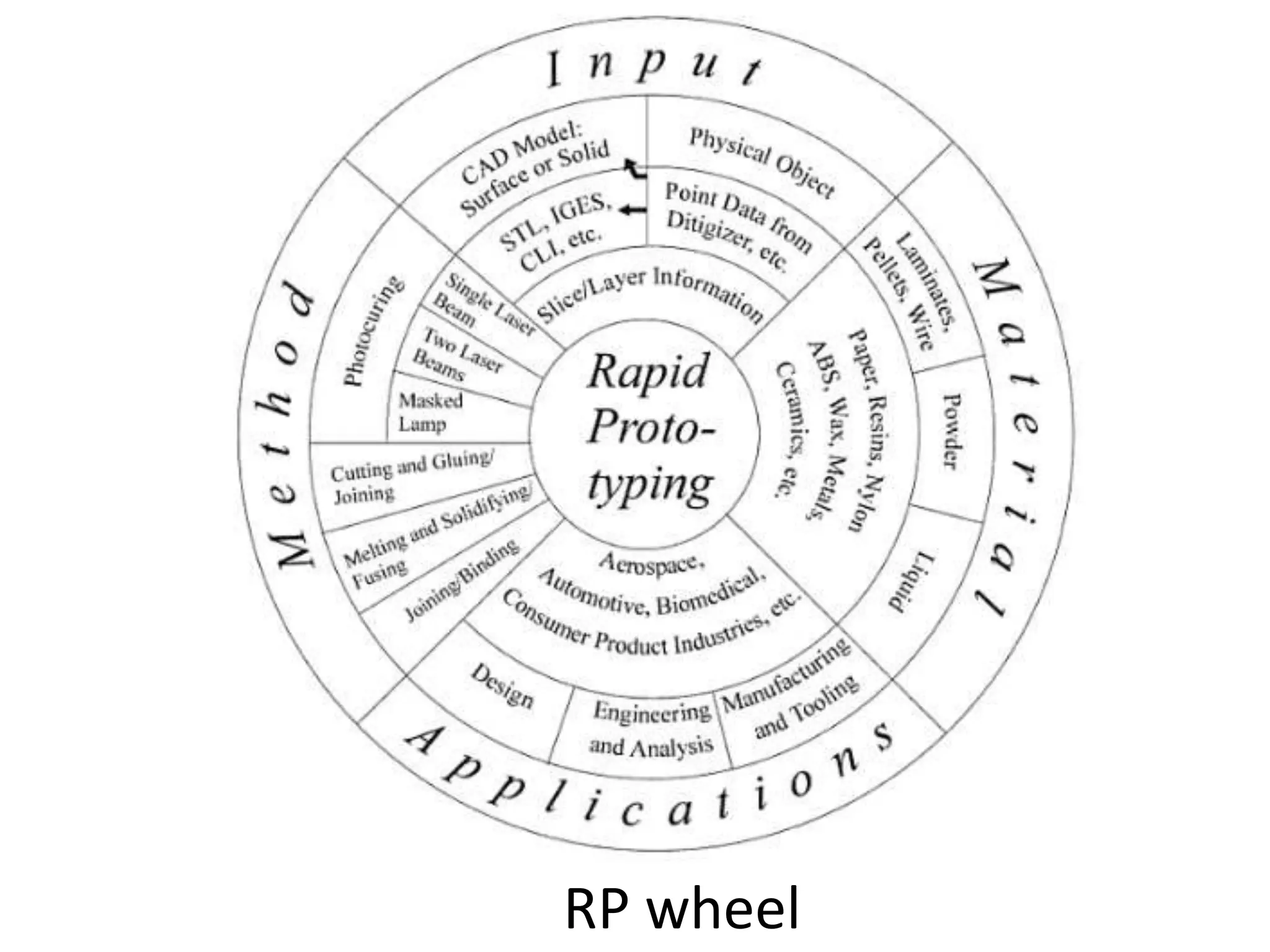
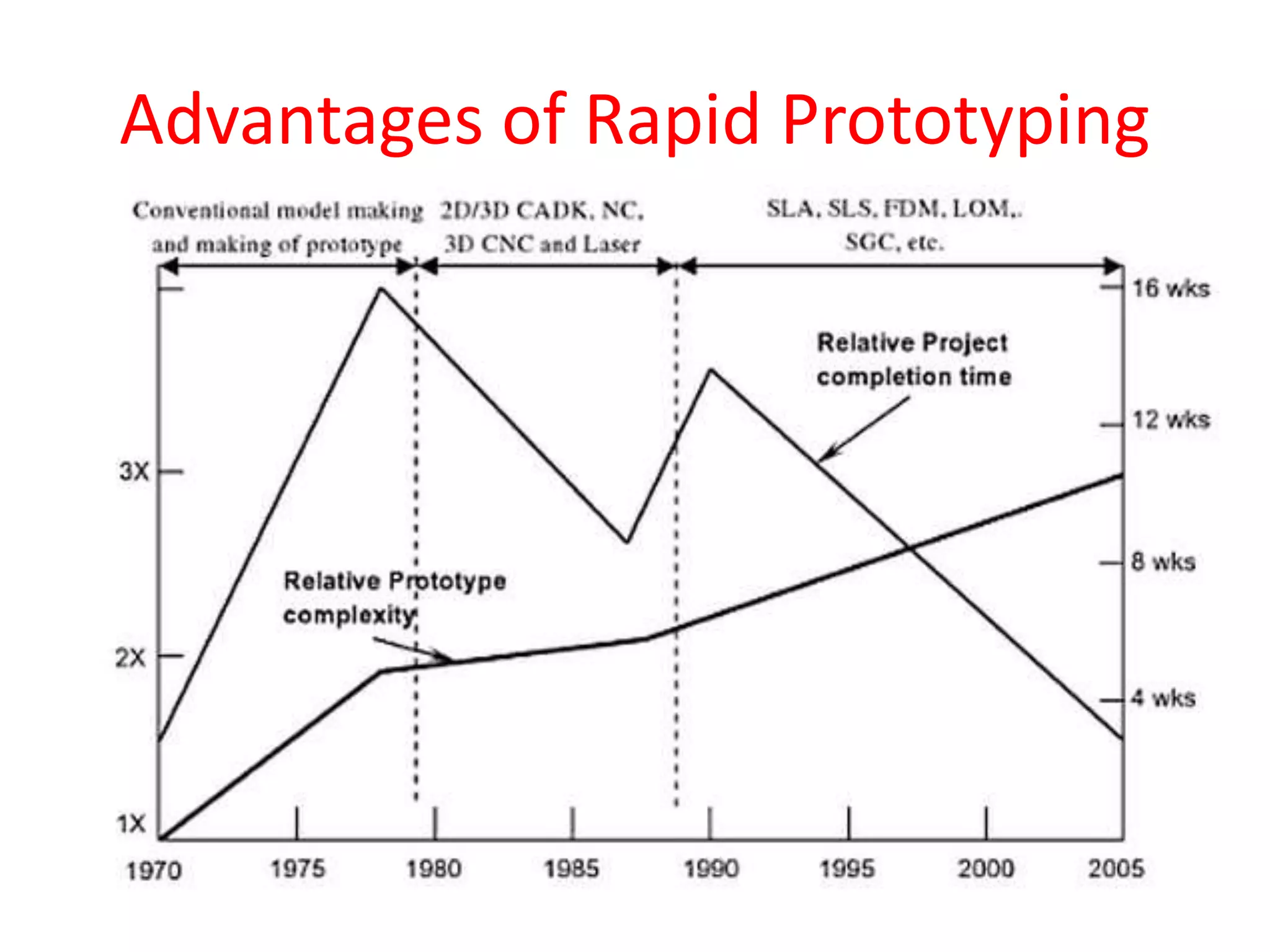
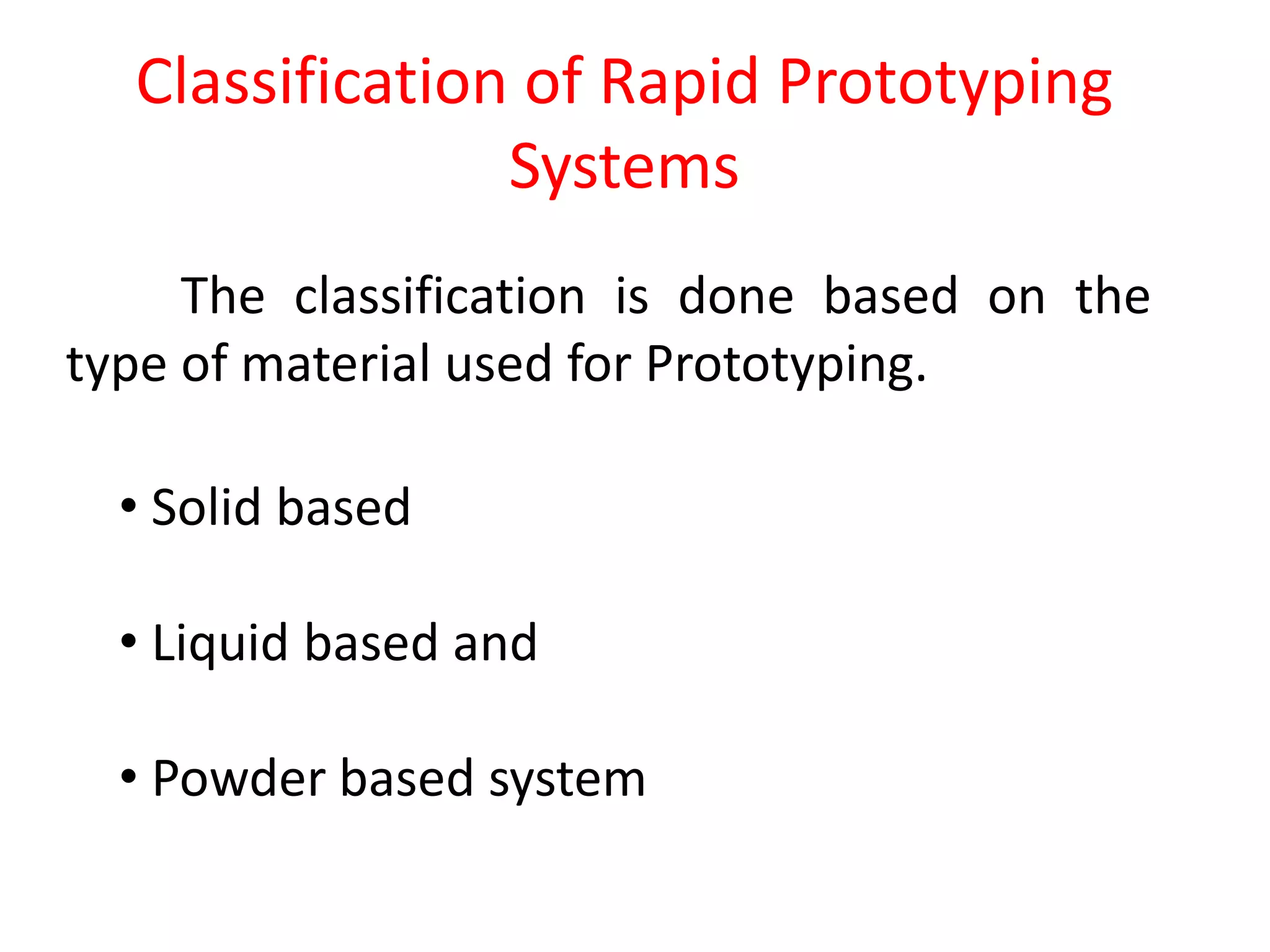
