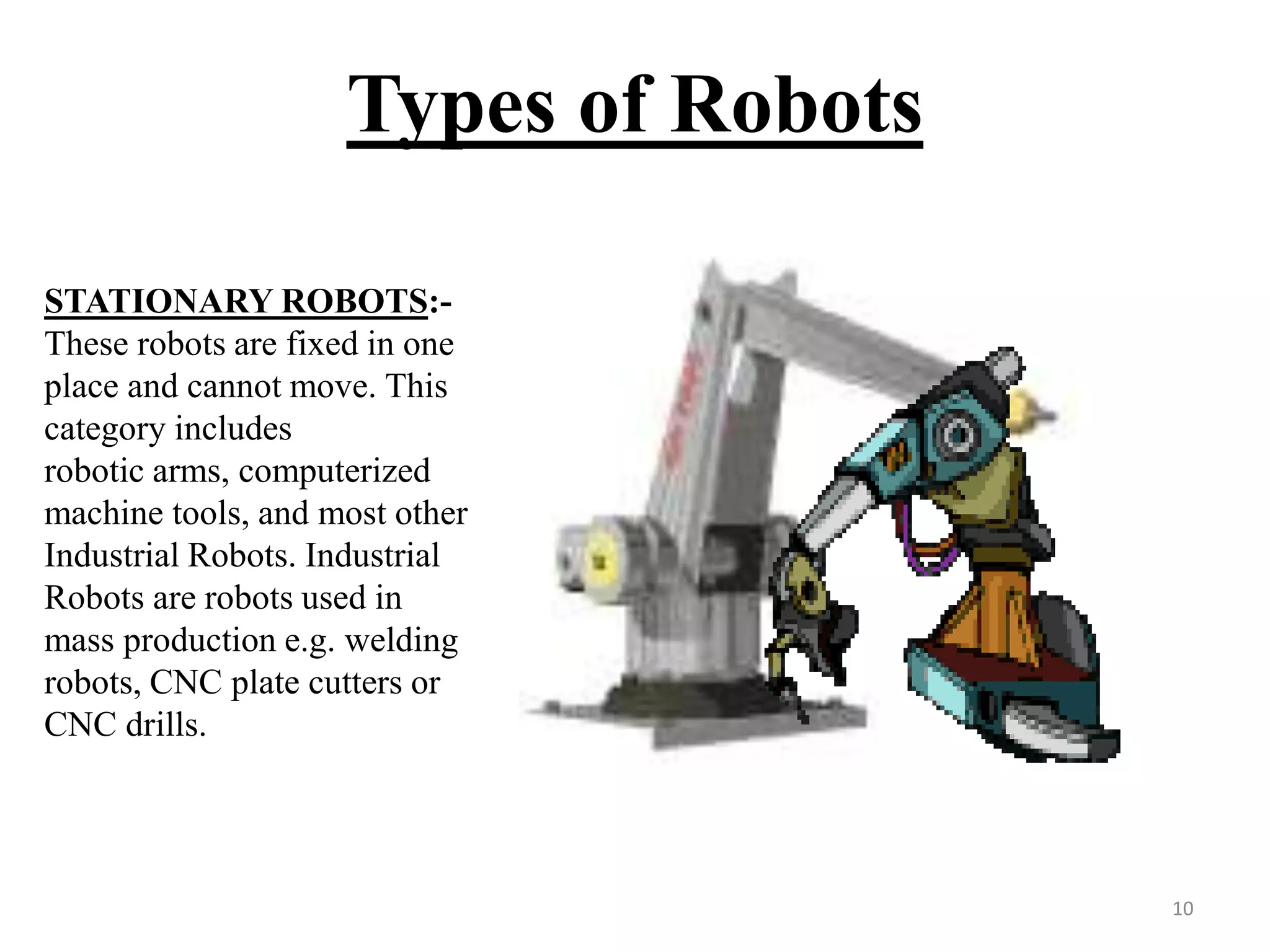
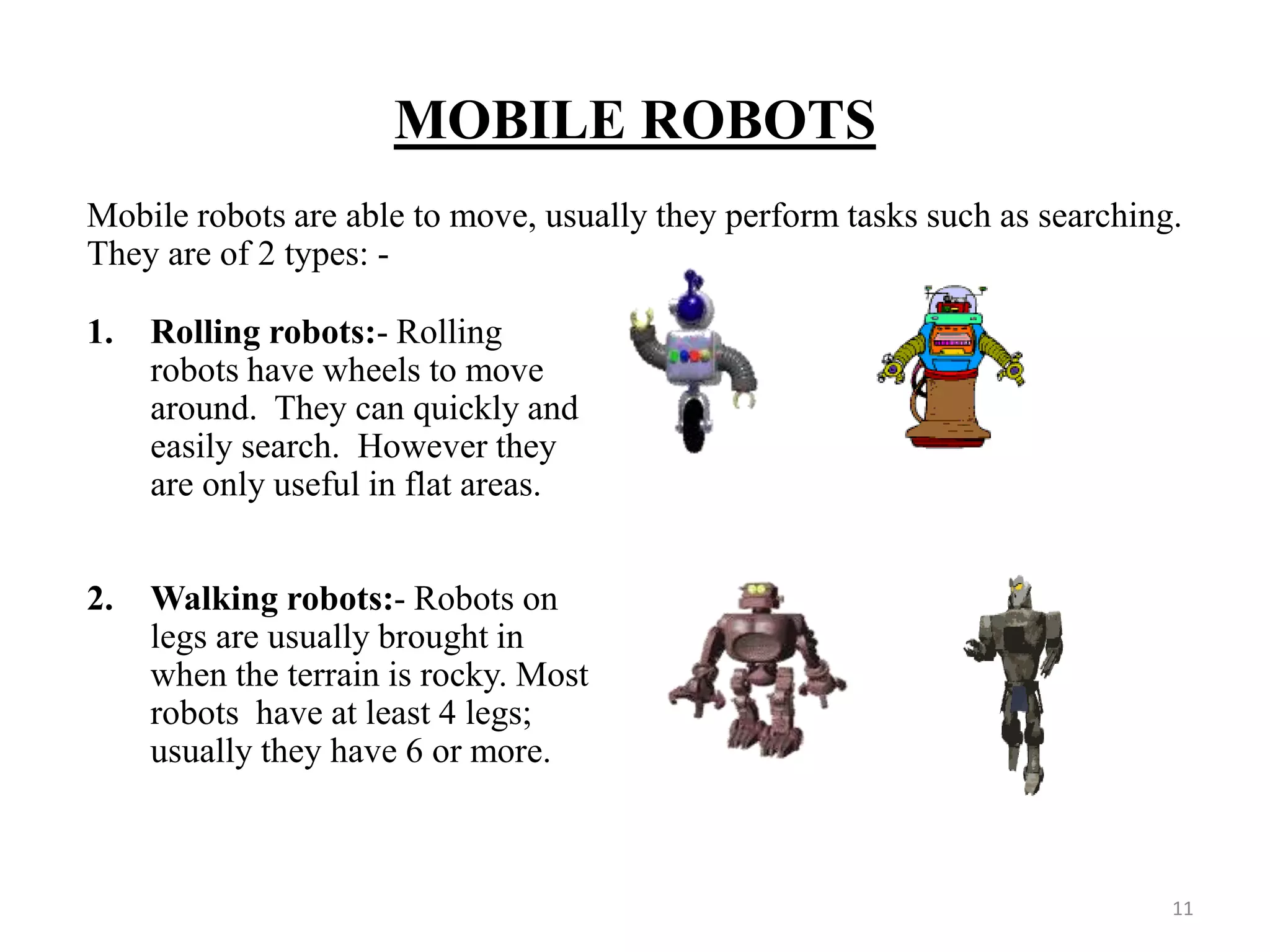
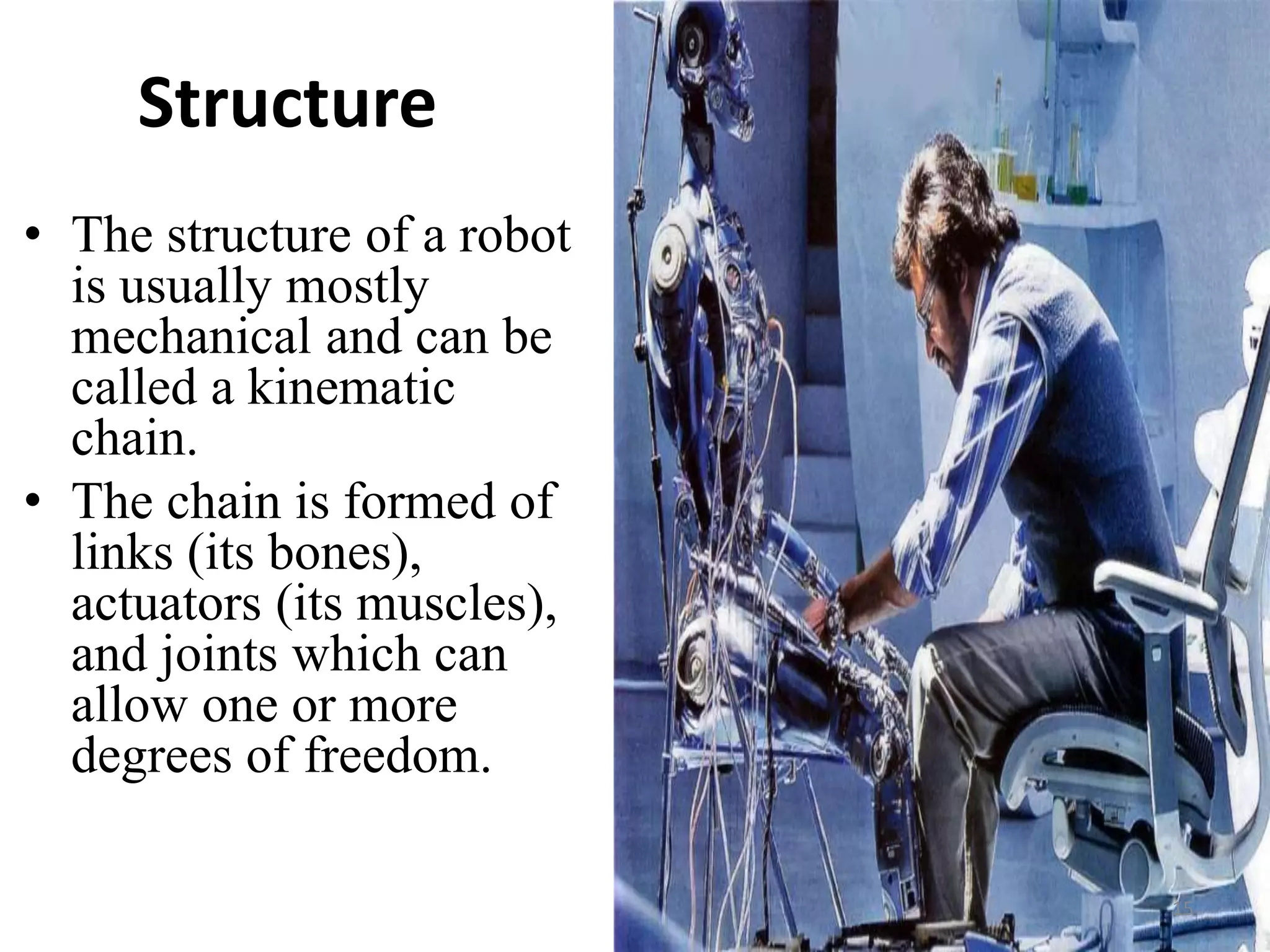
This document provides an introduction to robotics, including its history, types of robots, components, and applications. It discusses that robotics involves the design, construction, and control of robots through mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and computer science. The word "robot" was coined in 1920 and the term "robotics" was coined in the 1940s. The document outlines the Three Laws of Robotics proposed by Isaac Asimov and provides examples of early industrial robots. It describes different types of robots including stationary, mobile, autonomous, and remote-controlled robots. The key components of robots are also summarized.