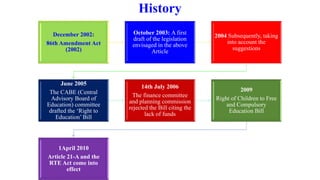
The Right to Education Act (RTE) provides free and compulsory elementary education to all children between ages 6-14. It aims to give effect to the constitutional amendment making education a fundamental right. Key aspects include mandatory admission of disadvantaged students, infrastructure standards for schools, teacher qualifications, and prohibitions on screening and fees for elementary education. However, challenges remain in implementation due to lack of funds, shortages of trained teachers, and inadequate infrastructure and support for inclusive education.