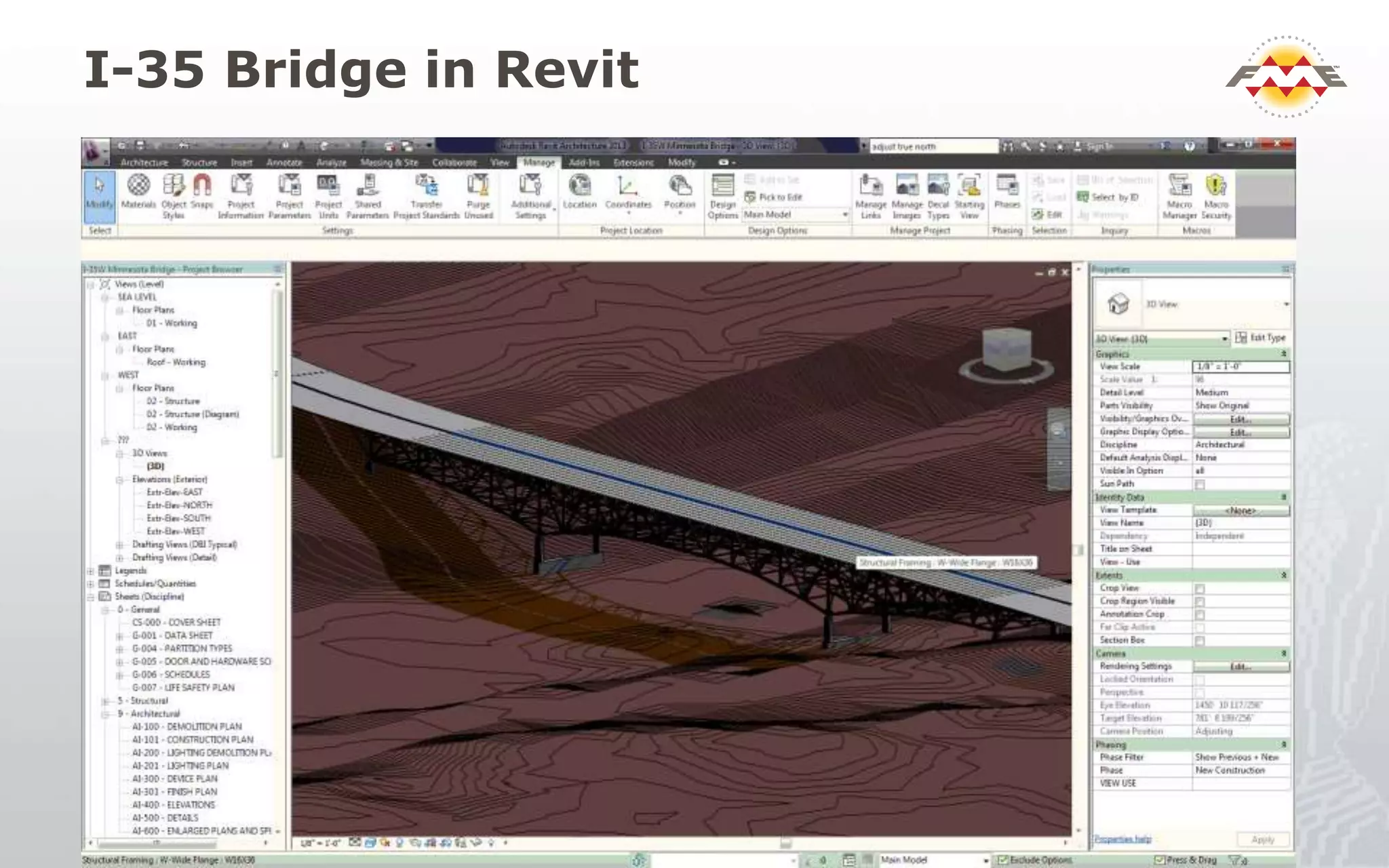
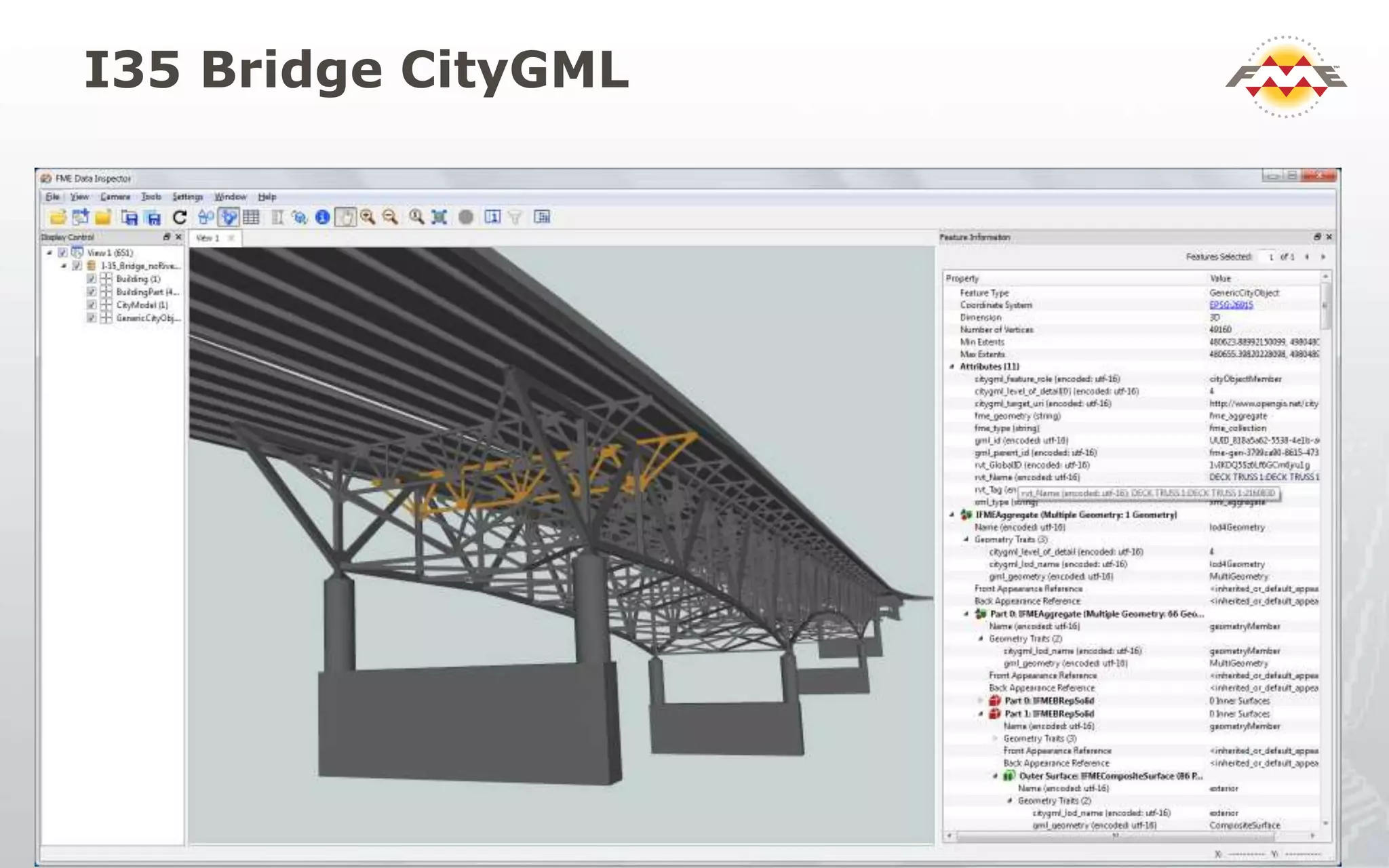
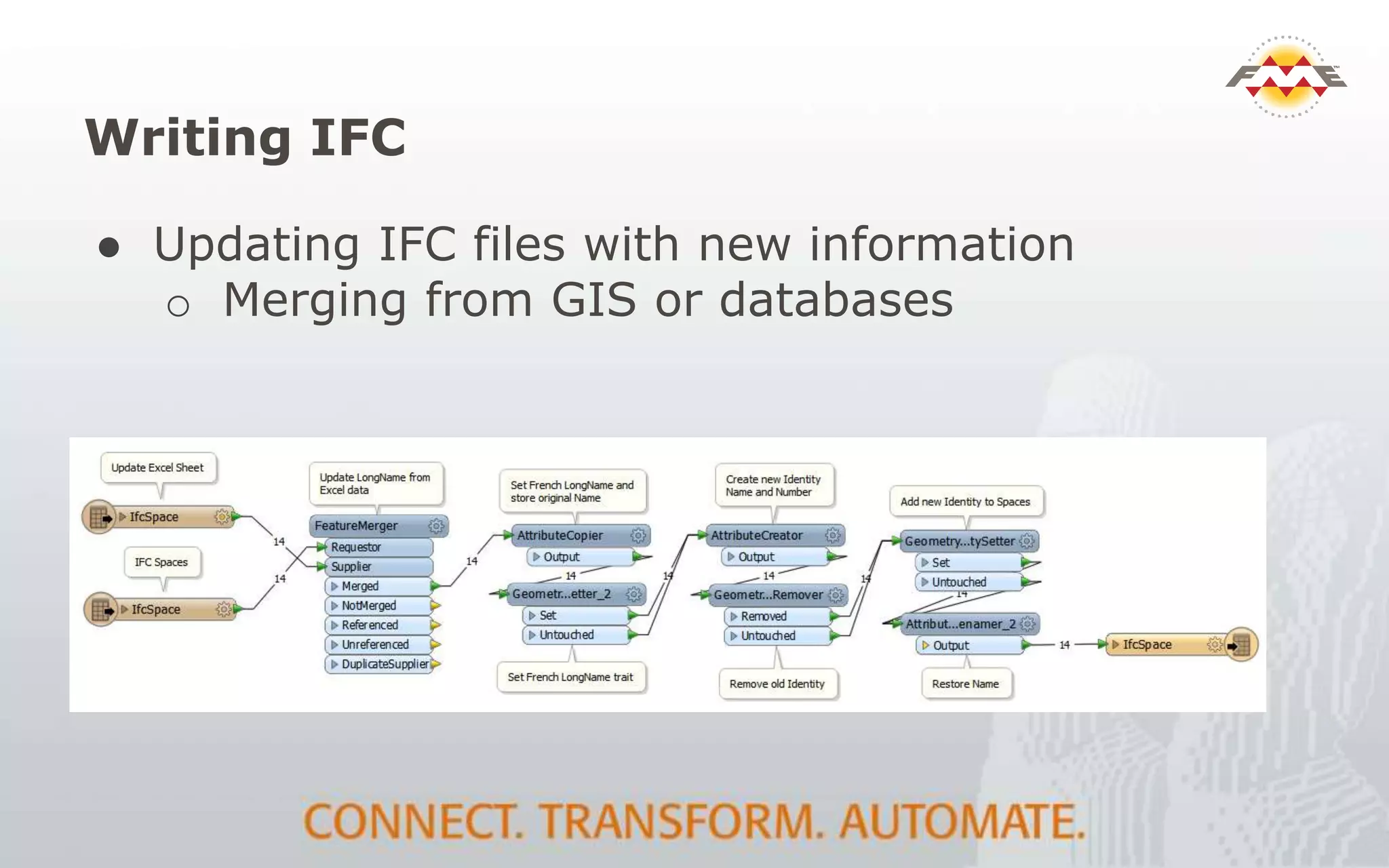
