The Bairstow method and Muller method are techniques for calculating the roots of polynomials.
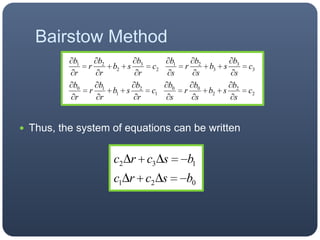
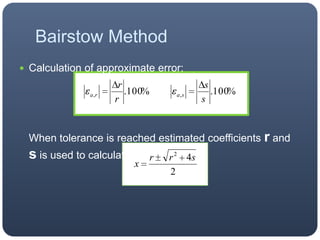
The Bairstow method uses synthetic division to iteratively calculate the roots of a polynomial by dividing it by quadratic factors (x^2 - rx - s) until the remainder is zero. It obtains better approximations of r and s at each iteration to isolate the roots.
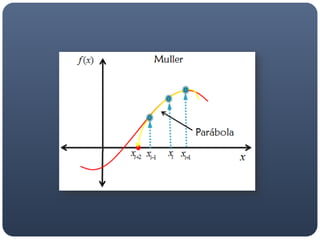
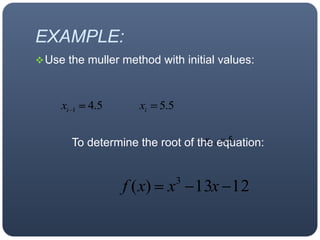
The Muller method fits a parabola through three initial guesses to obtain the coefficients a, b, c of the quadratic formula. It then uses the quadratic formula to find the root, and iterates with new guesses to converge on more accurate roots.
Both methods use iterative techniques to gradually converge on the real and complex roots of polynomials without