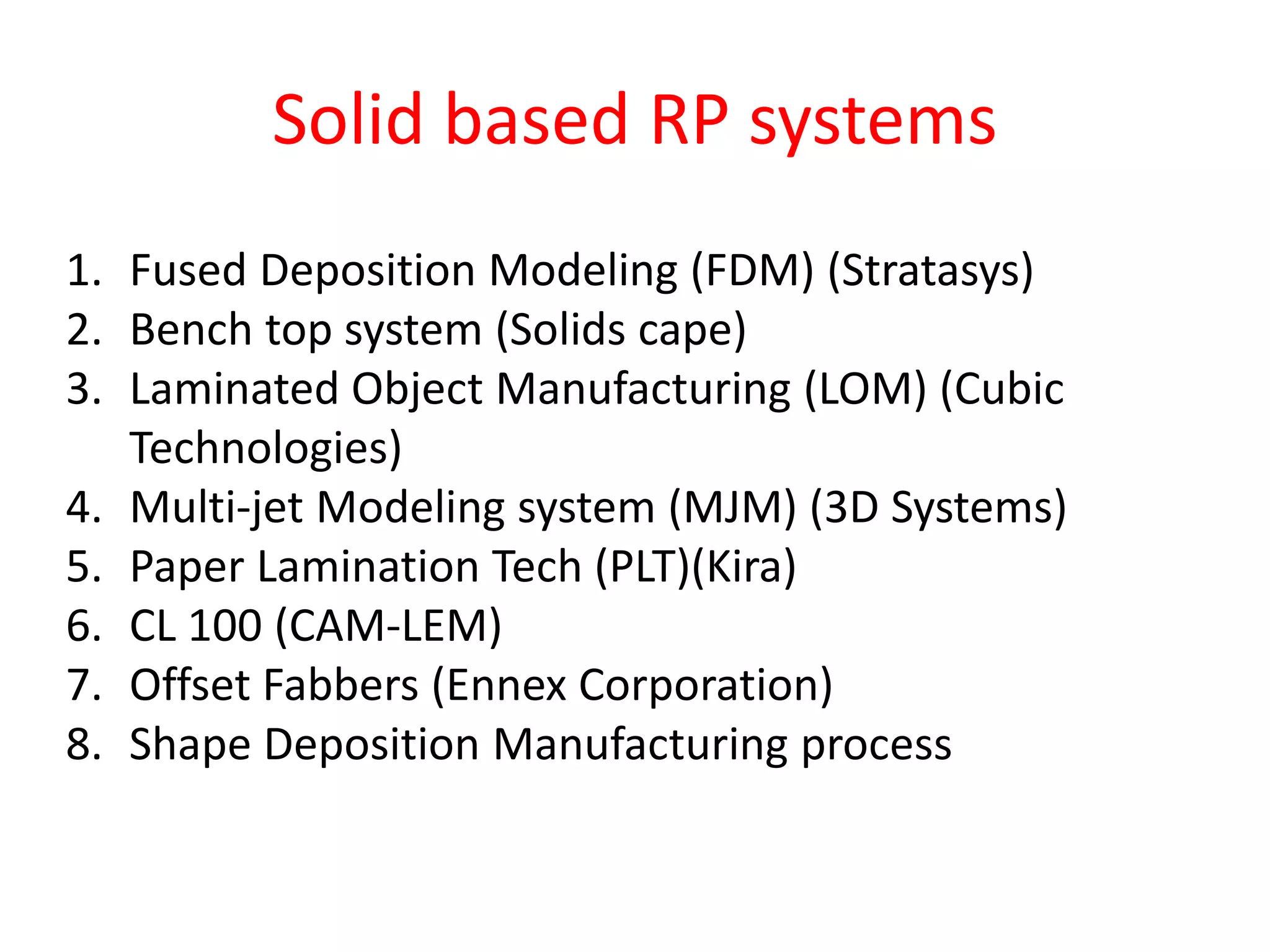
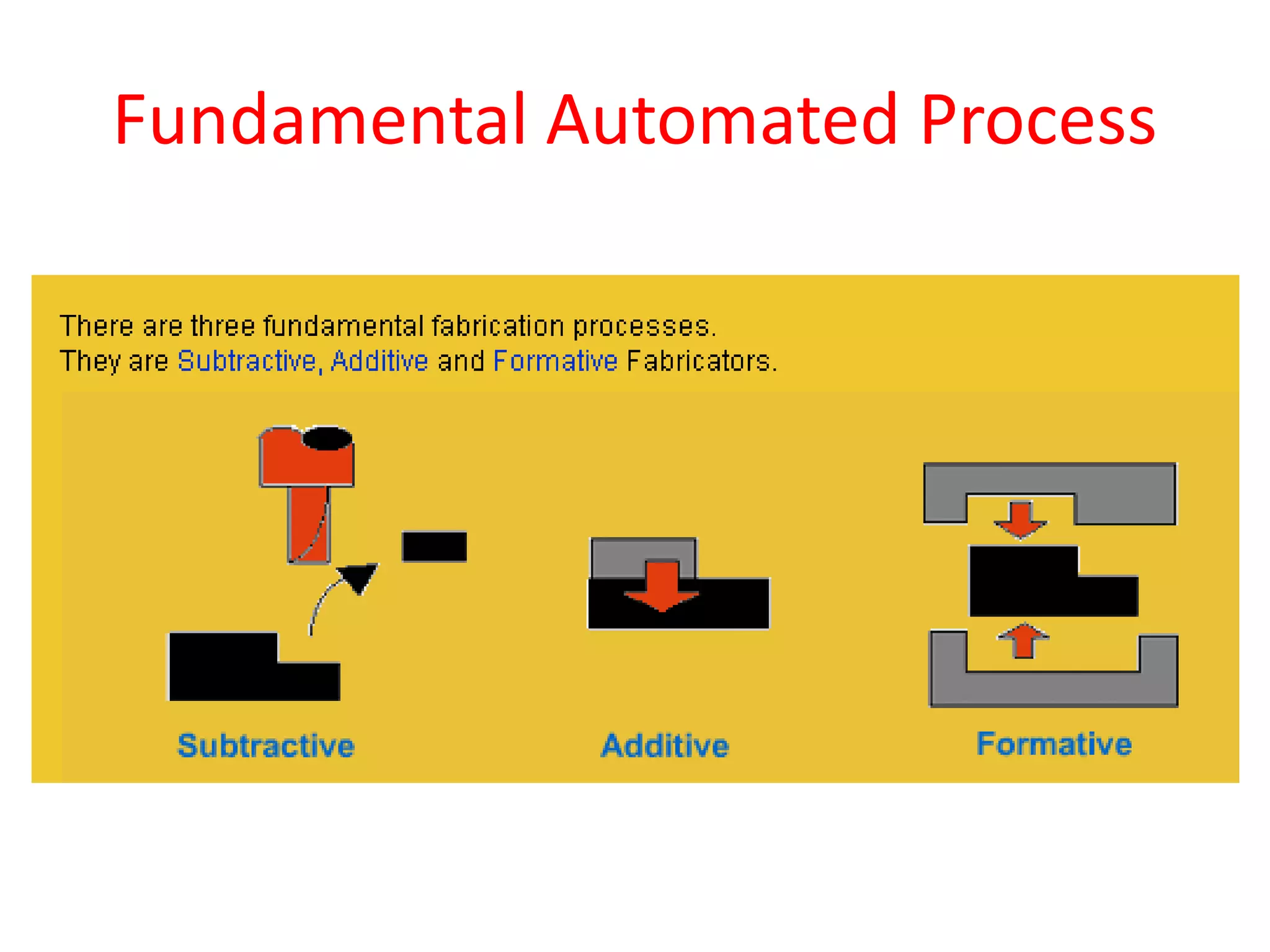
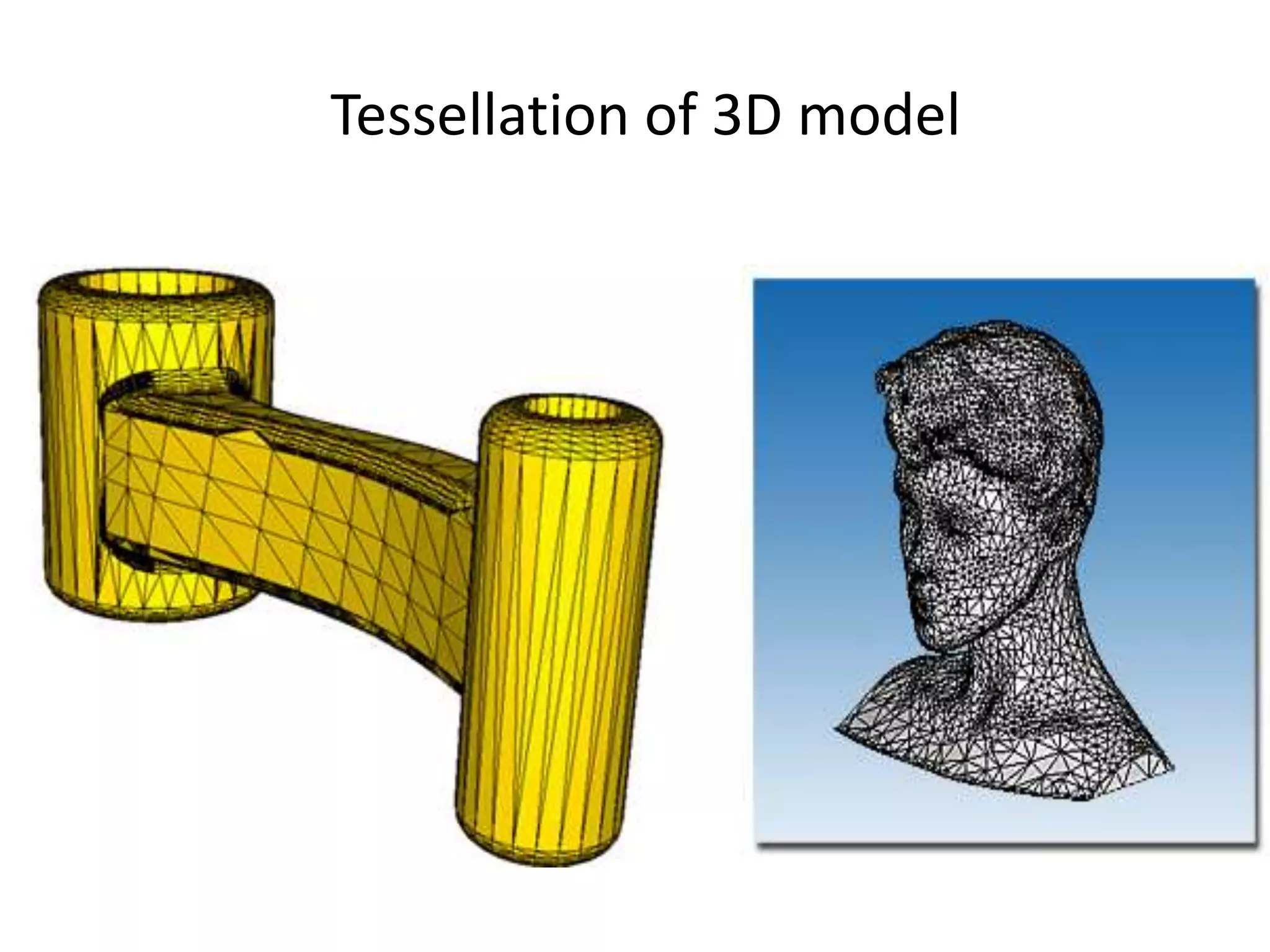