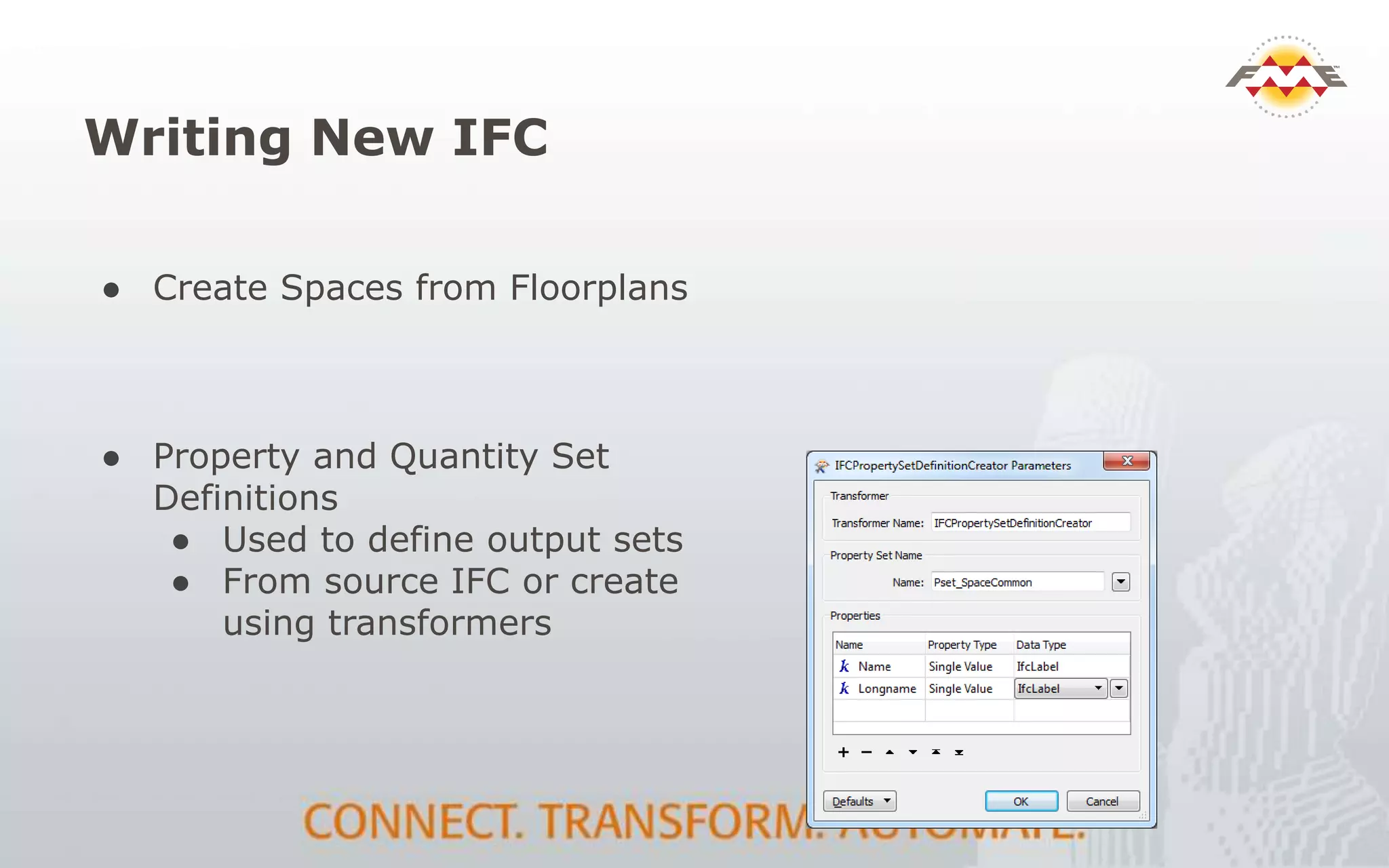
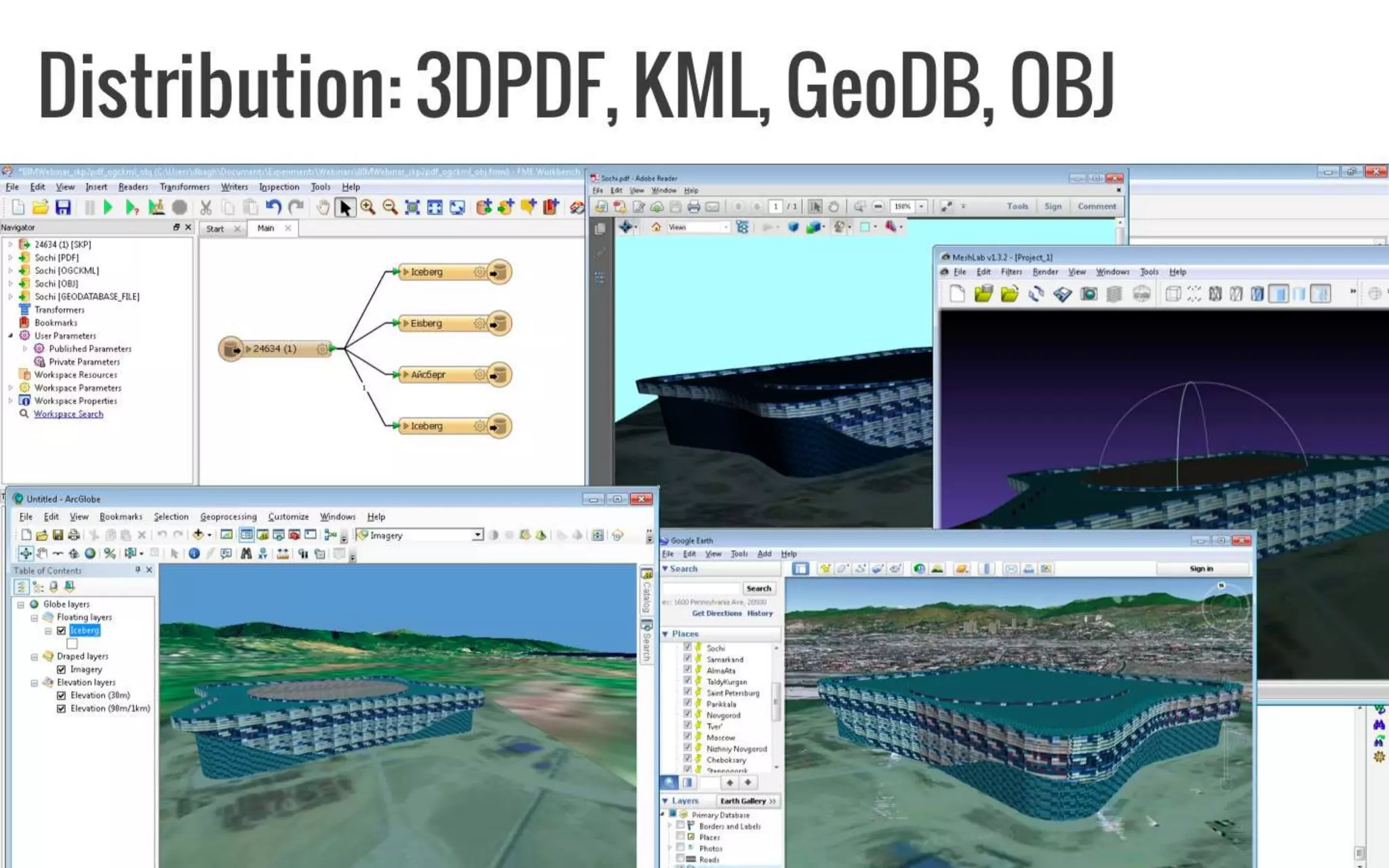
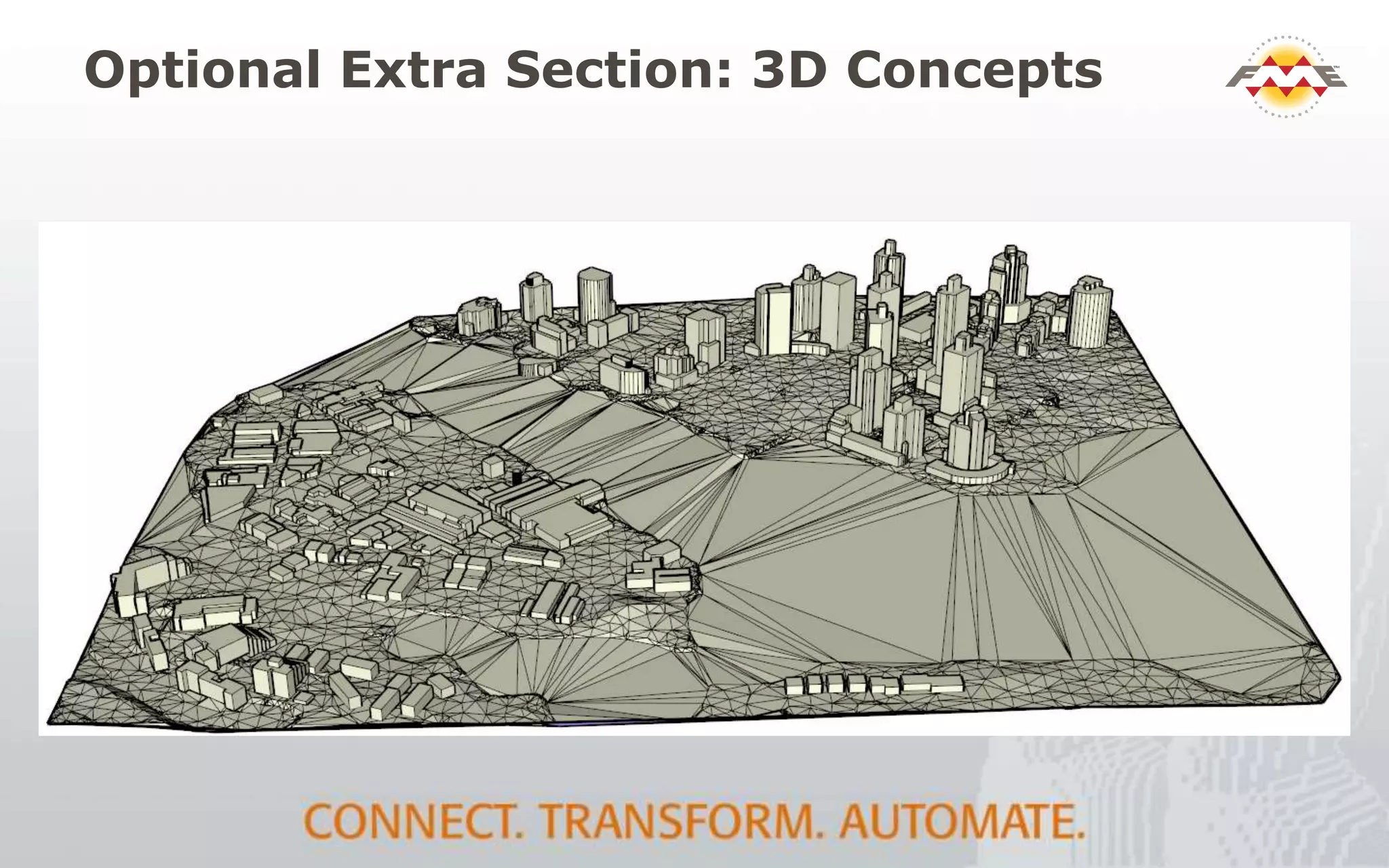
