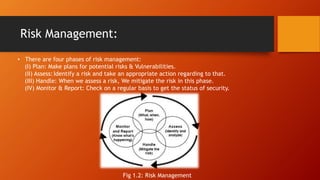
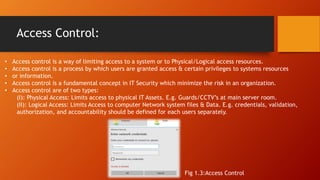
The document outlines fundamental concepts of IT security, focusing on confidentiality, integrity, and availability, collectively known as the CIA triad. It discusses risk management, risk assessment, and various controls to mitigate security threats, including preventive, detective, and corrective measures. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of access control, threat identification, and cryptography in safeguarding information systems.