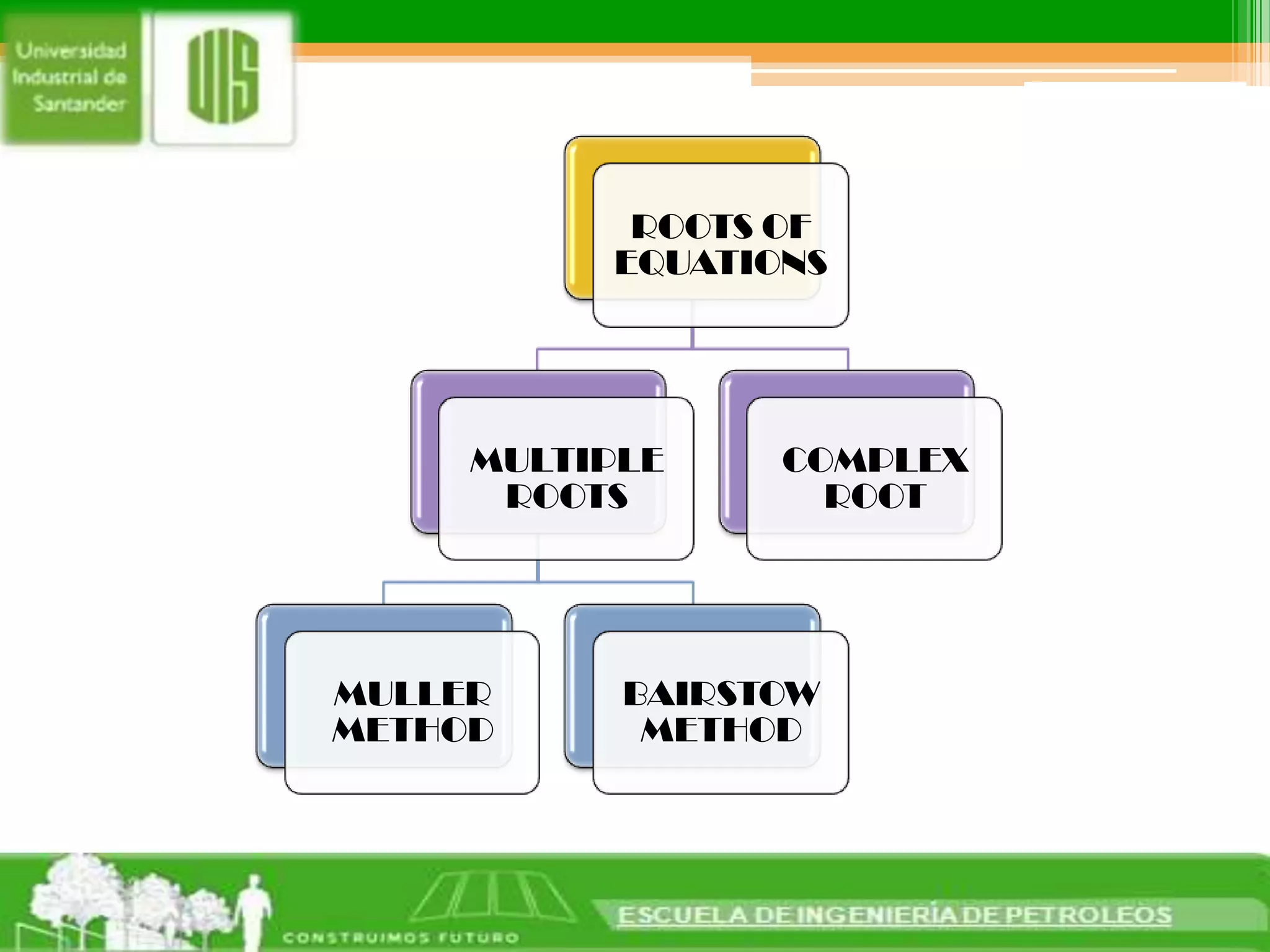
1. There are conventional methods for finding multiple roots of equations, such as the Muller method and Bairstow method. The Muller method uses three initial values to obtain the coefficients of a parabola, which are then substituted into the quadratic formula to estimate the root where the parabola intersects the x-axis. The Bairstow method iteratively calculates the factors of a polynomial to determine its roots.
