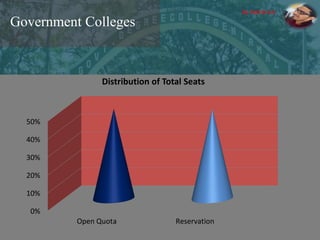
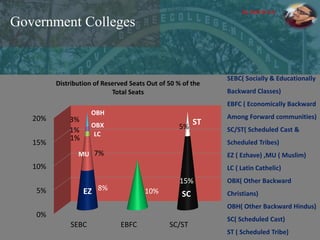
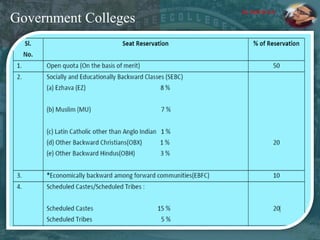
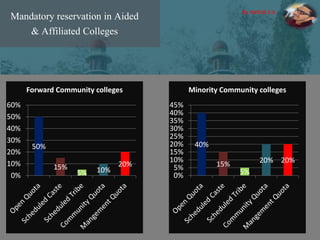
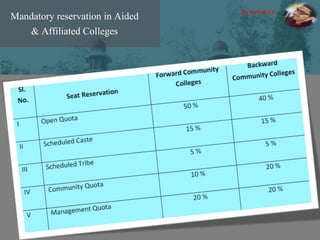
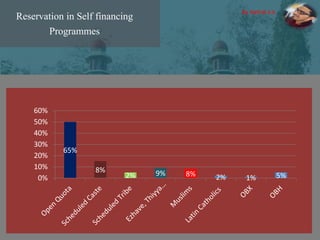
The document discusses the concept of inclusive education in India, highlighting the importance of integrating marginalized and differently abled children into mainstream schools. It elaborates on the definitions of marginalization, discrimination, and social exclusion, and outlines specific provisions in the Indian Constitution that promote the rights of these groups. It also identifies barriers to inclusion and suggests measures to improve educational access and support for these children.