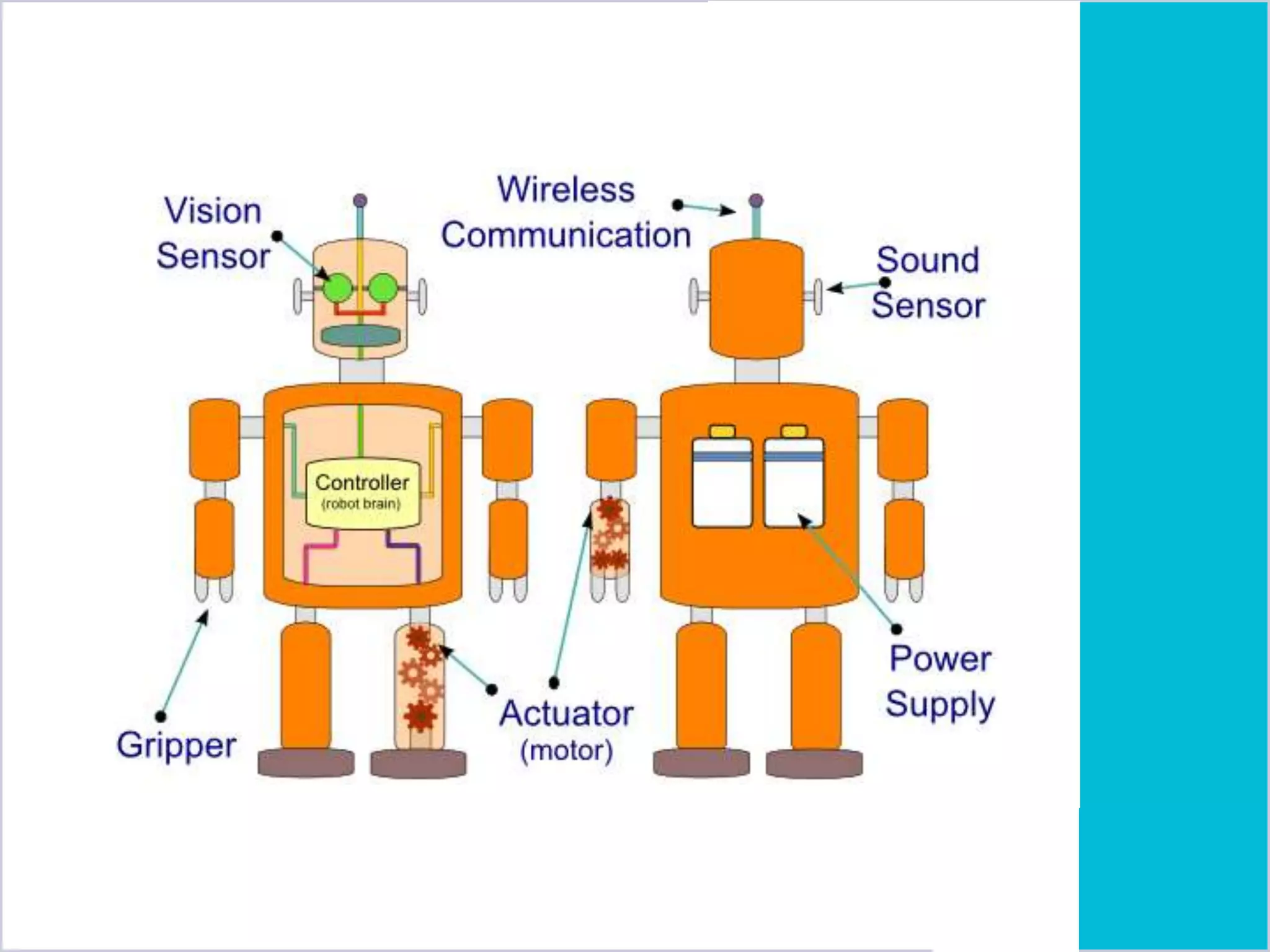
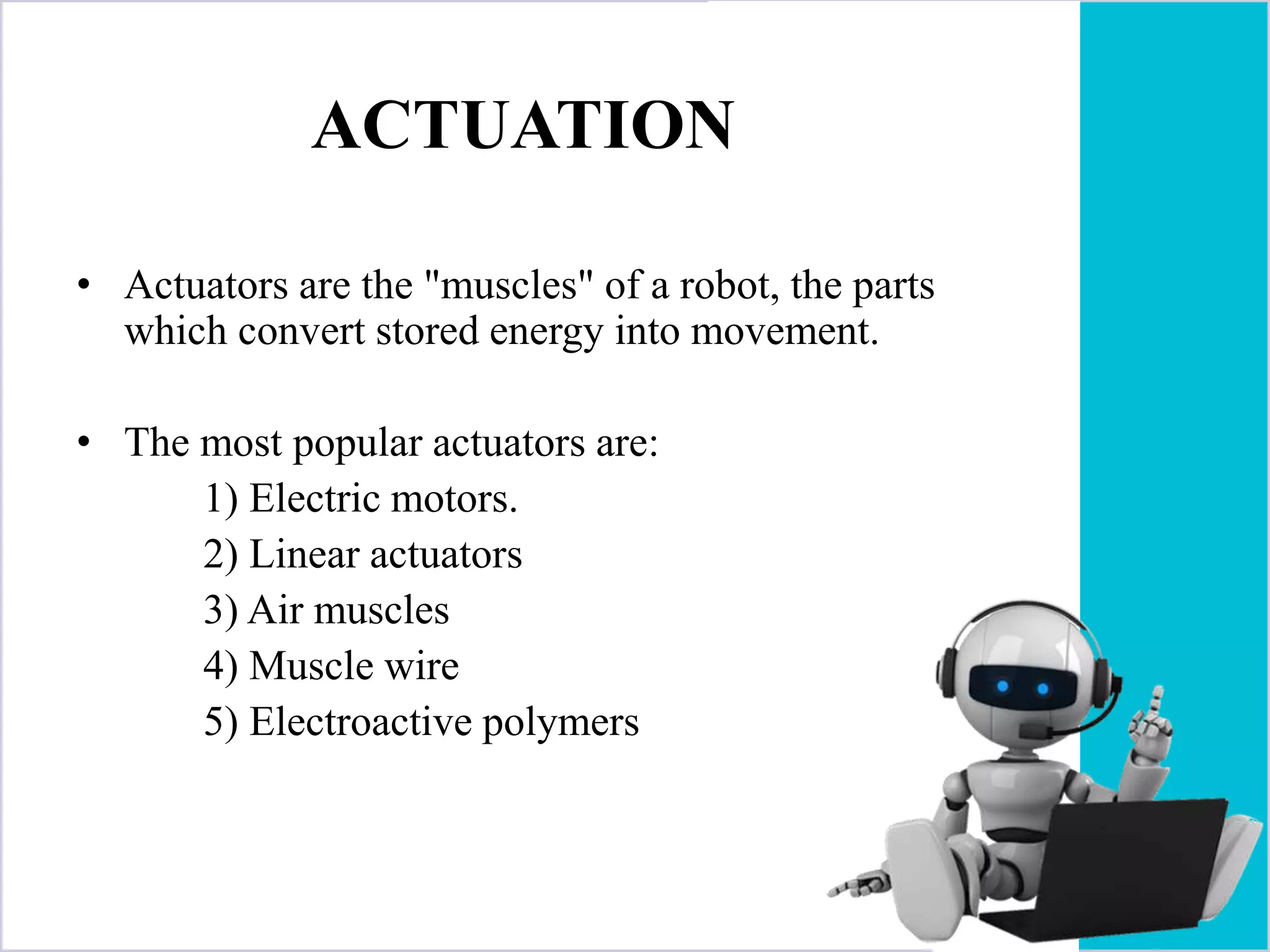
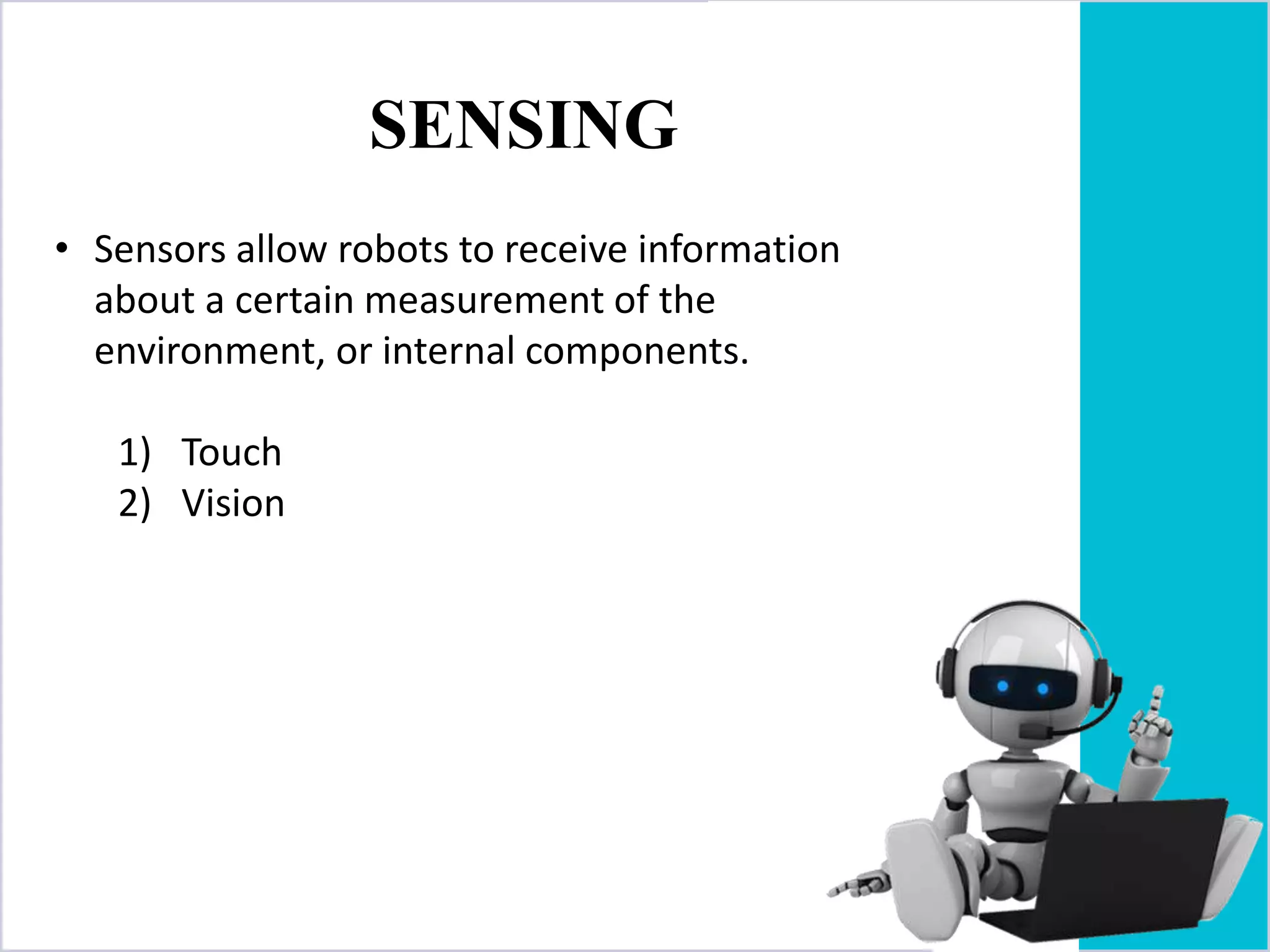
