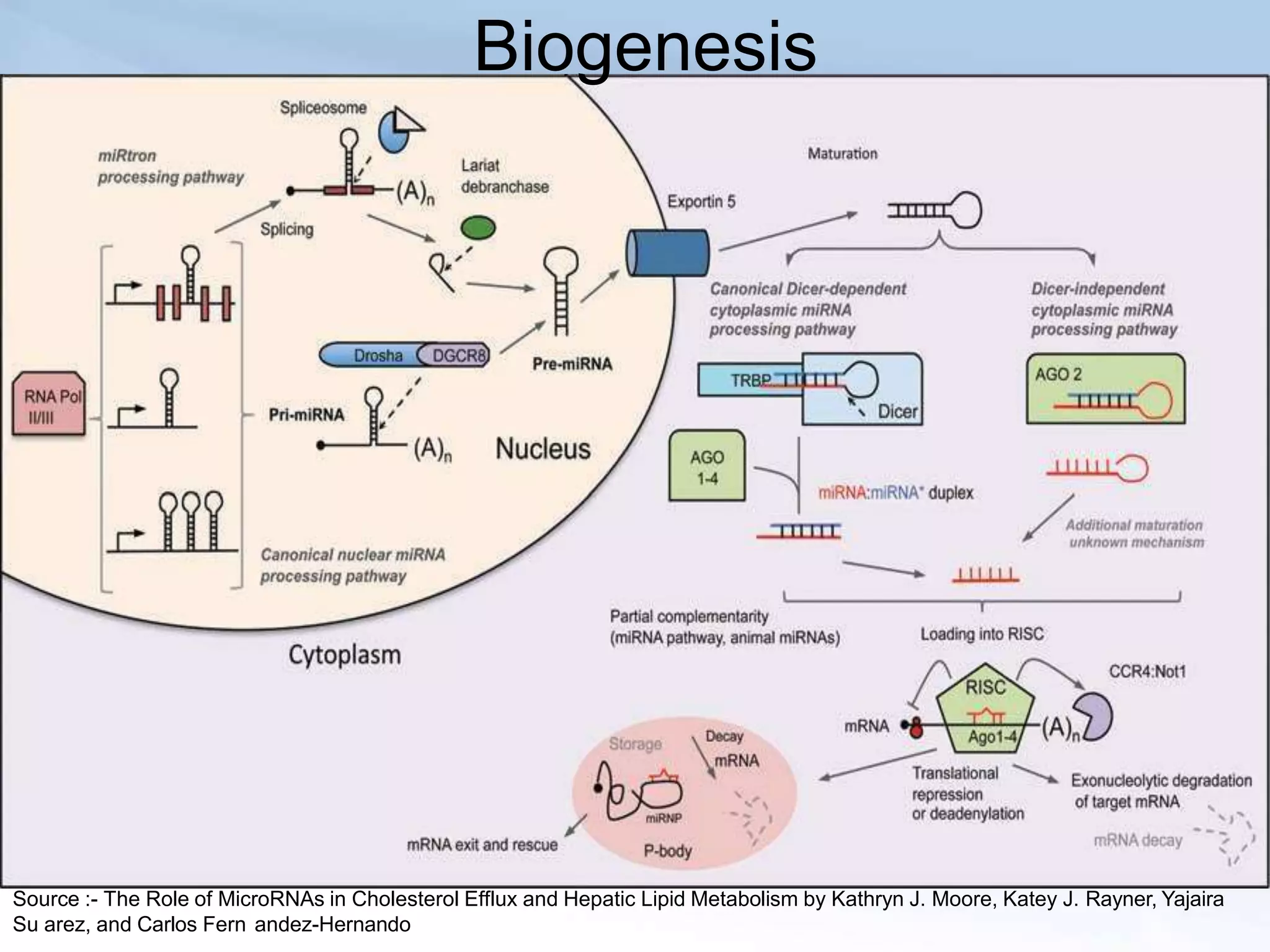
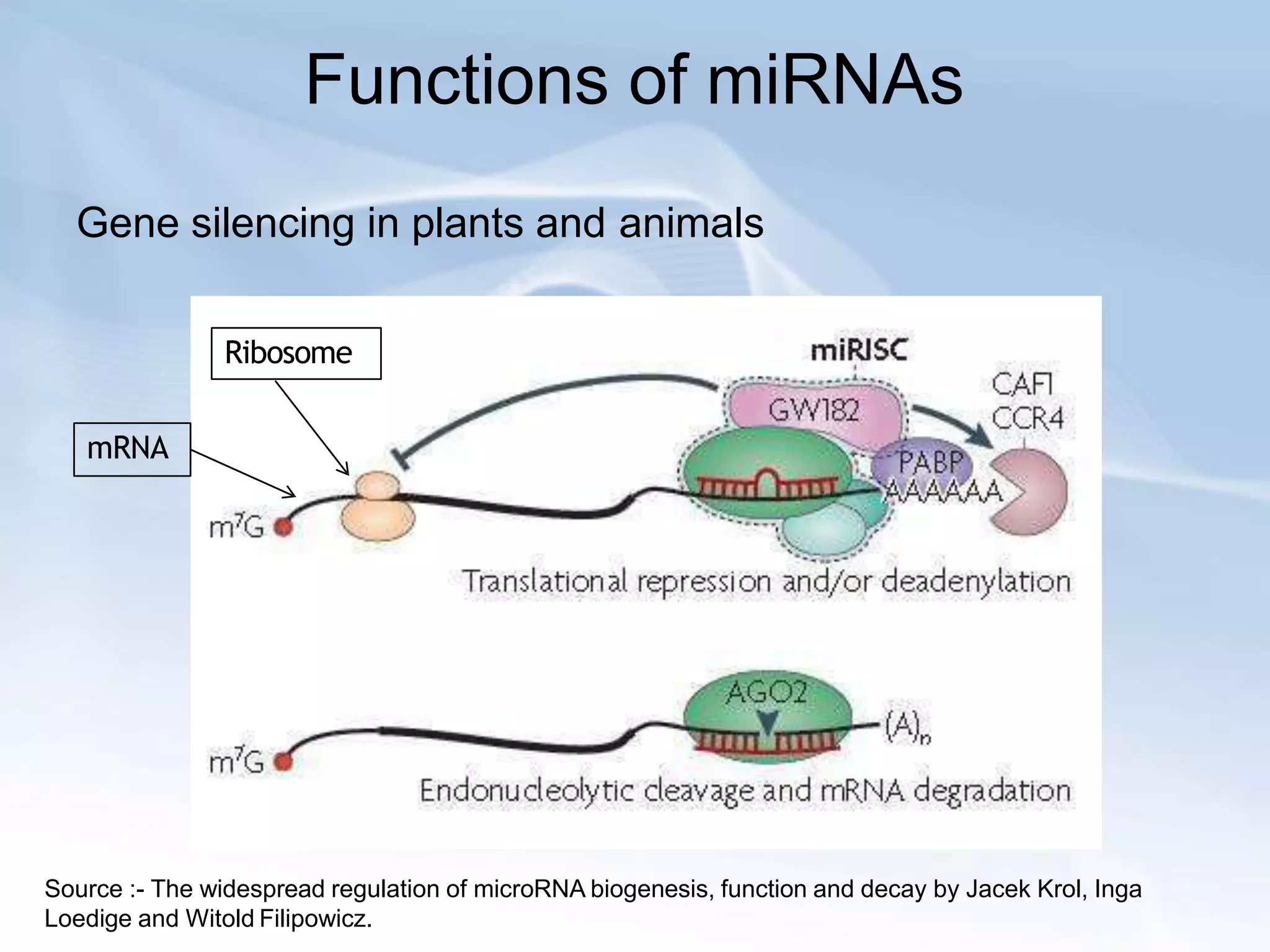
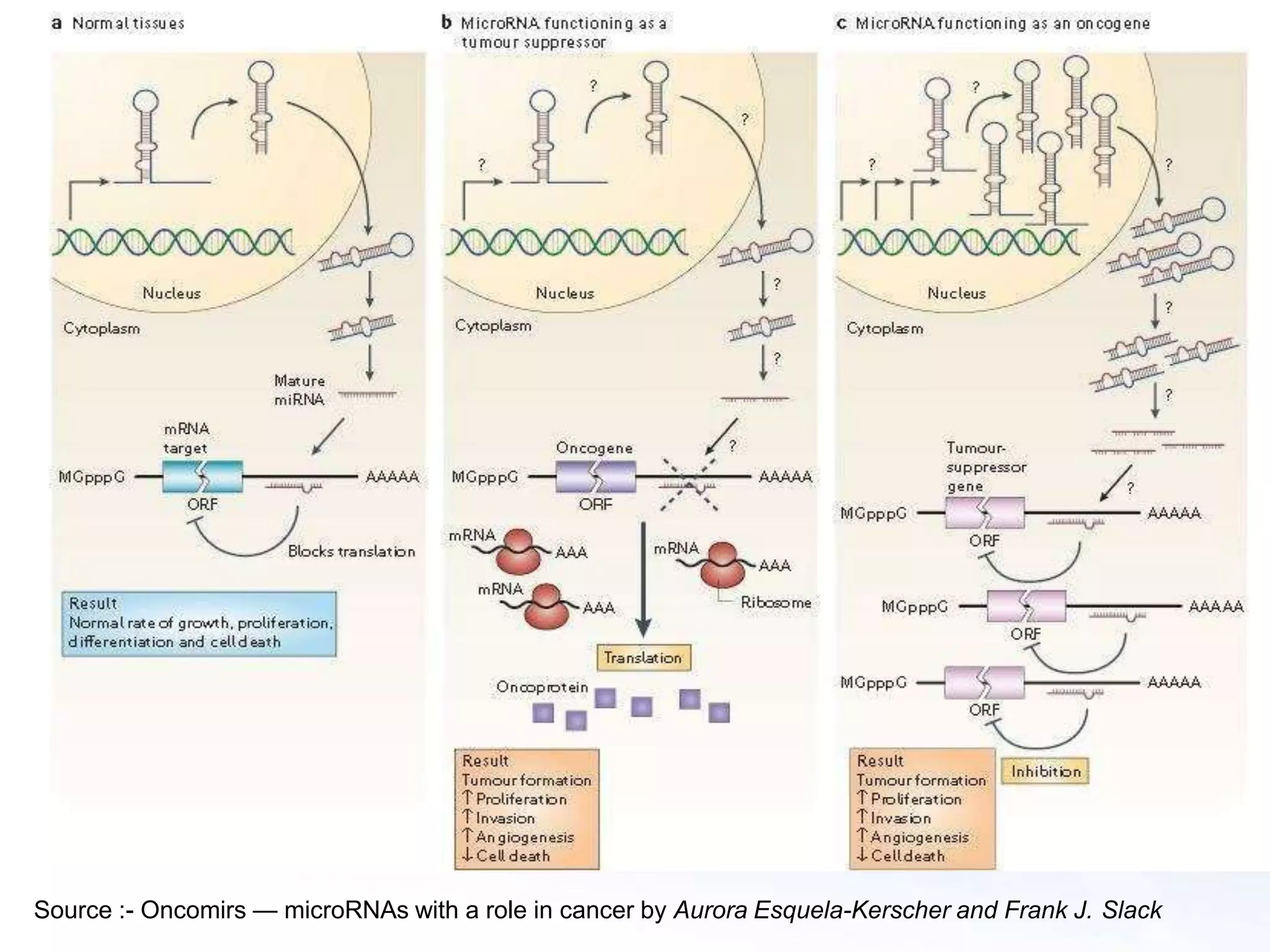
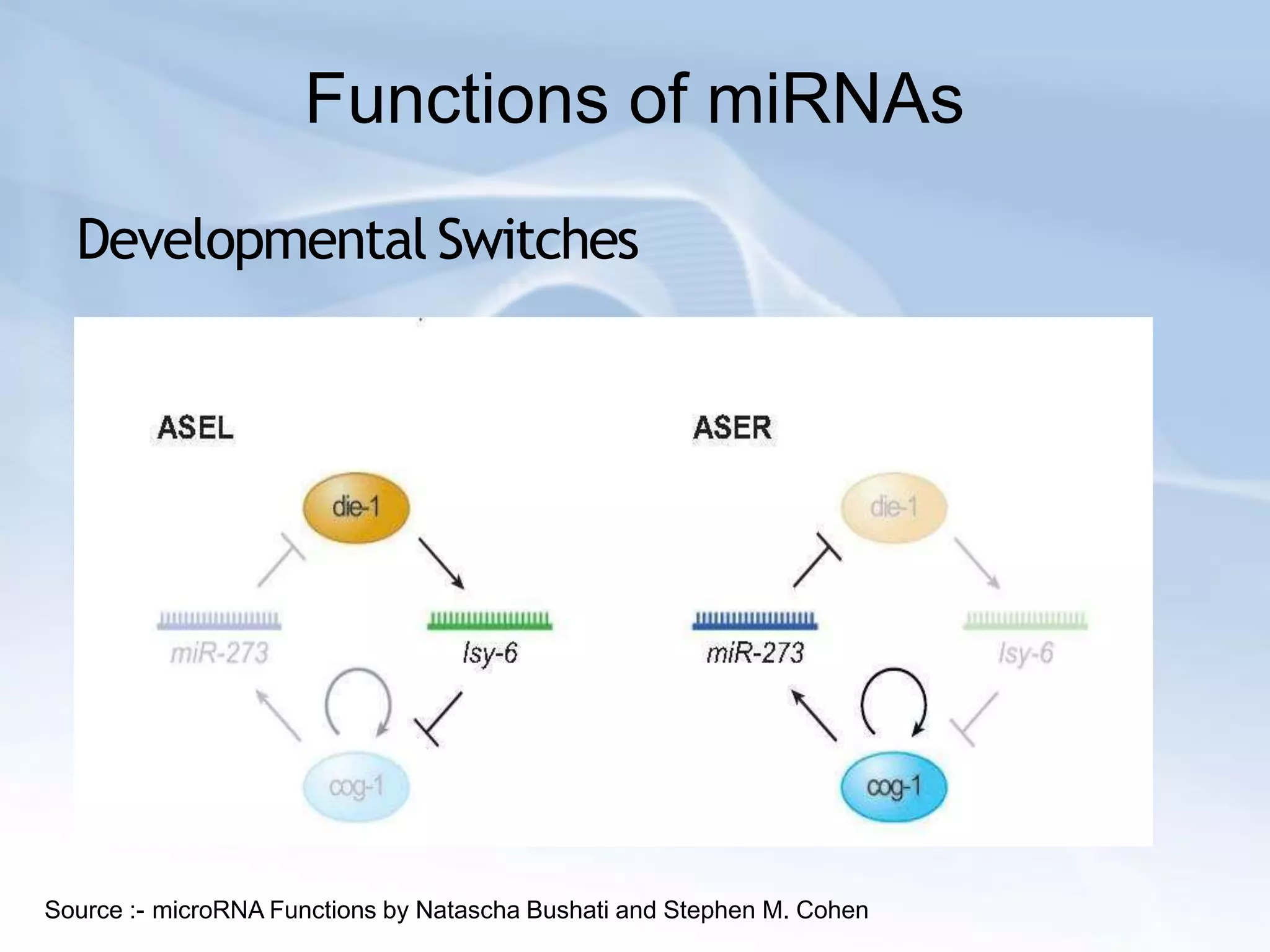