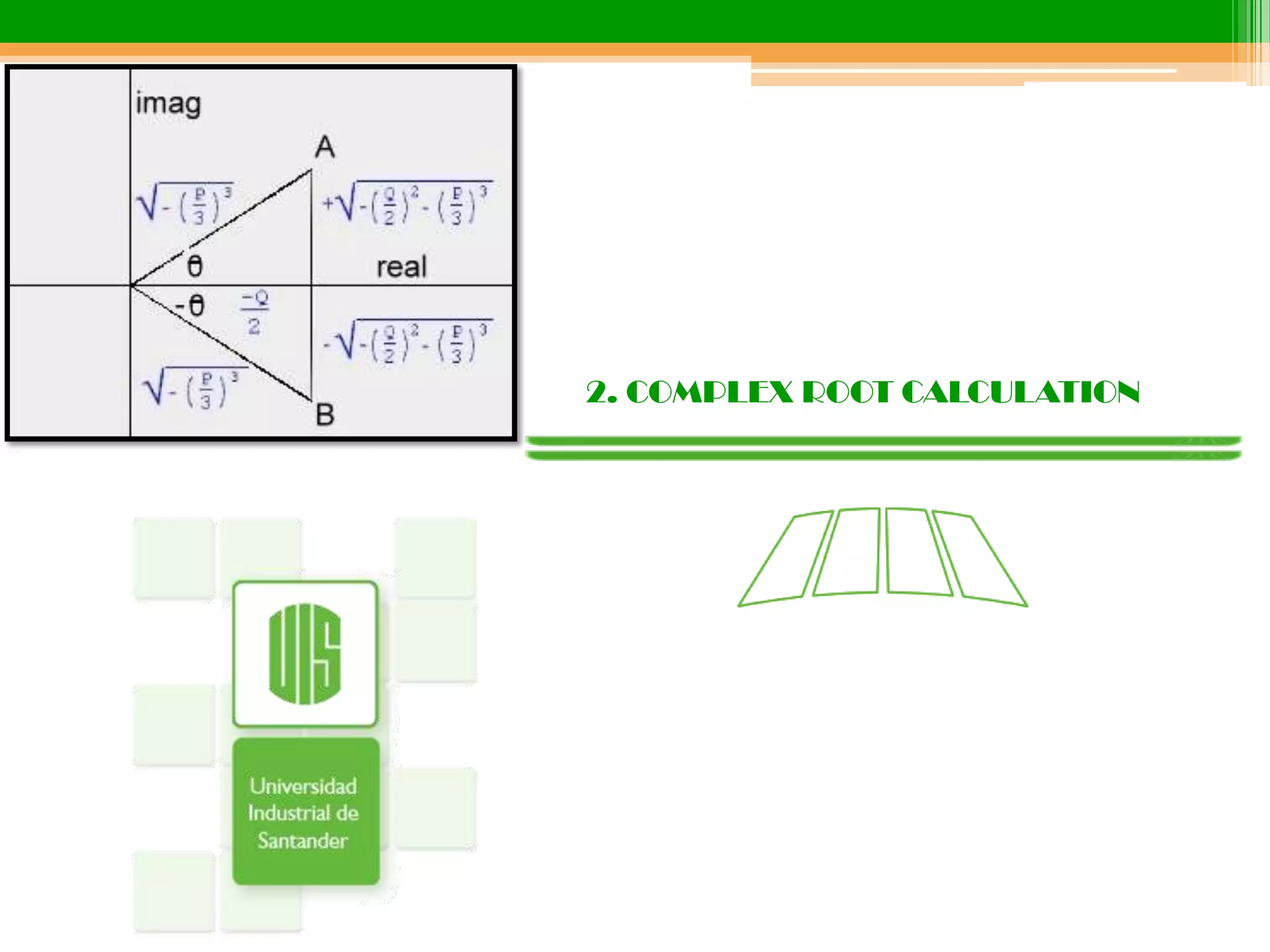
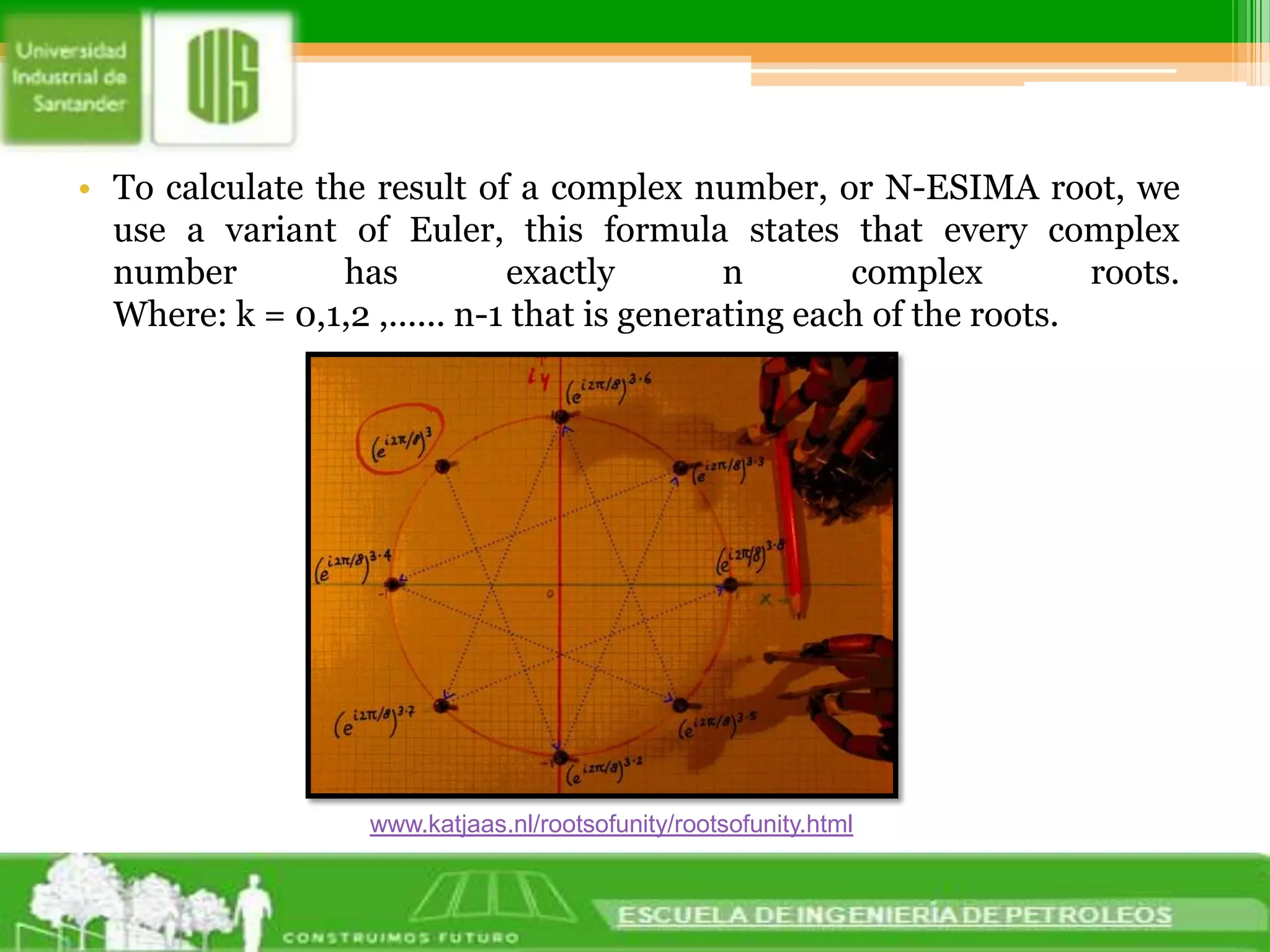
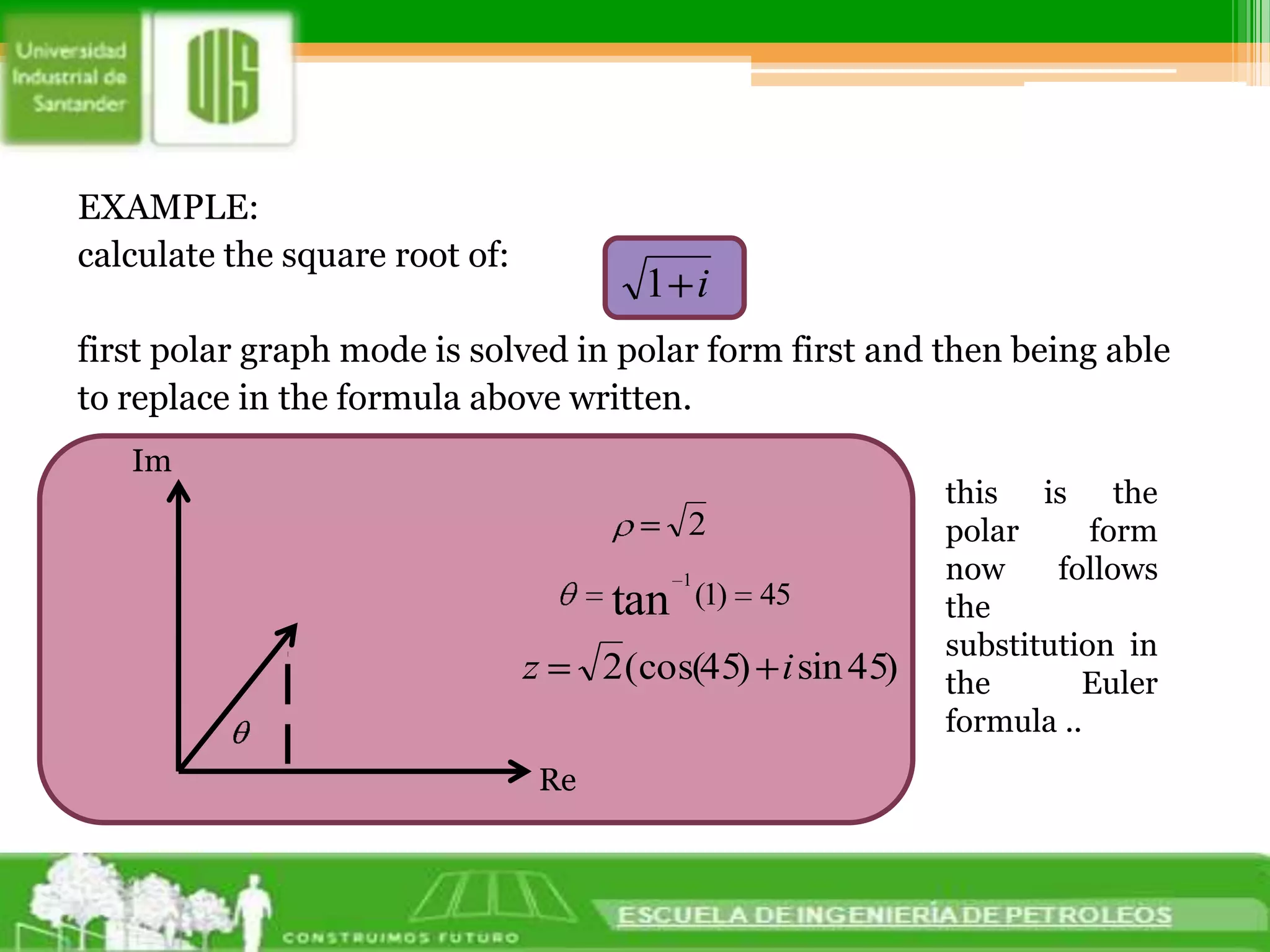
2. Complex roots of equations can be calculated using Euler's formula, which states that every complex number has exactly n complex roots. The formula generates each root by substituting different values for k between 0 and n-1. This allows polar forms of complex numbers to be substituted to find their roots



![The three initial values are denoted as xk, xk-1 y xk-2.The parabola passes through the points: (xk, f(xk)), (xk-1, f(xk-1)) y (xk-2, f(xk-2)), if it is written in the form of Newton, then: where [xk, xk-1] y f[xk, xk-1, xk-2] denote subtraction divided. This can be written as:WhereThe next iteration is given by the root that gives the equation y = 0.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raices-100514221905-phpapp02/75/ROOTS-OF-EQUATIONS-7-2048.jpg)