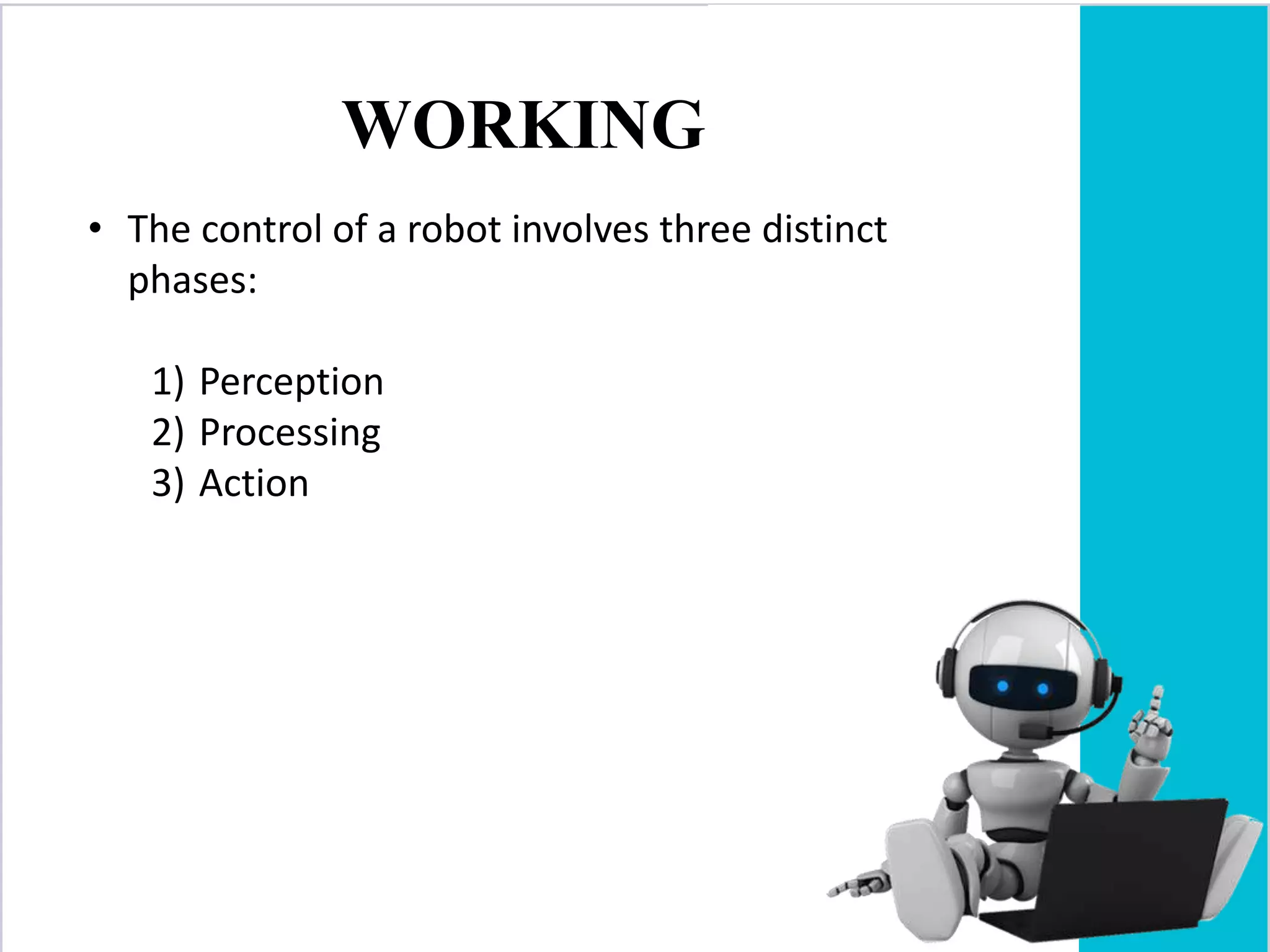
The document provides an overview of robotics, including its definition, history, types of robots, and their components. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of robots, along with various applications in different fields. Ultimately, it highlights the growing role of robots in industries and the potential for future advancements in the technology.