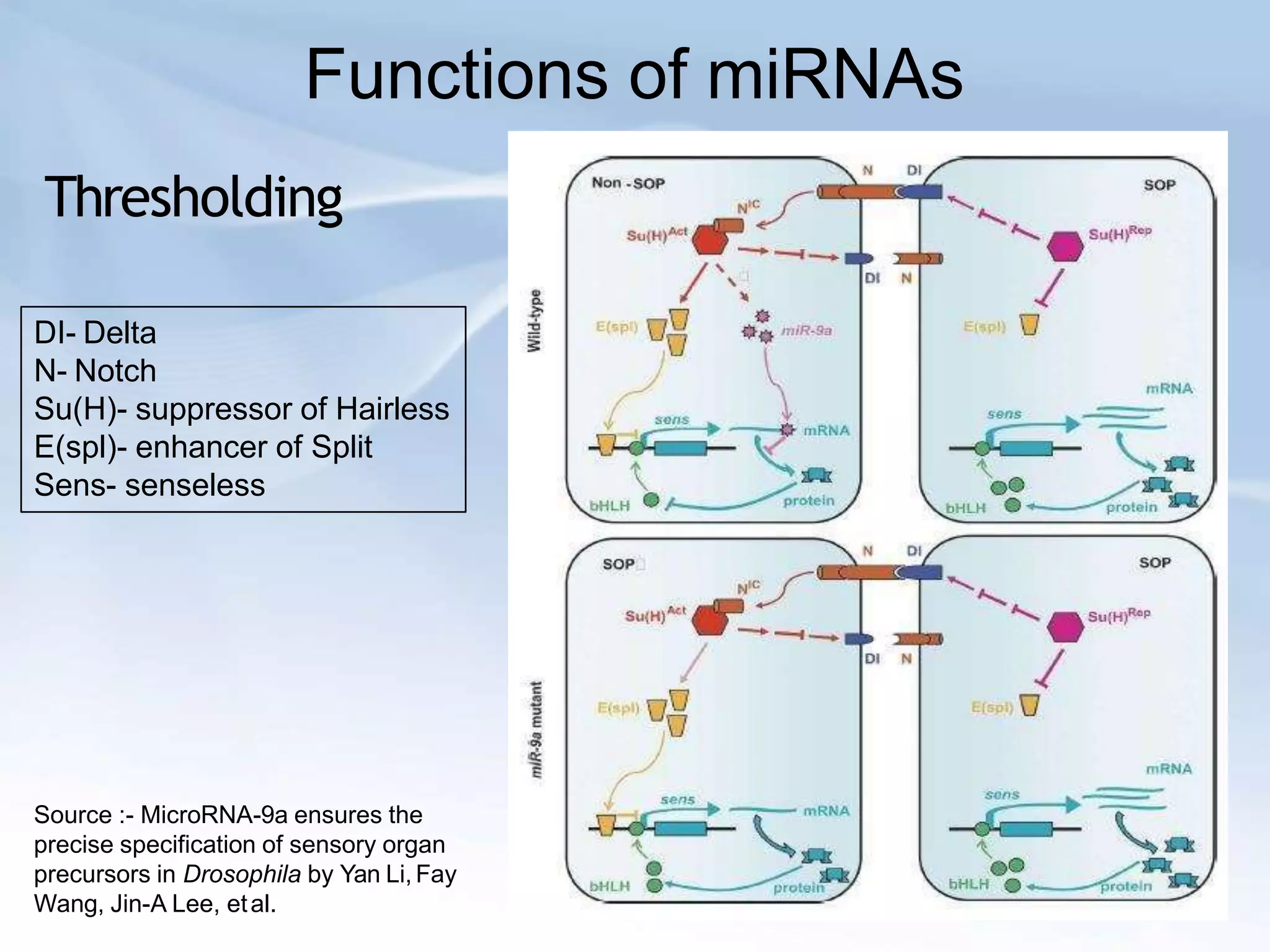
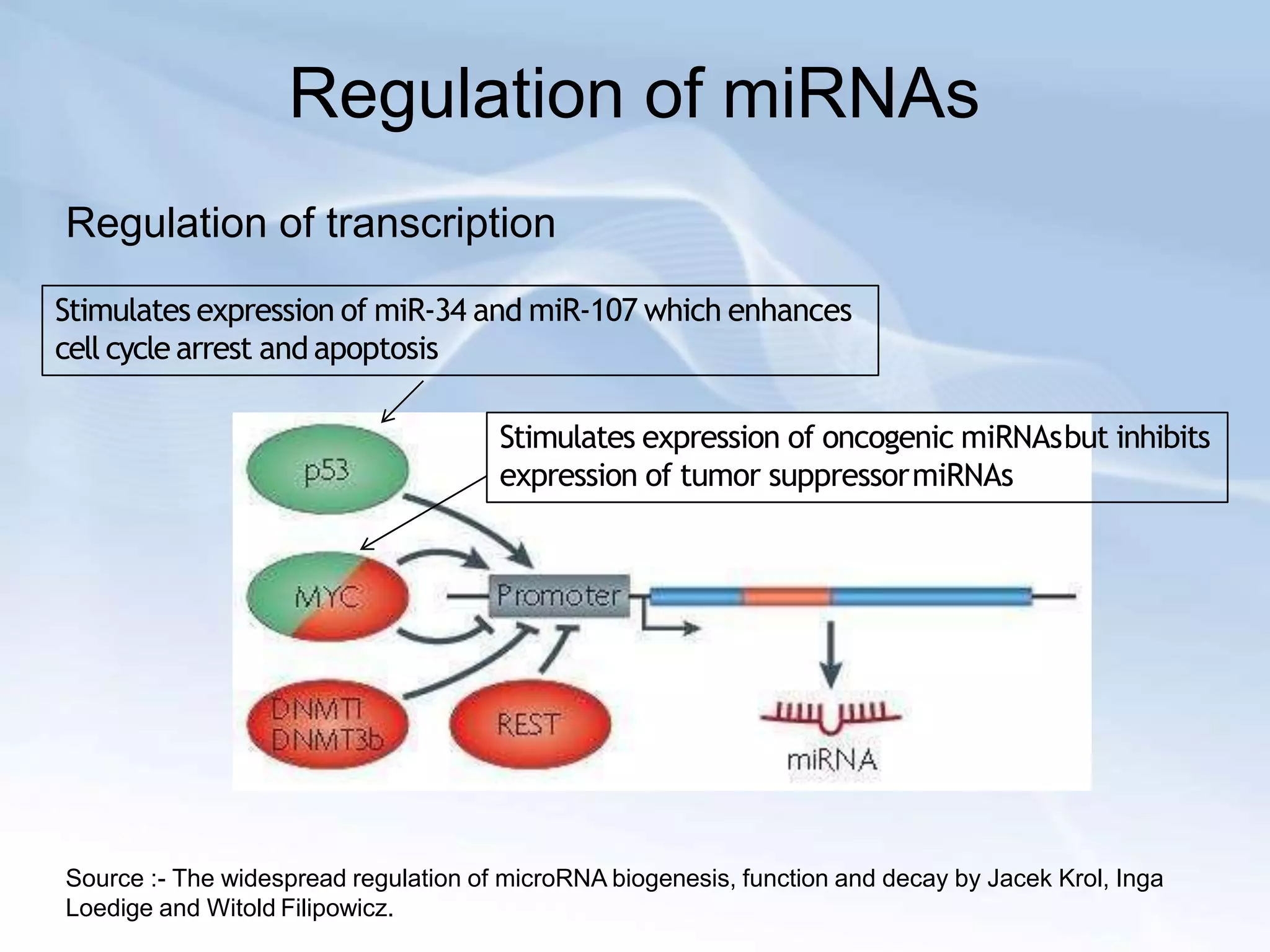
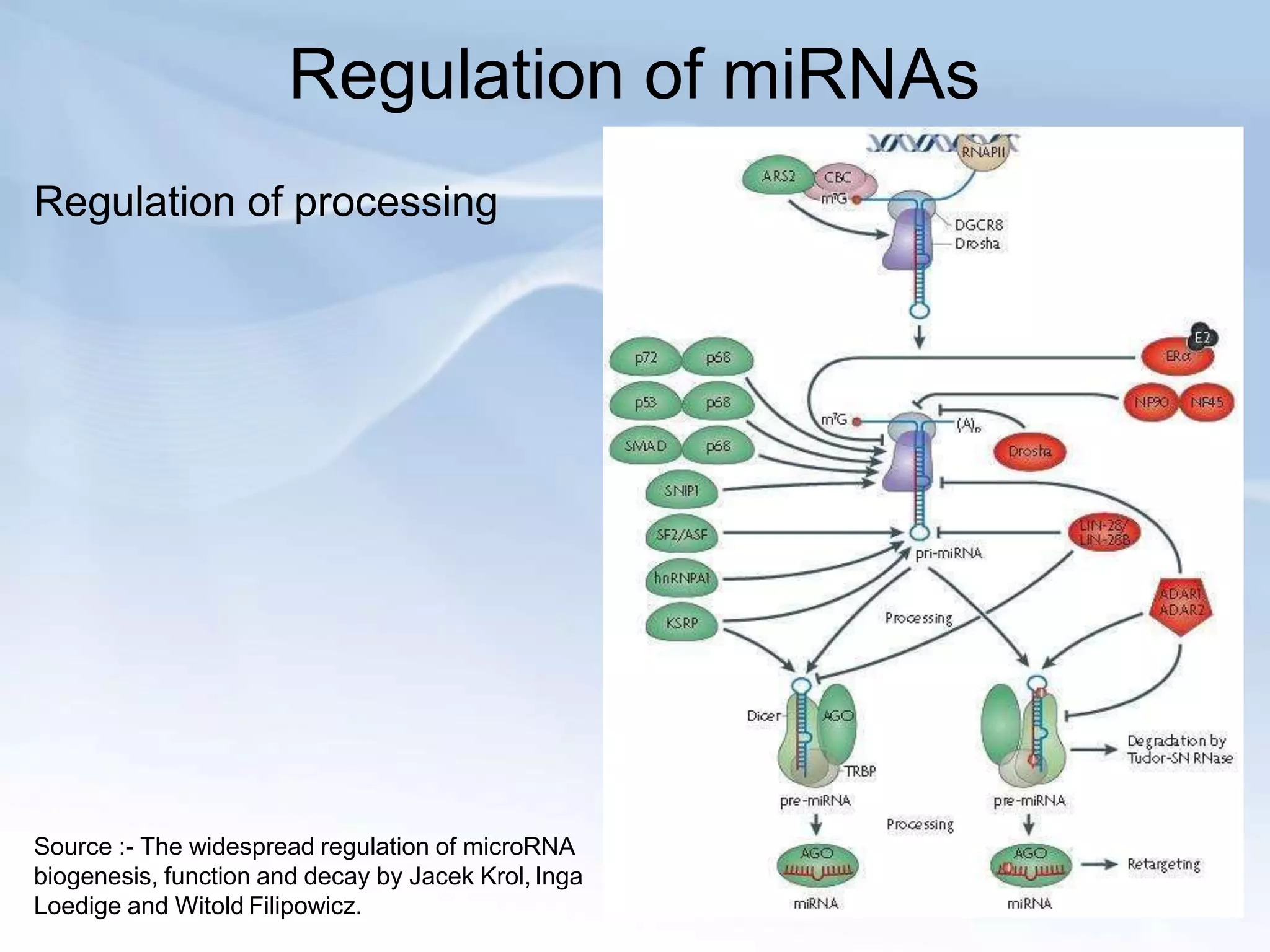
MicroRNAs are small non-coding RNAs that play important gene regulatory roles in eukaryotic cells. They are transcribed from independent genes or introns and are around 22 nucleotides long. MicroRNAs undergo a biogenesis process to silence gene expression in plants and animals by inhibiting translation or cleaving mRNA. They function as tumor suppressors or oncogenes and in developmental switches. The expression and activity of microRNAs is tightly regulated at the transcriptional and processing levels to control protein expression. While progress has been made in understanding microRNA biogenesis and function, further research is needed to elucidate their regulatory networks and roles in development, differentiation, and disease.