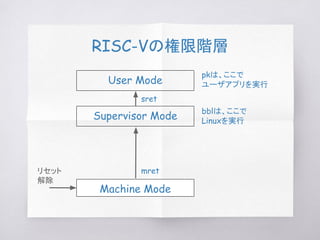
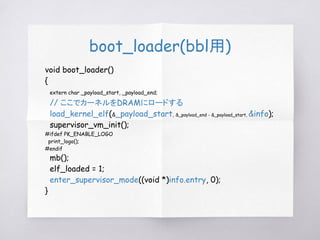
This document discusses RISC-V boot processes using the Berkeley Boot Loader (BBL) and RISC-V Proxy Kernel (PK). It explains how upon reset, code in Machine mode initializes the system and switches to Supervisor mode. The boot loader then loads an application ELF into memory. For BBL, it loads a Linux kernel, and for PK it loads a user application. Control is then transferred to the loaded program in User mode. Trap handling mechanisms involving different privilege modes are also covered.













![rest_of_boot_loader
static void rest_of_boot_loader(uintptr_t kstack_top)
{
arg_buf args;
size_t argc = parse_args(&args);
if (!argc)
panic("tell me what ELF to load!");
// load program named by argv[0]
long phdrs[128];
current.phdr = (uintptr_t)phdrs;
current.phdr_size = sizeof(phdrs);
// アプリケーション(args.argv[0])をDRAMにロードする
load_elf(args.argv[0], ¤t);
// ロードしたアプリケーションを実行する
run_loaded_program(argc, args.argv, kstack_top);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/riscv-pk-170109072427/85/RISC-V-Berkeley-Boot-Loader-Proxy-Kernel-15-320.jpg)


![tf : trapframe_t
pk/pk.h
typedef struct
{
long gpr[32];
long status; // LOAD t0, 32*REGBYTES(a0) : t0 => sstatus
long epc; // LOAD t1, 33*REGBYTES(a0) : t1 => sepc
long badvaddr;
long cause;
long insn;
} trapframe_t;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/riscv-pk-170109072427/85/RISC-V-Berkeley-Boot-Loader-Proxy-Kernel-18-320.jpg)









![.Lhandle_trap_in_machine_mode
.Lhandle_trap_in_machine_mode:
// 途中略
1:auipc t0, %pcrel_hi(trap_table) # t0 <- %hi(trap_table)
STORE t1, 6*REGBYTES(sp)
sll t1, a1, 2 # t1 <- mcause << 2
STORE t2, 7*REGBYTES(sp)
add t1, t0, t1 # t1 <- %hi(trap_table)[mcause]
STORE s0, 8*REGBYTES(sp)
LWU t1, %pcrel_lo(1b)(t1) # t1 <- trap_table[mcause]
STORE s1, 9*REGBYTES(sp)
mv a0, sp # a0 <- regs
STORE a2,12*REGBYTES(sp)
csrr a2, mepc # a2 <- mepc
STORE a3,13*REGBYTES(sp)
csrrw t0, mscratch, x0 # t0 <- user sp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/riscv-pk-170109072427/85/RISC-V-Berkeley-Boot-Loader-Proxy-Kernel-29-320.jpg)







![mcall_trap
machine/mtrap.c
Supervisor modeからのコール( pk用として用意されている)
void mcall_trap(uintptr_t* regs, uintptr_t mcause, uintptr_t mepc)
{
uintptr_t n = regs[17], arg0 = regs[10], arg1 = regs[11], retval;
switch (n)
{
case MCALL_HART_ID:
retval = mcall_hart_id();
break;
// case が続く](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/riscv-pk-170109072427/85/RISC-V-Berkeley-Boot-Loader-Proxy-Kernel-37-320.jpg)
