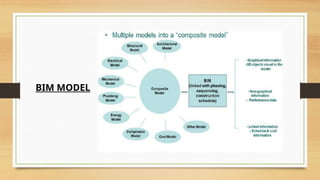
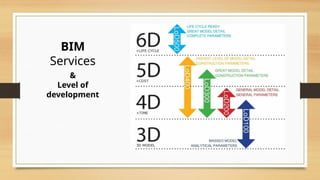
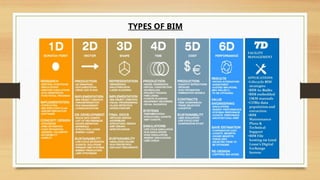
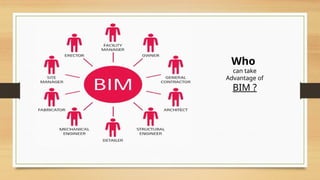
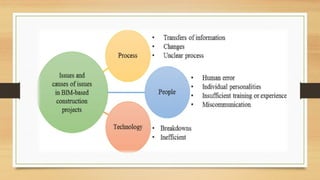
The document discusses Building Information Modelling (BIM), emphasizing its significance in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) sectors. It outlines the historical development of BIM, its various dimensions (3D to 7D), and the benefits of using BIM for project planning, cost management, and sustainability. Additionally, it identifies the stakeholders who can leverage BIM and the objectives of exploring BIM processes and software.