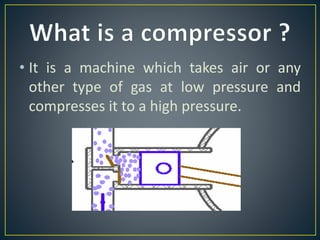
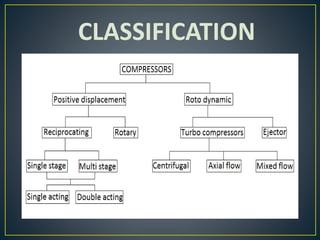
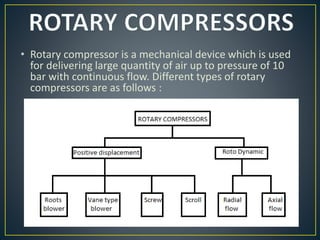
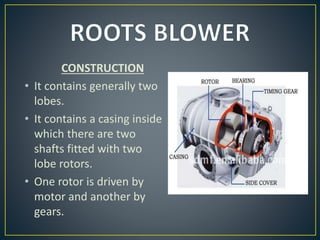
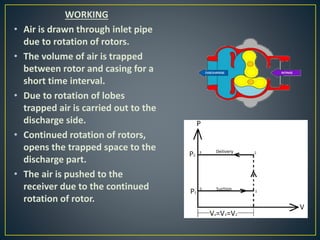
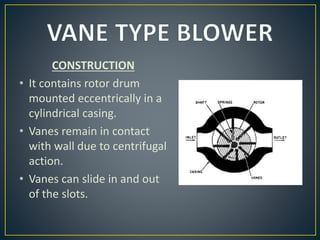
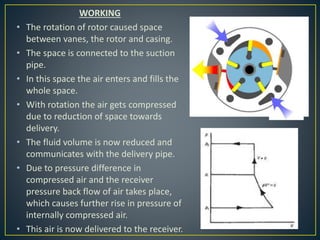
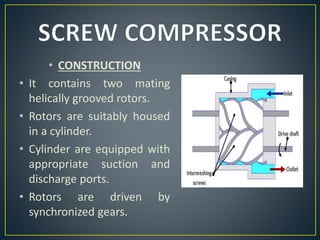
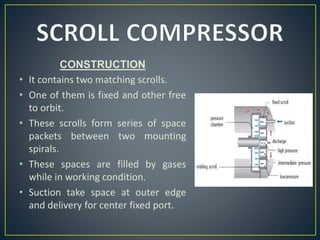
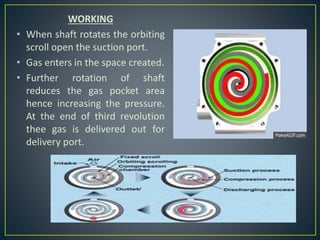
This document discusses different types of rotary compressors used to compress air or gas. It describes positive displacement and roto dynamic rotary compressors. It then provides details on the construction and working of rotary lobe compressors, rotary vane compressors, rotary screw compressors, and scroll compressors. For each type, it outlines the key components and explains how compression is achieved as the gas is drawn in and compressed spaces are reduced in size.