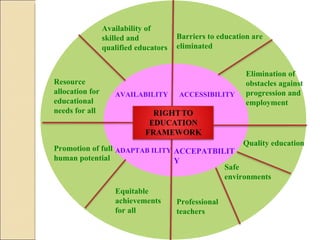
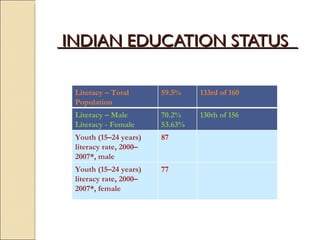
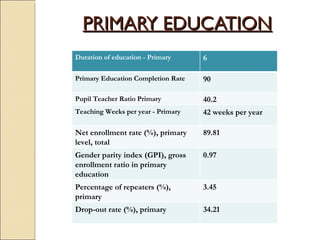
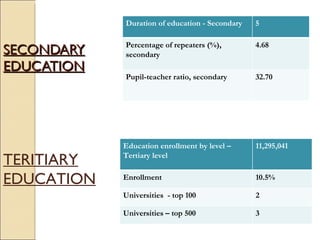
The document discusses the right to education and major initiatives in India to promote education. It highlights that education is a tool for empowerment and promoting individual freedom. It outlines key principles of availability, accessibility, adaptability and acceptability of education. It also provides statistics on literacy rates in India and challenges in the education system like dropouts, illiteracy among adults and women, lack of vocational skills, corruption and inadequate resources.