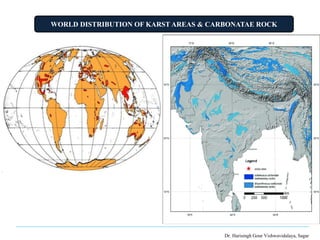
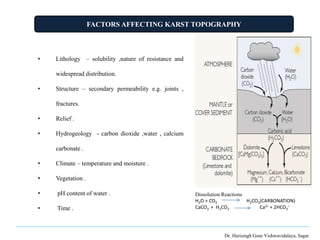
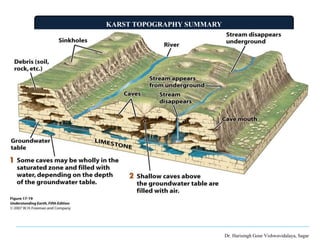
The document presents a presentation on karst topography given by Ahmad Raza. It defines karst topography as areas with limestone or dolomite bedrock that have distinctive landforms formed by the dissolution of bedrock by water. It discusses the worldwide distribution of karst areas and the conditions required for karst formation. Key erosional landforms of karst include sinkholes, dolines, swallow holes, and caves. Depositional landforms include stalactites, stalagmites, and columns. Karst landscapes progress through youth, mature, and old stages as surface streams disappear underground over time. Karst is important for engineering projects, water resource studies, and paleoclimate research.