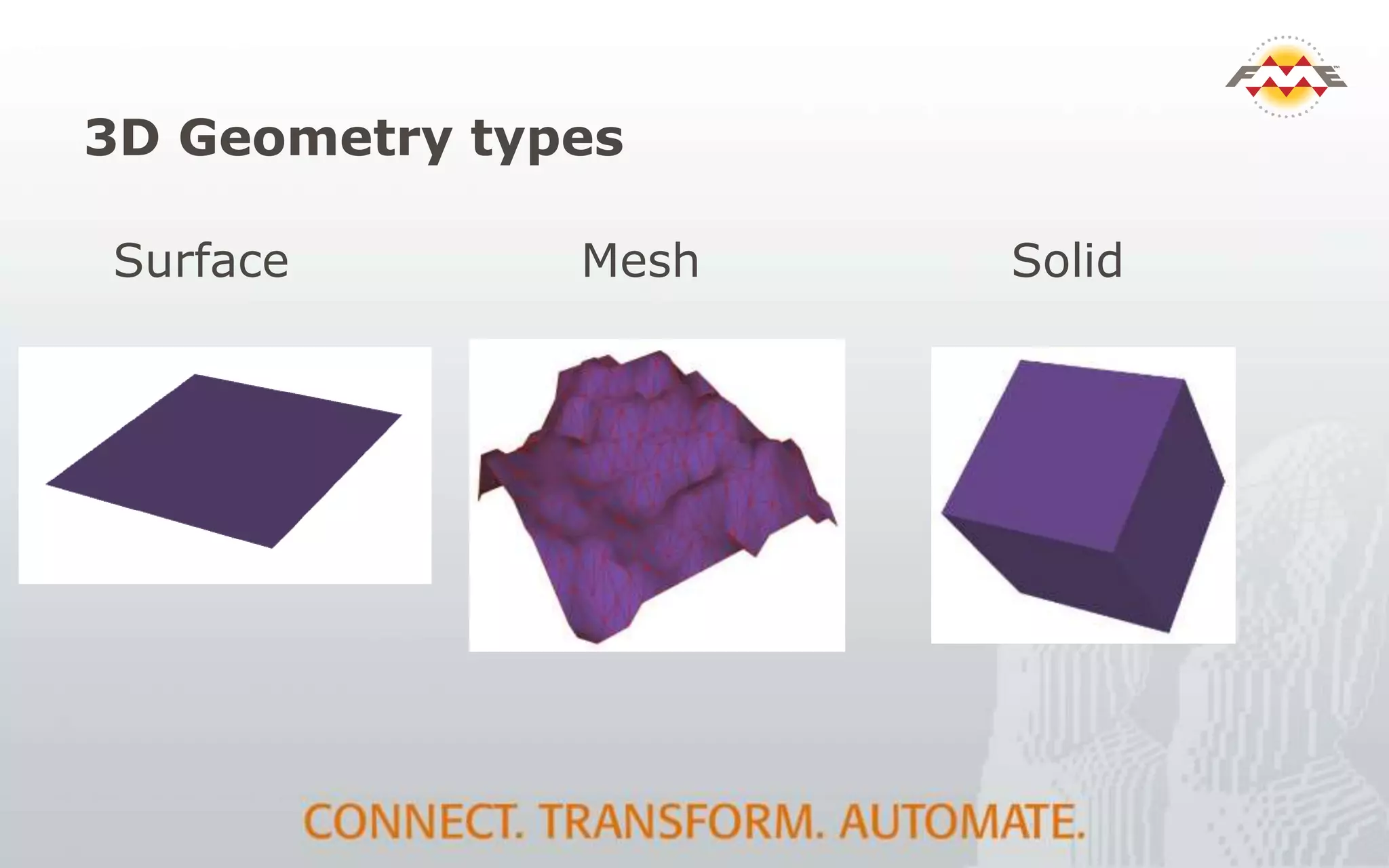
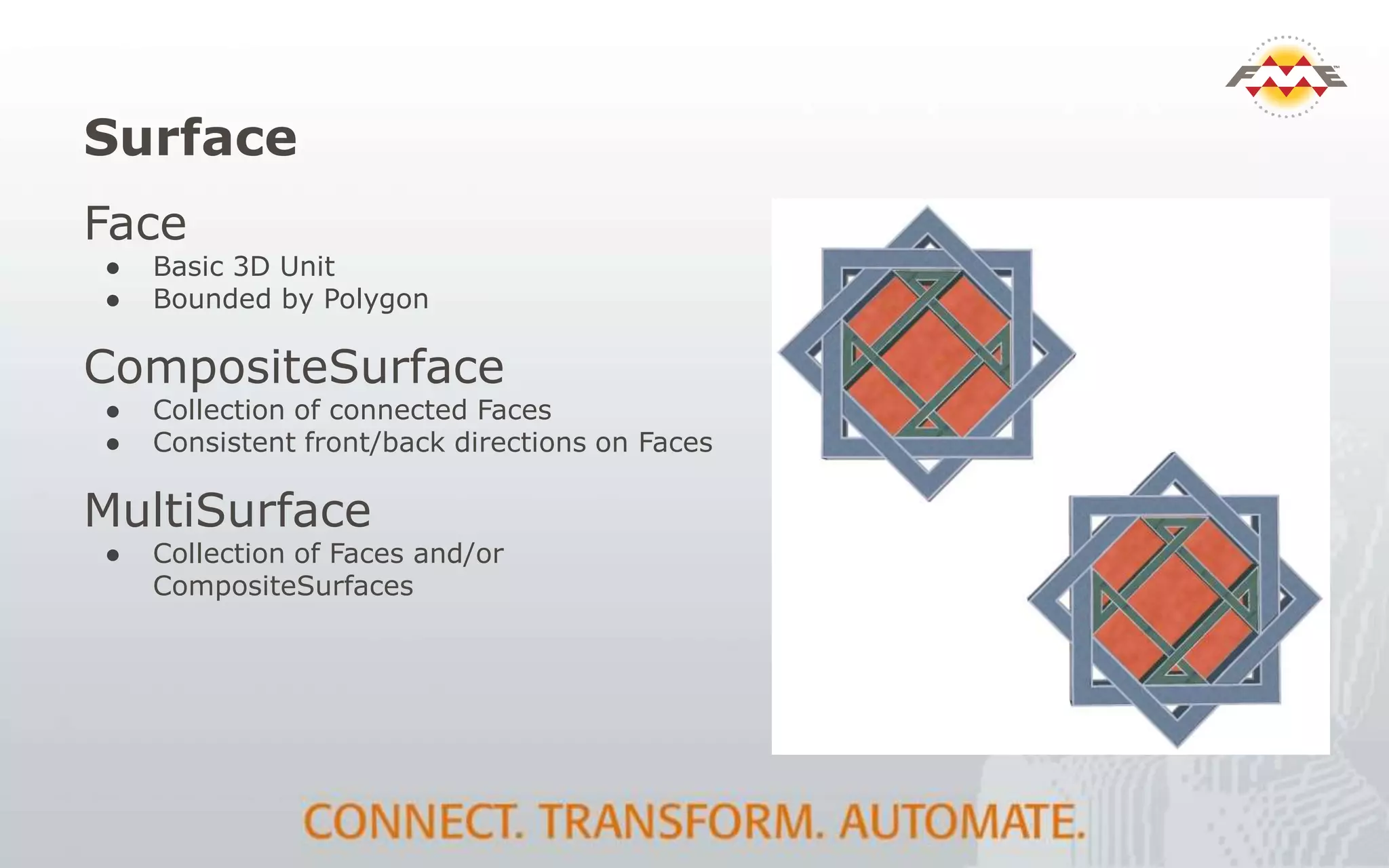
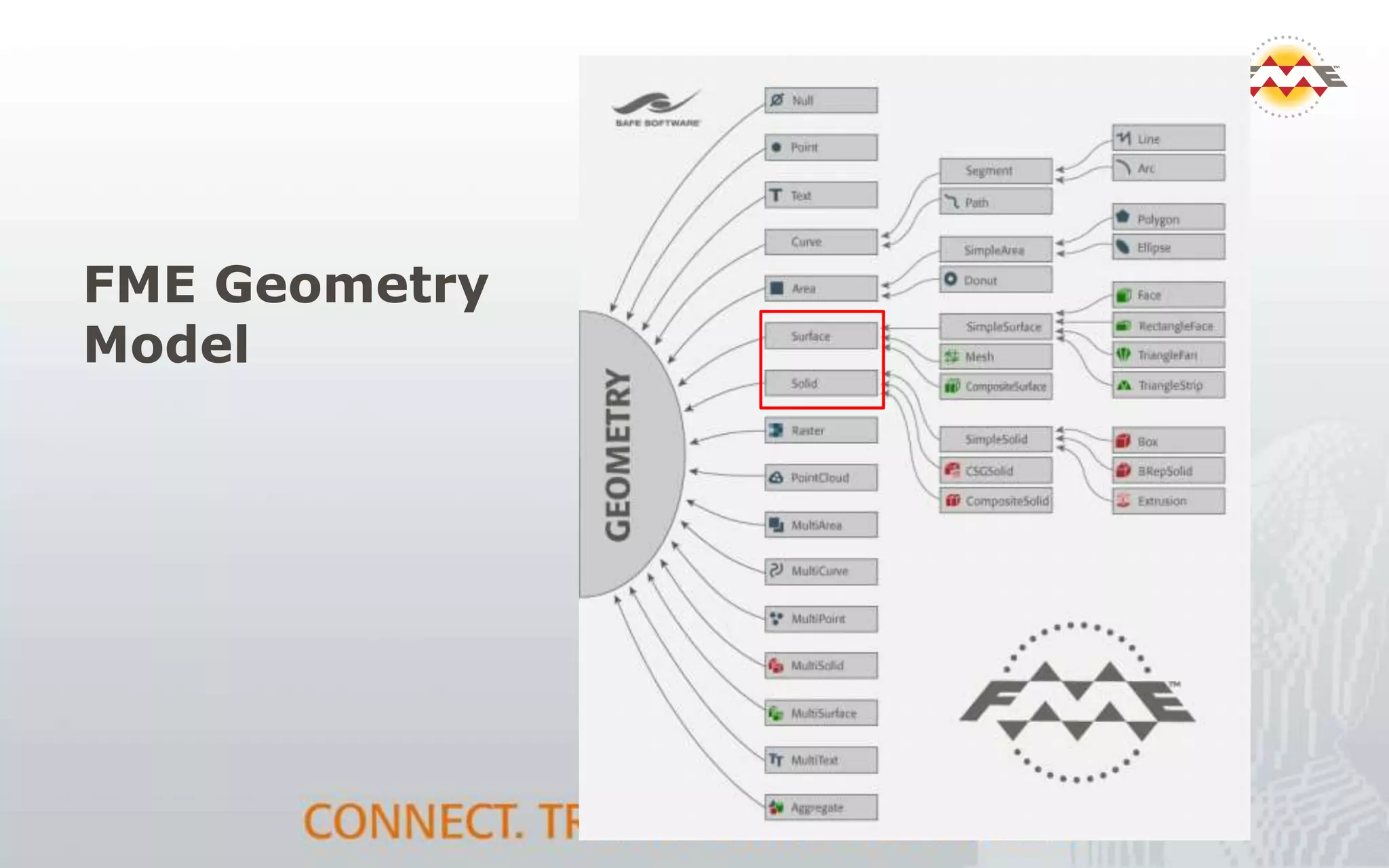
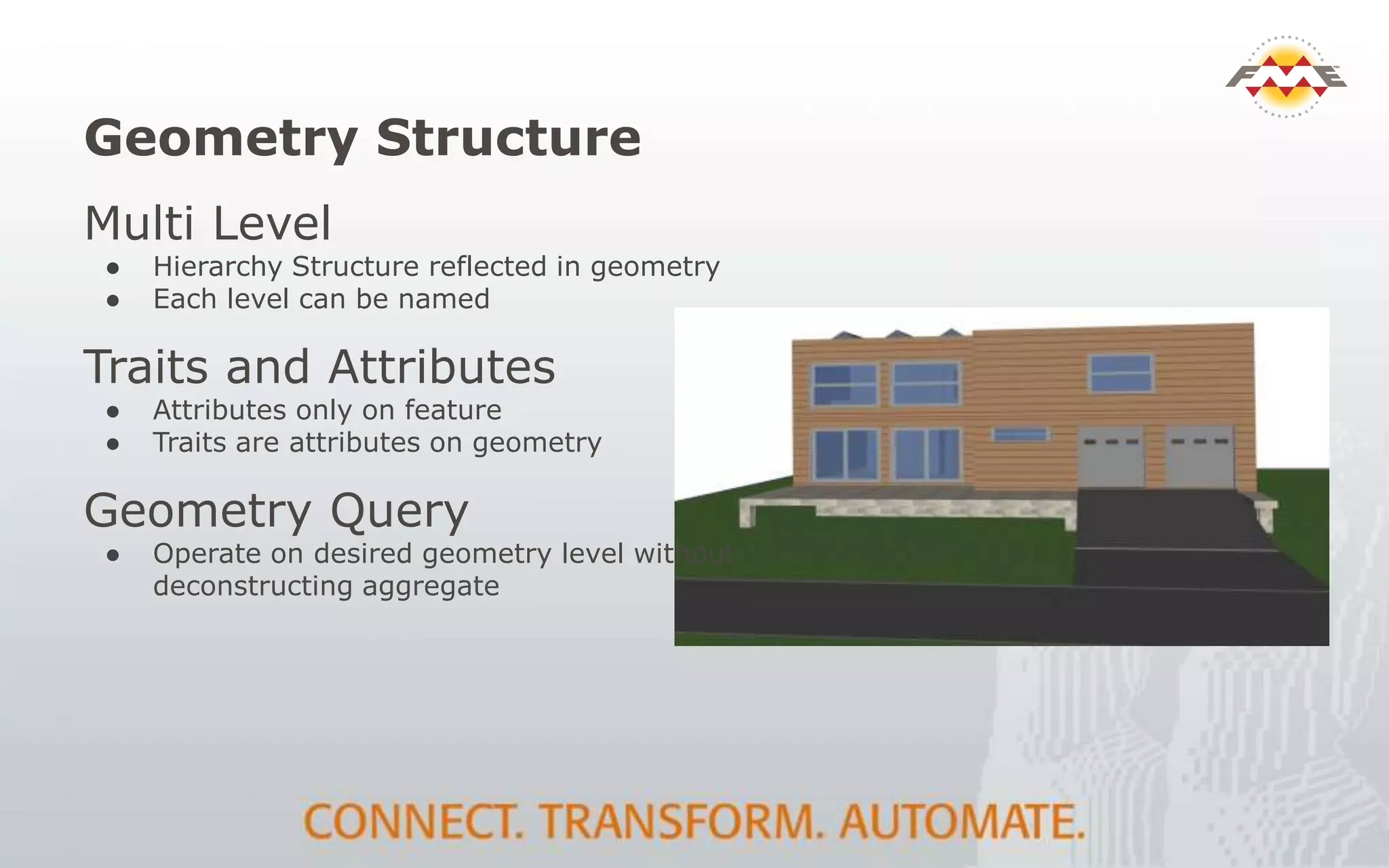
