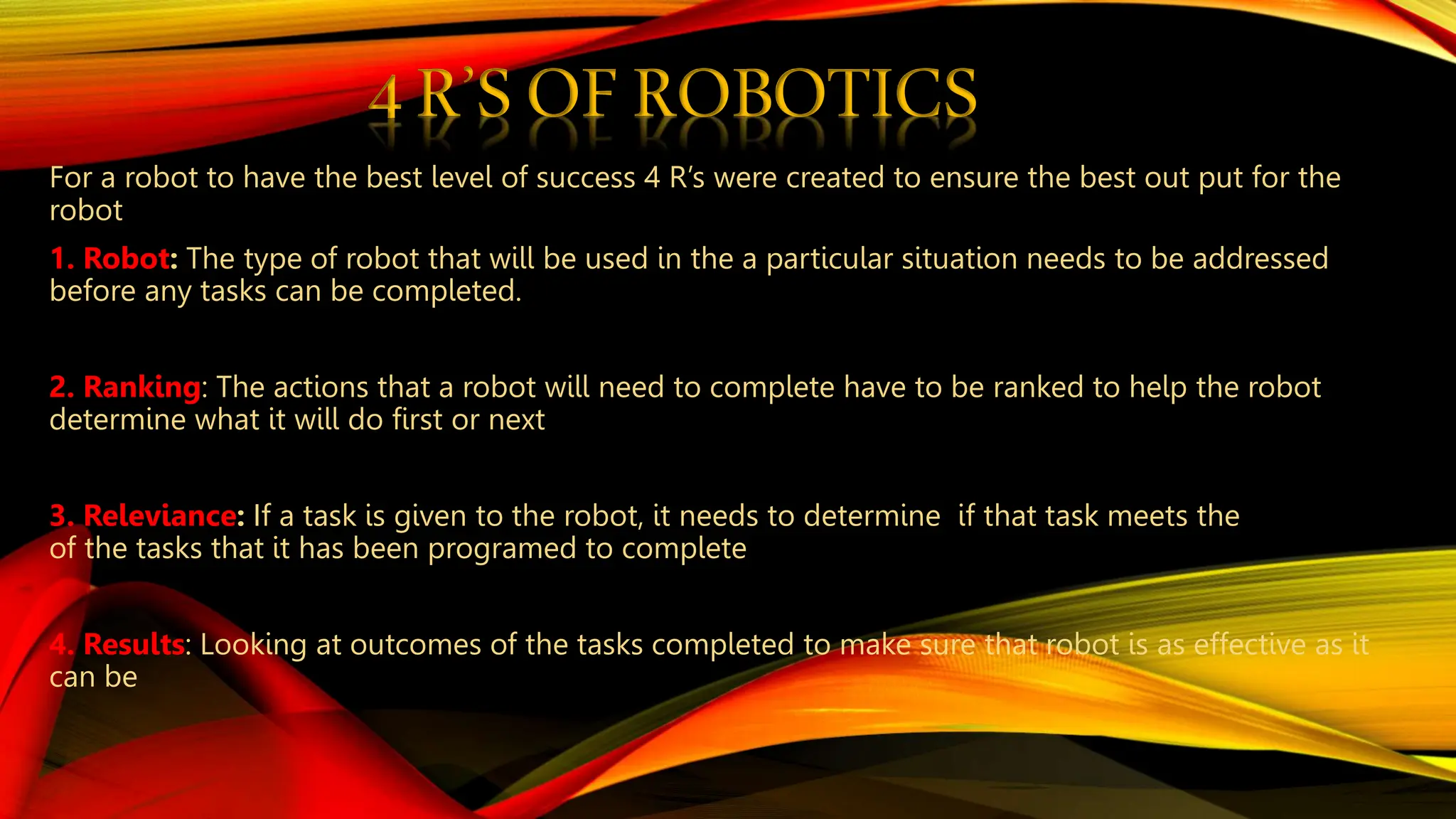
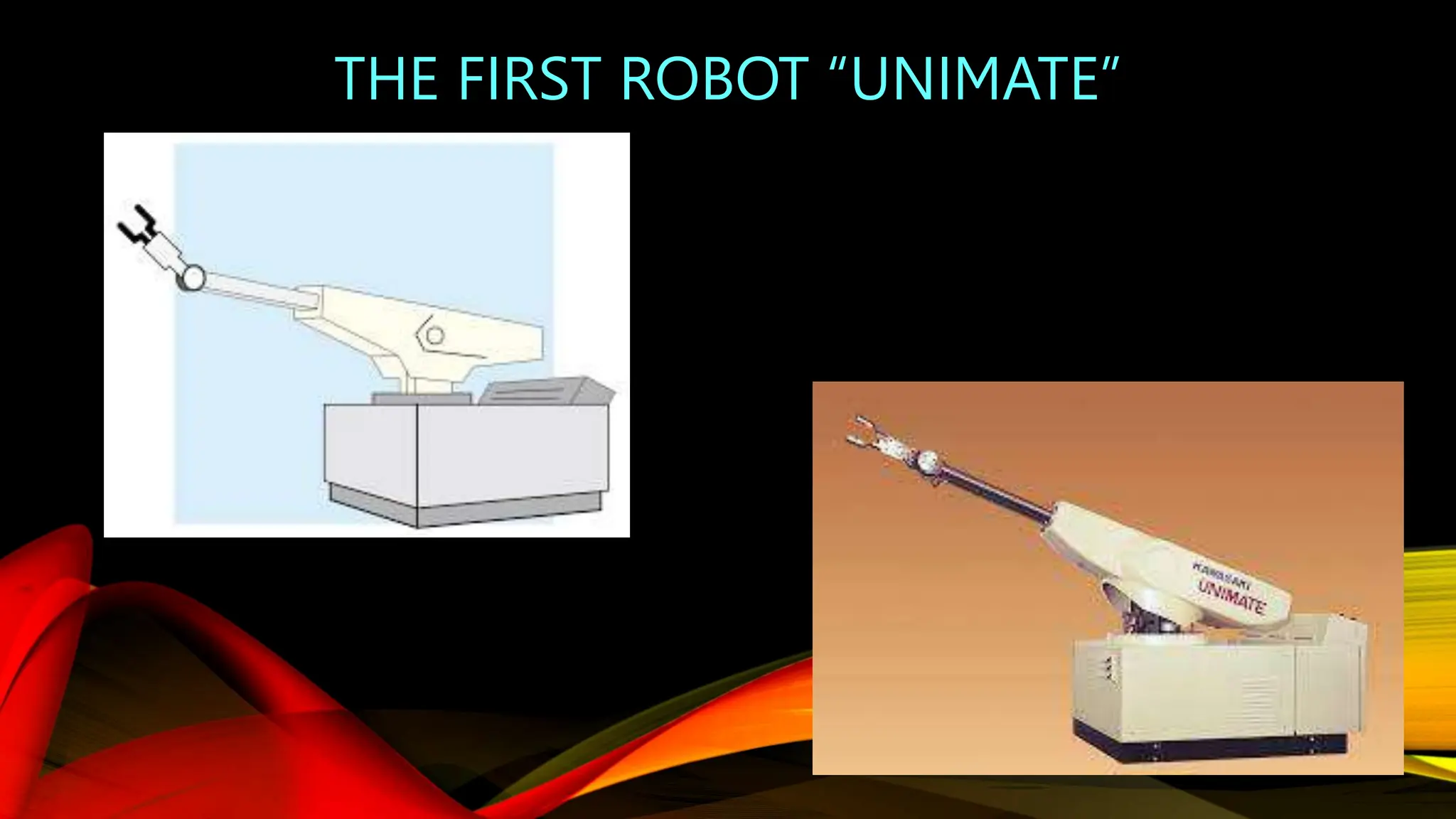
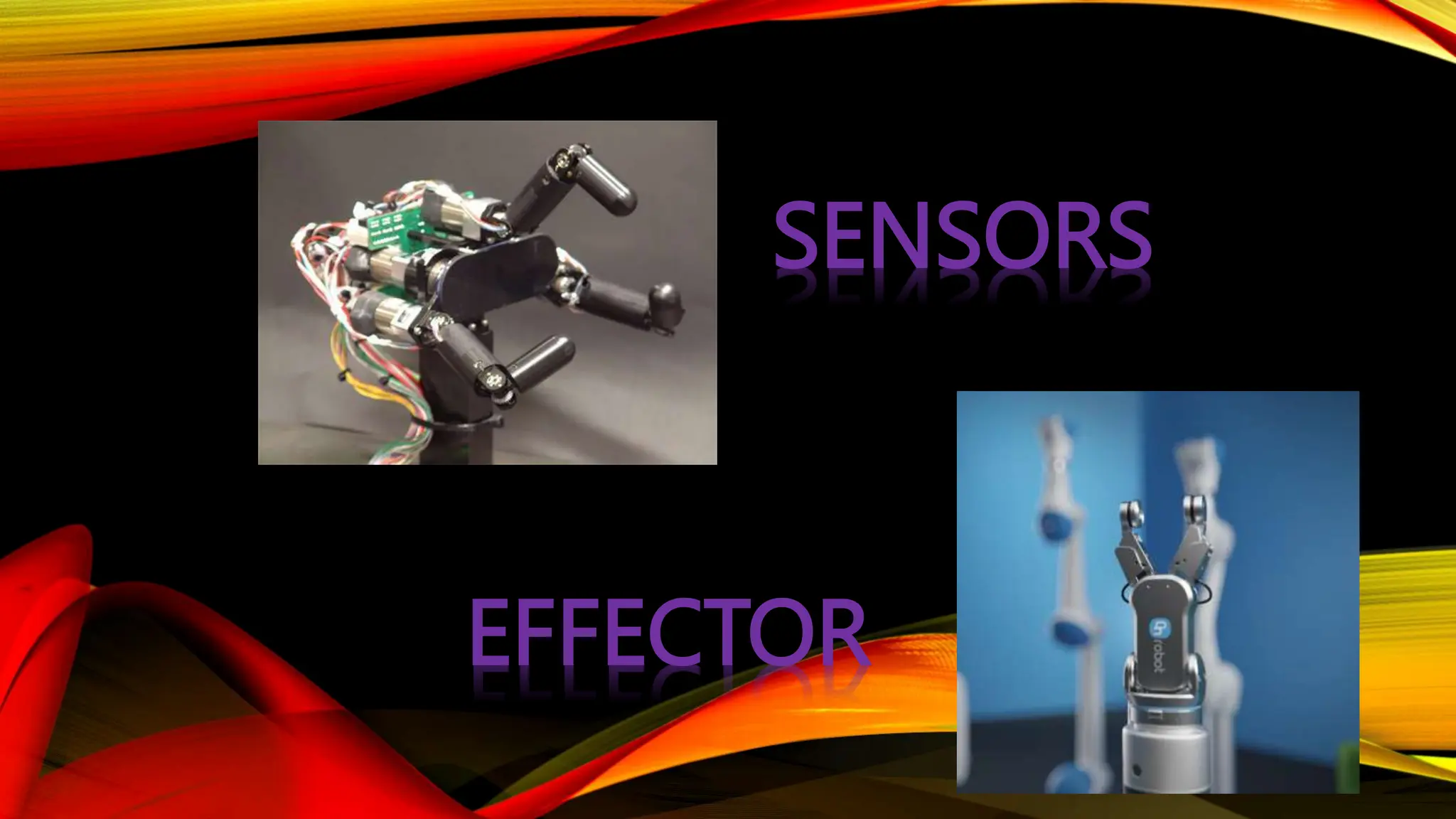
Robotic is the science of designing and building robots. A robot is a reprogrammable machine that can replace humans in hazardous work. The first use of the term "robotics" was in 1920 in a play, and the field was further developed in the 1940s. There are several types of robots including mobile, stationary, autonomous, and remote-controlled robots. Robots have advantages like working in dangerous environments and performing repetitive tasks quickly and accurately, but also have disadvantages like potential job losses and maintenance costs.