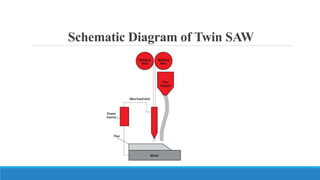
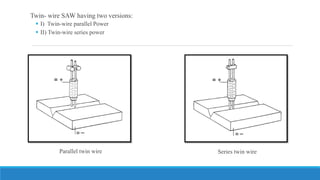
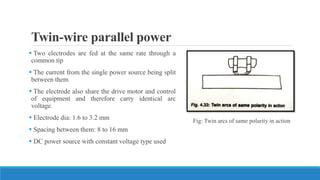
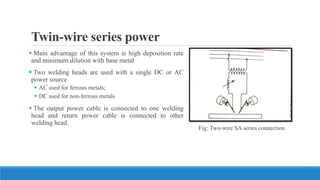
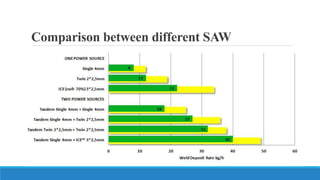
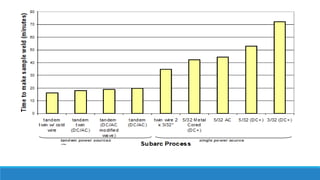
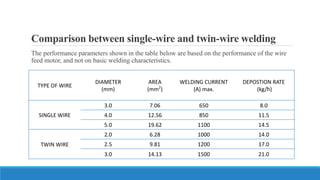
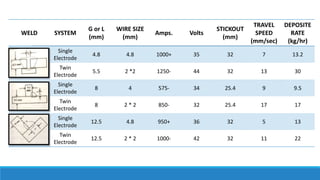
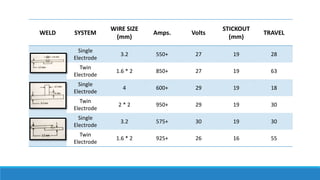
This document discusses multi-wire submerged arc welding. It describes the basic equipment used, which includes a wire feeder, welding power source, and flux feeding arrangement. It then focuses on twin submerged arc welding, which involves feeding two wires in parallel through the same contact tip to increase melt production and stability compared to a single wire. Schematics and diagrams show how twin welding is arranged. Higher deposition rates of up to 38kg/h are possible using four 2.5mm diameter wires in a tandem twin configuration. Parallel and series twin wire configurations are also explained and compared. Charts provide data on deposition rates achievable using single versus twin wire setups. Applications of the twin arc system are mentioned.