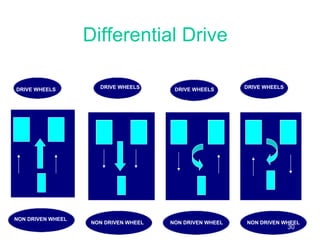
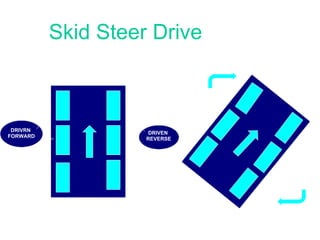
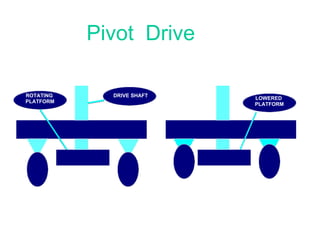
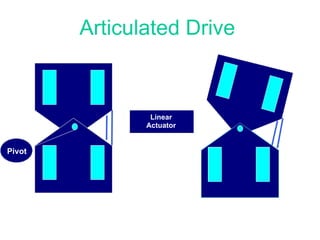
This document provides an overview of robotics, including definitions of robotics, the different types of robots, laws of robotics, why robotics is needed, components of robots, industries using robots, advantages of robots, and future prospects of robotics. It discusses topics such as Isaac Asimov's Three Laws of Robotics, the structure, power sources, actuation, sensing, manipulation, and locomotion of robots.