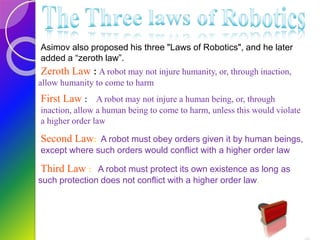
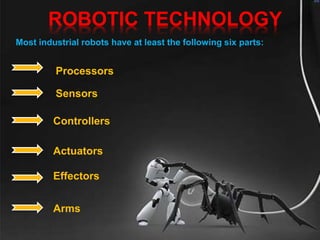
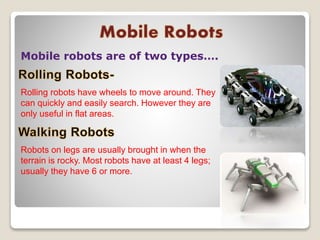
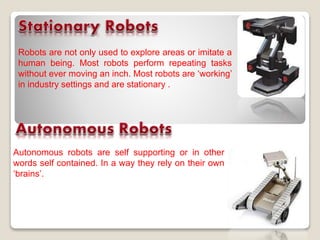
Robots are re-programmable machines that can perform hazardous tasks like removing mines or working in space. The field of robotics involves designing and building robots. The word "robot" was coined in 1920 by Karel Capek in his play R.U.R., while the term "robotics" was coined by Isaac Asimov in the 1940s. George Devol invented the first digital and programmable robot called Unimate in 1954 to lift hot metal from die casting machines. Robots typically have sensors, effectors, actuators, controllers, processors and arms. Common types of robots include mobile, stationary, autonomous, and virtual robots.