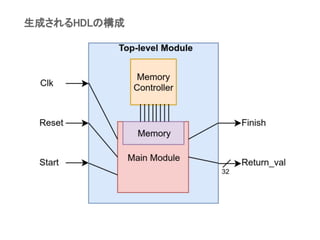
The document discusses leflow, a tool that enables flexible FPGA high-level synthesis of TensorFlow deep neural networks, detailing its optimization process using LLVM IR for better FPGA compatibility. It highlights the current limitations of leflow while suggesting potential areas for improvement, such as specific FPGA-targeted kernels in the XLA backend and enhanced memory partitioning algorithms for machine learning. Additionally, it mentions future enhancements like fixed-point representation support and improved debugging infrastructure for developers.




![最適化
Algorithm 1
%0 = bitcast i8** %params to [2 x float]**
%arg0 = load [2 x float] %0, align 8
=> @arg0 を global に変更し、ゼロで初期化
Algorithm 2
%arg0 = global [2 x float] zeroinitializer, align 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leflow-180722031411/85/LeFlow-6-320.jpg)
![MNIST
with tf.devide(“device:XLA_CPU:0”):
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.add(tf.matmul(input, weights)[0], bias))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leflow-180722031411/85/LeFlow-7-320.jpg)





