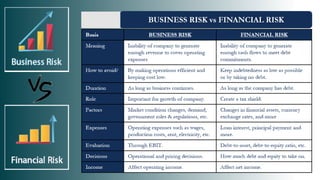
The document discusses different types of business risks and financial risks. It defines business risk as threats that could prevent a company from achieving its financial goals. The main types of business risks are strategic risk, operational risk, legal risk, reputational risk, compliance risk. Financial risk is the possibility of losing money on investments. The primary types of financial risks are credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, valuation risk. Credit risk is the risk of defaulting on loans. Market risk relates to volatility in markets. Liquidity risk impacts the ability to meet short-term financial obligations. Valuation risk is the loss from a difference between accounting and market values.