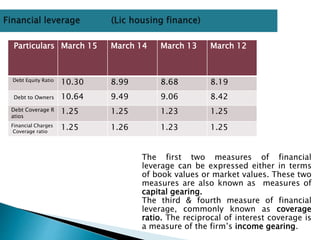
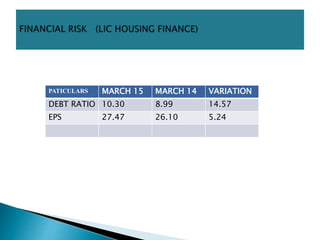
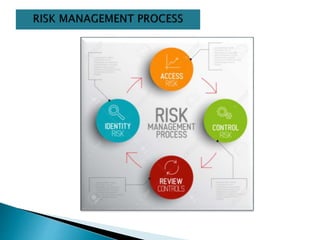
This document discusses various types of risk including business risk, financial risk, credit risk, market risk, operational risk, legal risk, political risk, and liquidity risk. It provides definitions and examples for each type of risk. Business risk depends on factors like competitive environment, consumer preferences, and government policies. Financial risk depends on a company's debt-to-equity ratio and coverage ratios. Credit risk is the risk of default on debt obligations. Market risk includes risks from changes in currency exchange rates, interest rates, equity prices, and commodity prices.






![ Compliance Risk(Legal Risk): These are risks
associated with the need to comply with the rules
and regulations of the government.
1) socio and regulatory factors
2) Political Risk
3) Business cycle
Other risks: There would be different risks like
natural disaster(floods) and others depend upon
the nature and scale of the industry.[8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amanppta-150831013420-lva1-app6891/85/Aman-FMS-BHU-7-320.jpg)


![ In the United States, a section on market risk is mandated by the SEC.2] in
all annual reports submitted on Form 10-K. The company must detail how
its own results may depend directly on financial markets.
Significant resources and sophisticated programs are used to analyze and
manage risk. Some companies run a credit risk department whose job is to
assess the financial health of their customers, and extend credit (or not)
accordingly.
They may use in house programs to advise on avoiding, reducing and
transferring risk. They also use third party provided intelligence.
Companies like Standard & Poor's, Moody's, Fitch Ratings, DBRS, Dun
and Bradstreet, Bureau van Dijk and Rapid Ratings International provide
such information for a fee.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amanppta-150831013420-lva1-app6891/85/Aman-FMS-BHU-10-320.jpg)