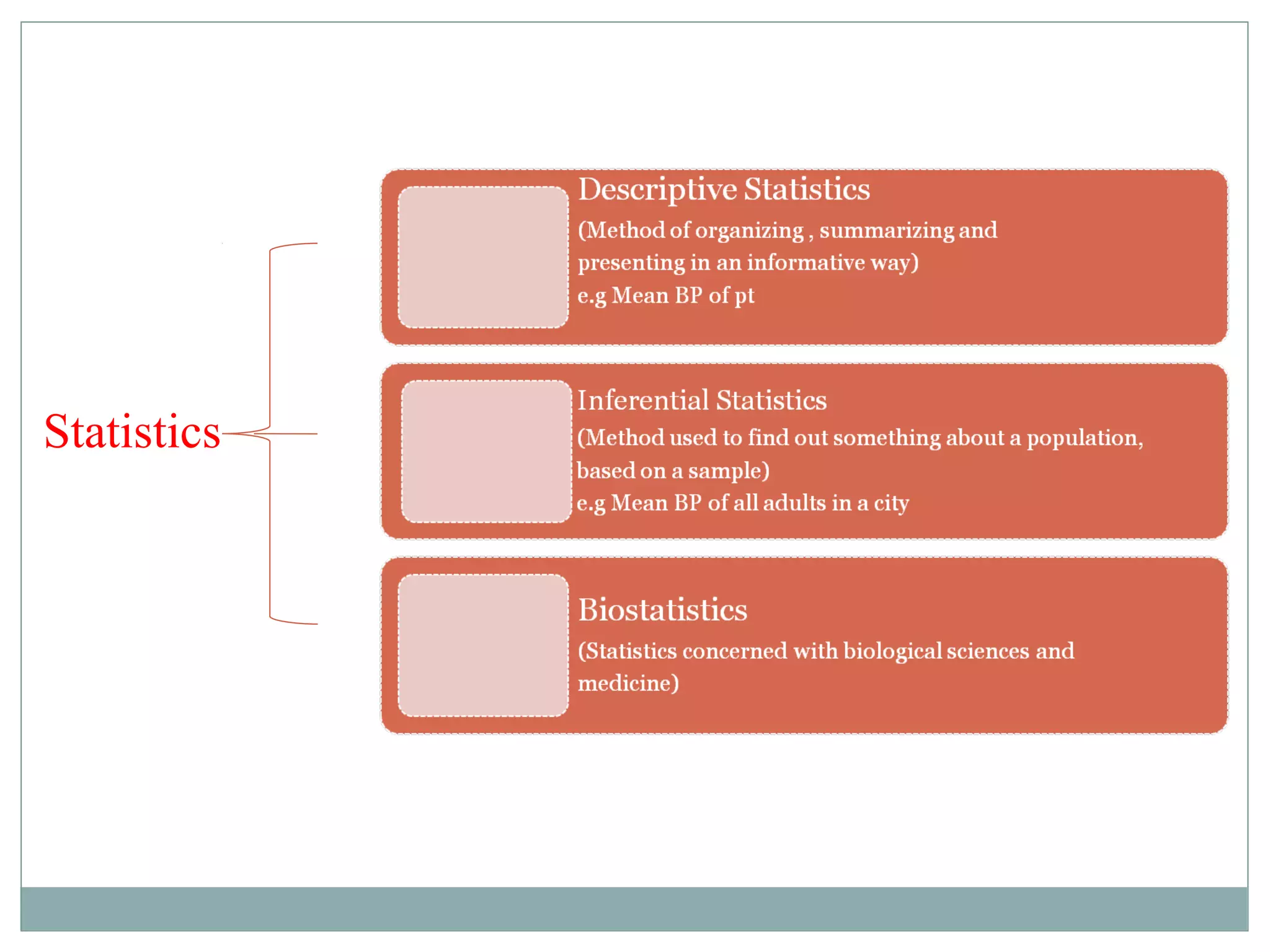
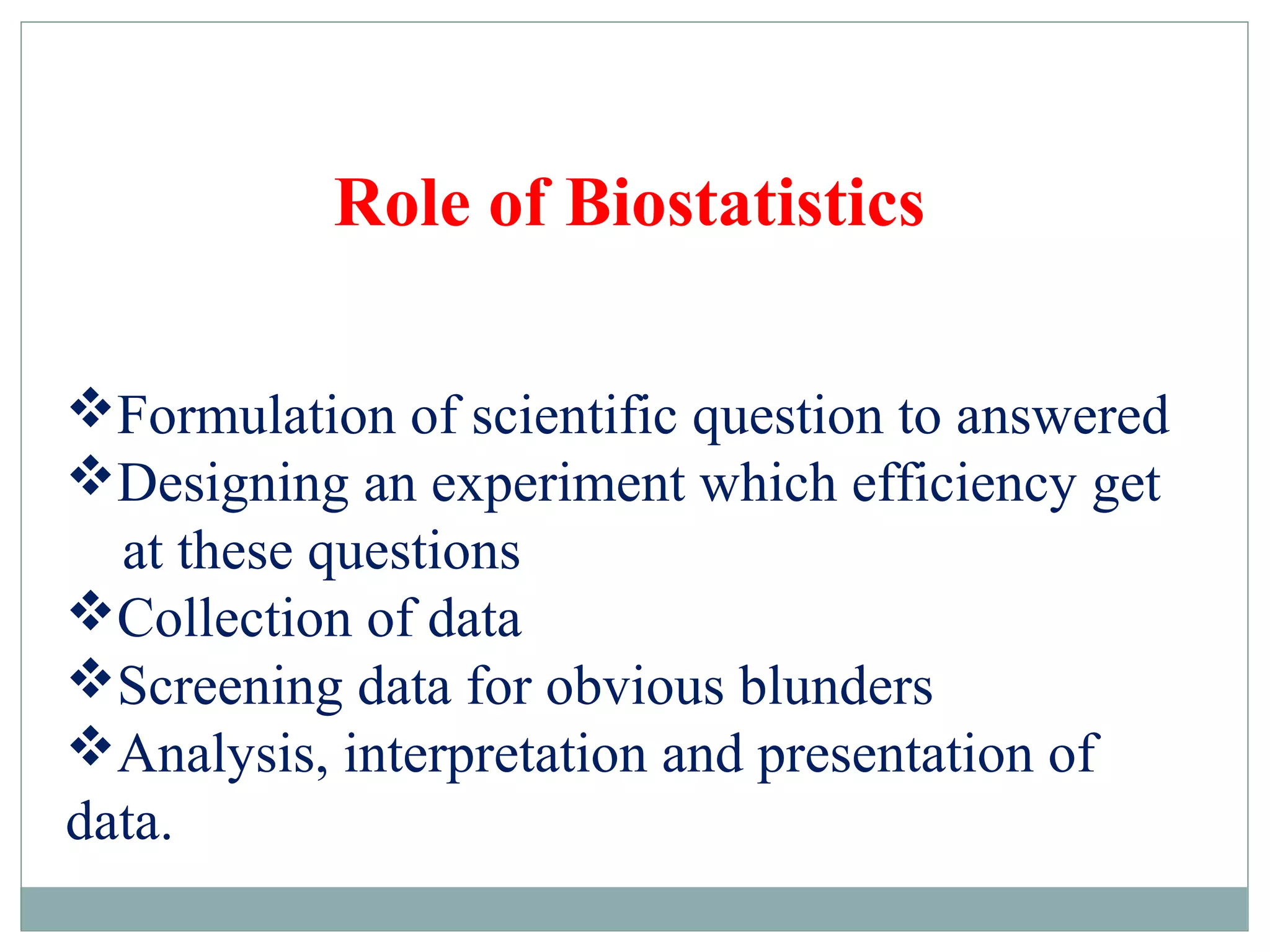
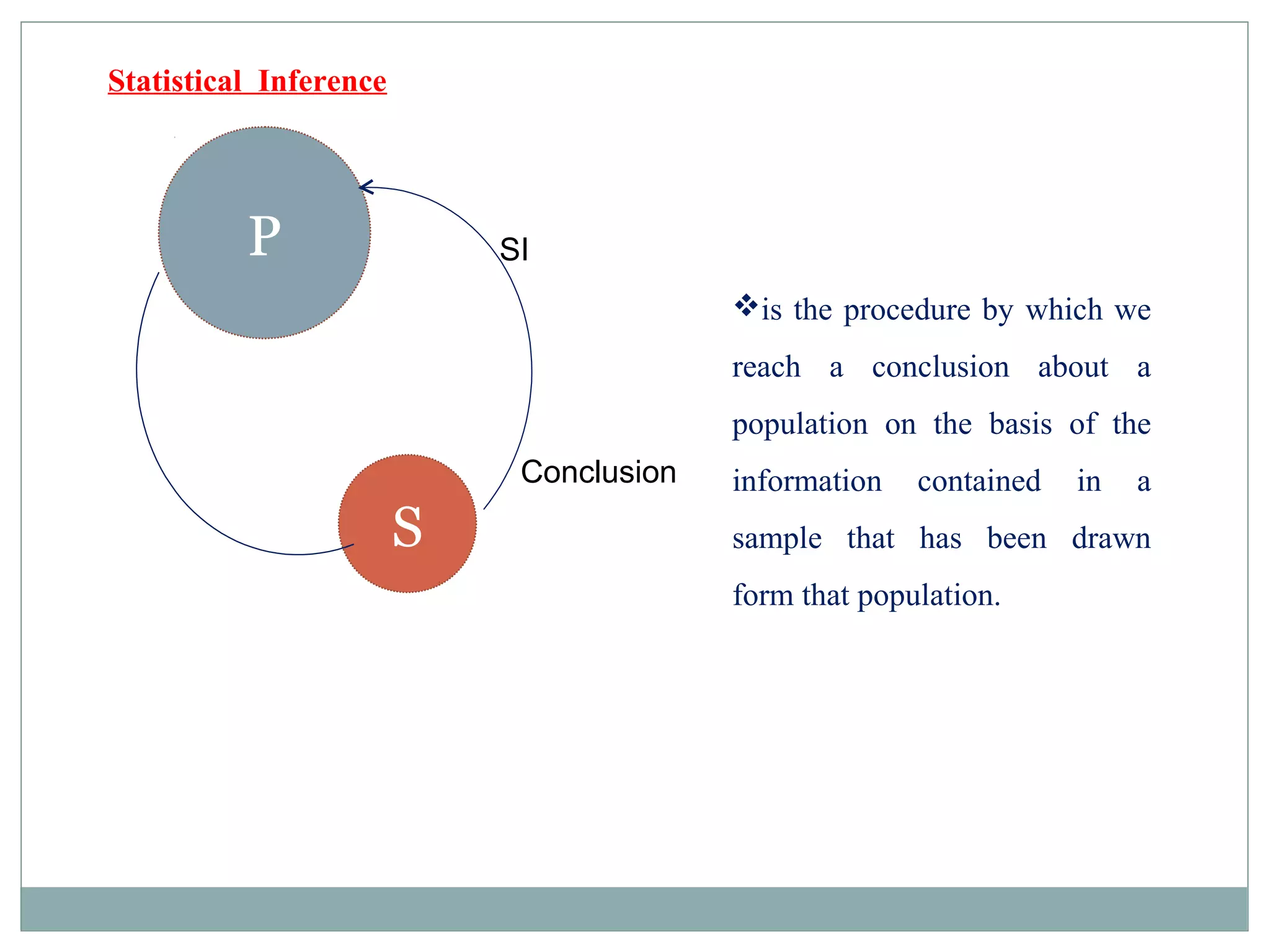
This document discusses the role of biostatistics in public health and research. It covers topics such as the definition of statistics, the collection and analysis of data, basic statistical concepts like variables and populations, different measurement scales, sampling methods, and statistical inference. Biostatistics is involved in formulating scientific questions, designing experiments, collecting and screening data, analyzing and interpreting results, and presenting findings. It also discusses the importance of probability and non-probability sampling techniques as well as using computer software programs for statistical analysis in health sciences research.