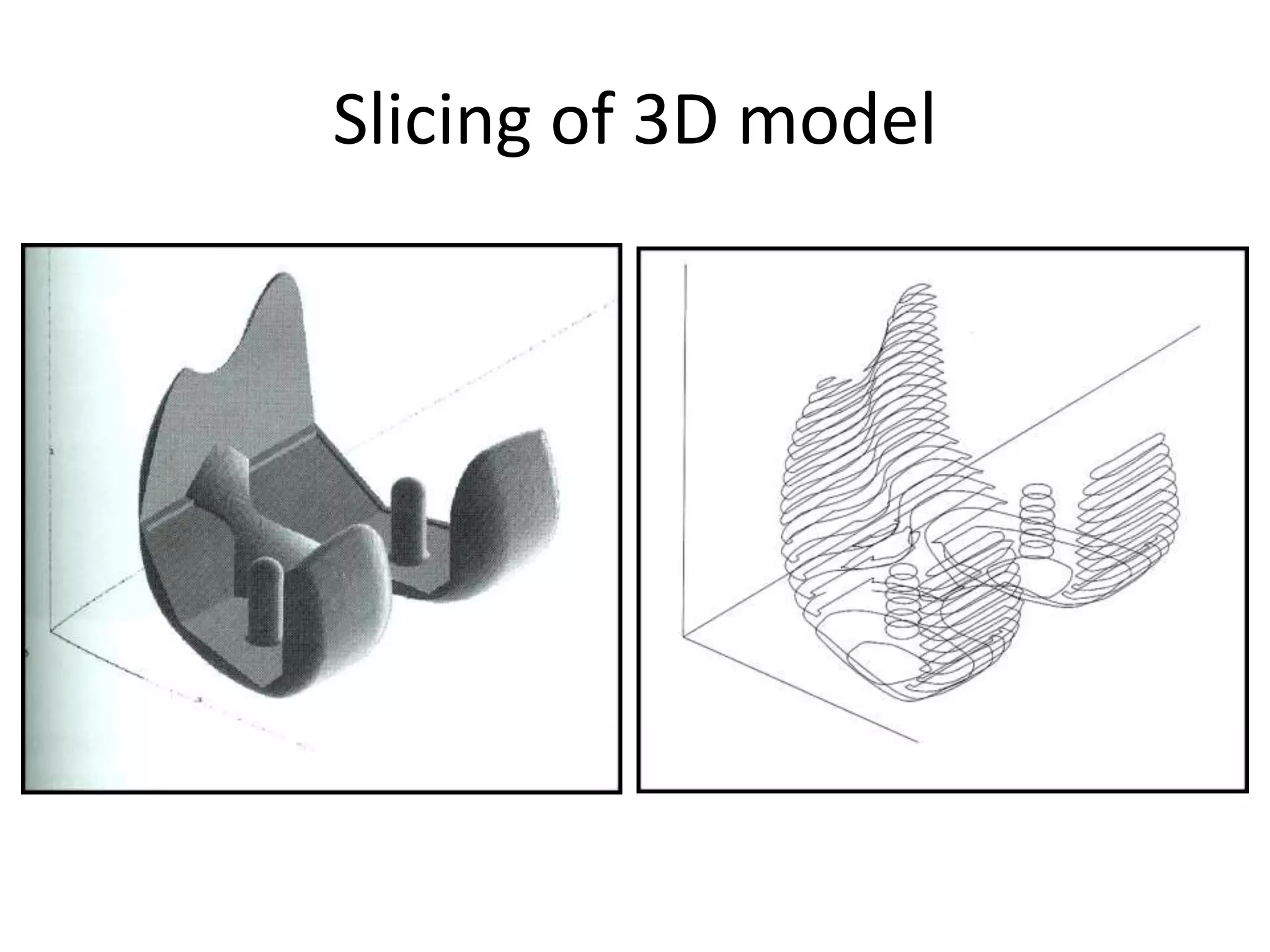
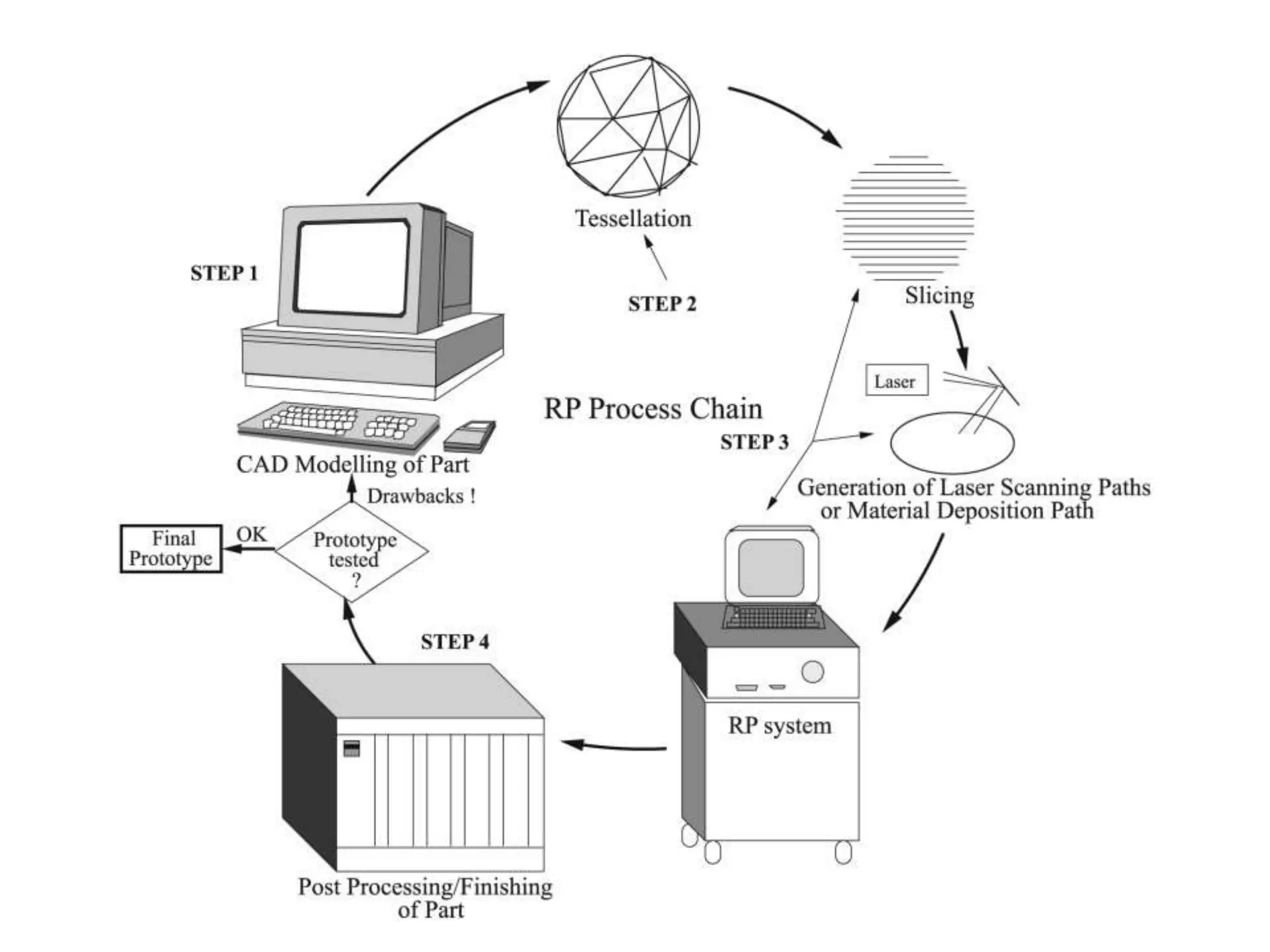
Rapid prototyping allows for the creation of preliminary versions or prototypes of products through various additive manufacturing methods. It has several benefits including testing designs, communicating designs to others, and reducing the time and costs associated with traditional prototyping. There are various types of rapid prototyping systems categorized by the material used - solid-based systems use plastics, liquid-based use photopolymers cured by UV light, and powder-based systems use metal or ceramic powders fused by a laser. Rapid prototyping has gone through several phases of development and now allows for highly accurate, physical models to be created quickly.