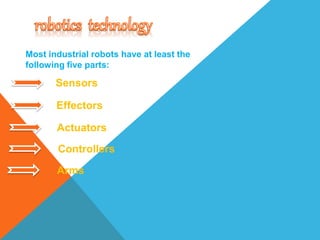
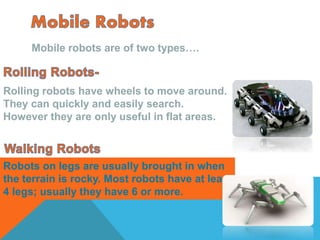
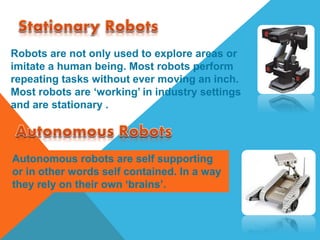
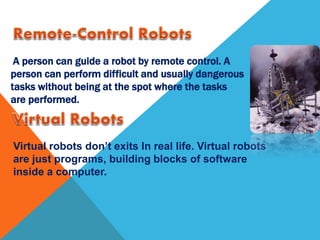
Robots are re-programmable machines that can perform tasks in place of humans in hazardous environments. They use sensors to perceive their environment, actuators for movement and manipulation, and controllers to direct their behavior. The main types of robots are mobile robots that can move via wheels or legs, stationary industrial robots used in factories, and autonomous robots that function independently using onboard systems. Robots are applied in exploration, medical, assembly, and other tasks to expand what is possible for humans.