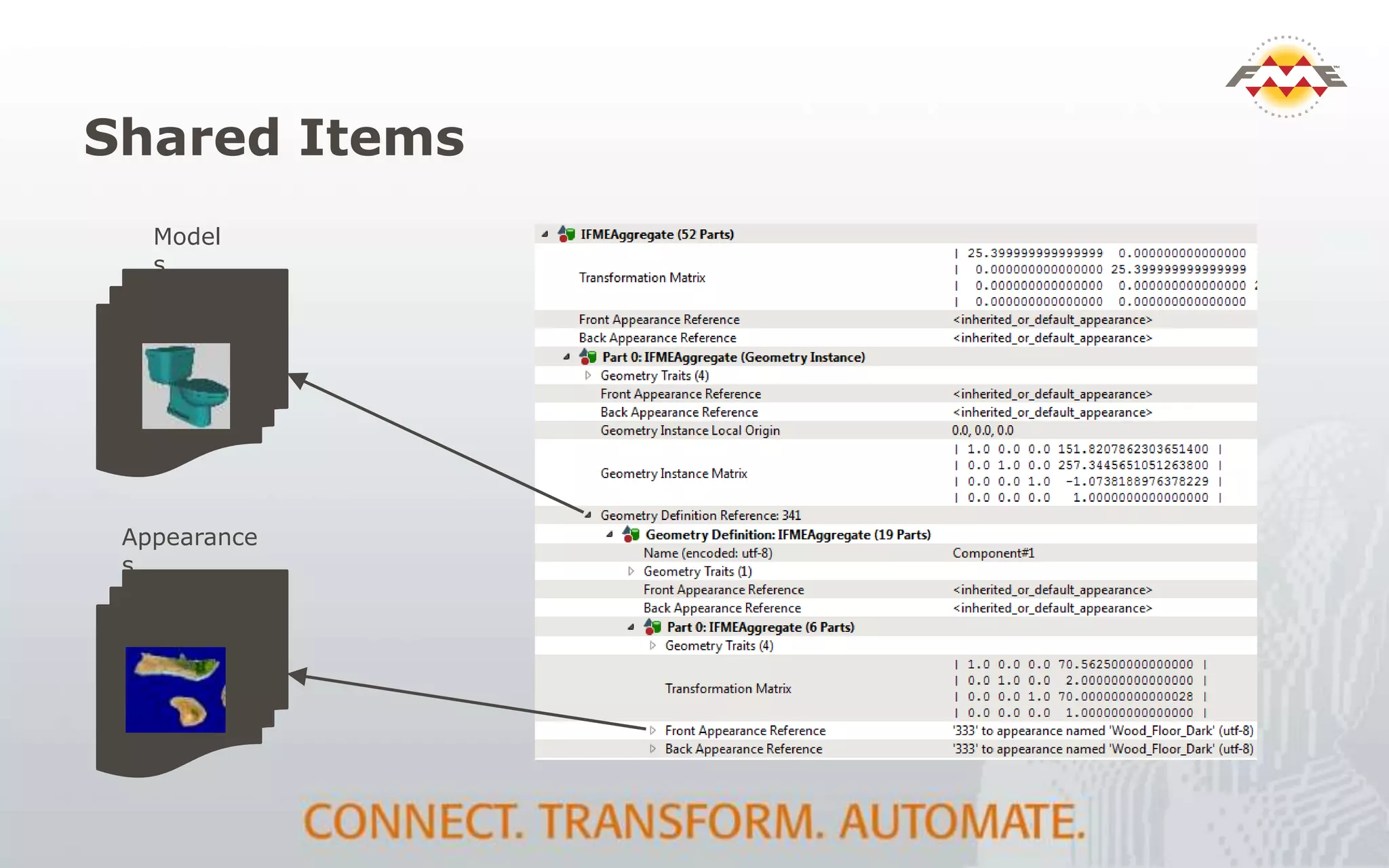
The document provides an overview of the integration between Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Geographic Information Systems (GIS), highlighting the challenges and opportunities in leveraging BIM data for various applications such as facilities management and construction. It discusses tools like FME for the conversion and management of complex BIM data formats like IFC and Revit into GIS-compatible formats such as CityGML and KML. Additionally, it addresses key concepts in 3D geometry types, data validation, and schema mapping essential for successful BIM to GIS transformation.