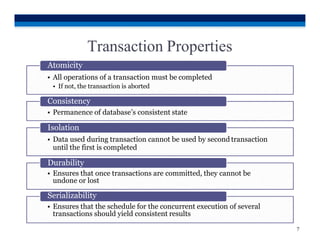
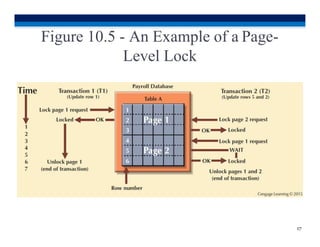
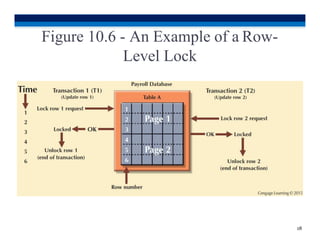
This document discusses transaction processing and concurrency control in database systems. It covers topics such as transactions and their properties including atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability. It also discusses concurrency control and how locking methods work to ensure serializability by coordinating concurrent transactions through the use of locks at different levels of granularity like the database, table, page, and row levels. The scheduler establishes the execution order of operations for concurrent transactions.