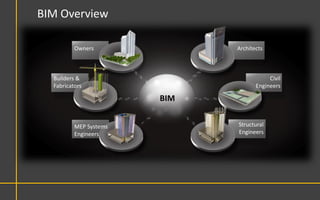
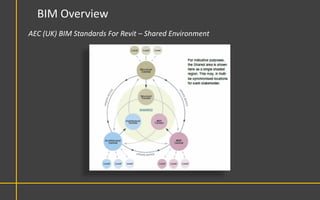
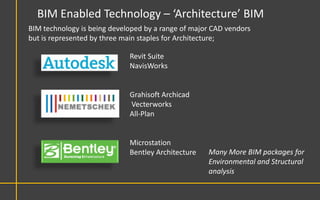
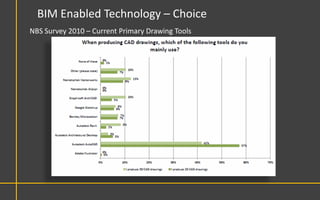
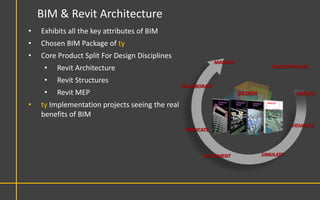
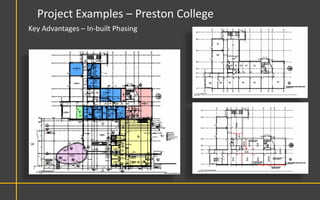
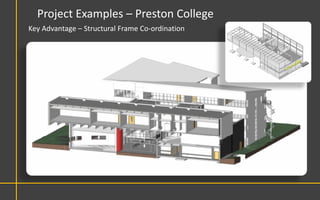
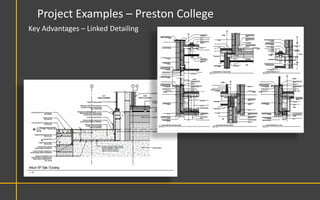
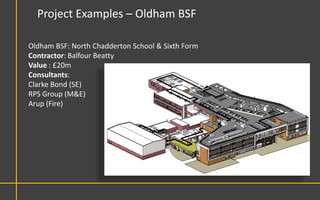
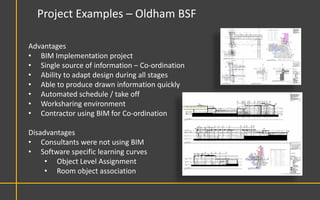
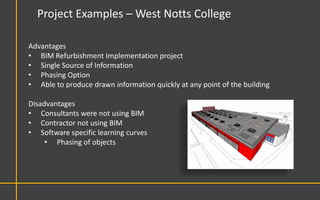
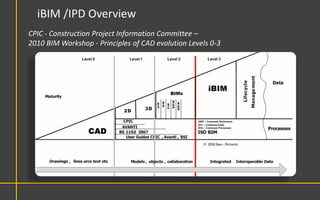
This document discusses Building Information Modeling (BIM) concepts and implementation using Revit. It defines BIM as a digital representation of physical and functional building characteristics that can be used as a shared knowledge resource throughout a building's life. The document outlines BIM definitions, drivers for change, advantages for design, construction and facilities management, and examples of BIM implementation on projects in the UK. It concludes that BIM adoption requires establishing best practices and that its true potential is realized through integrated BIM and integrated project delivery.