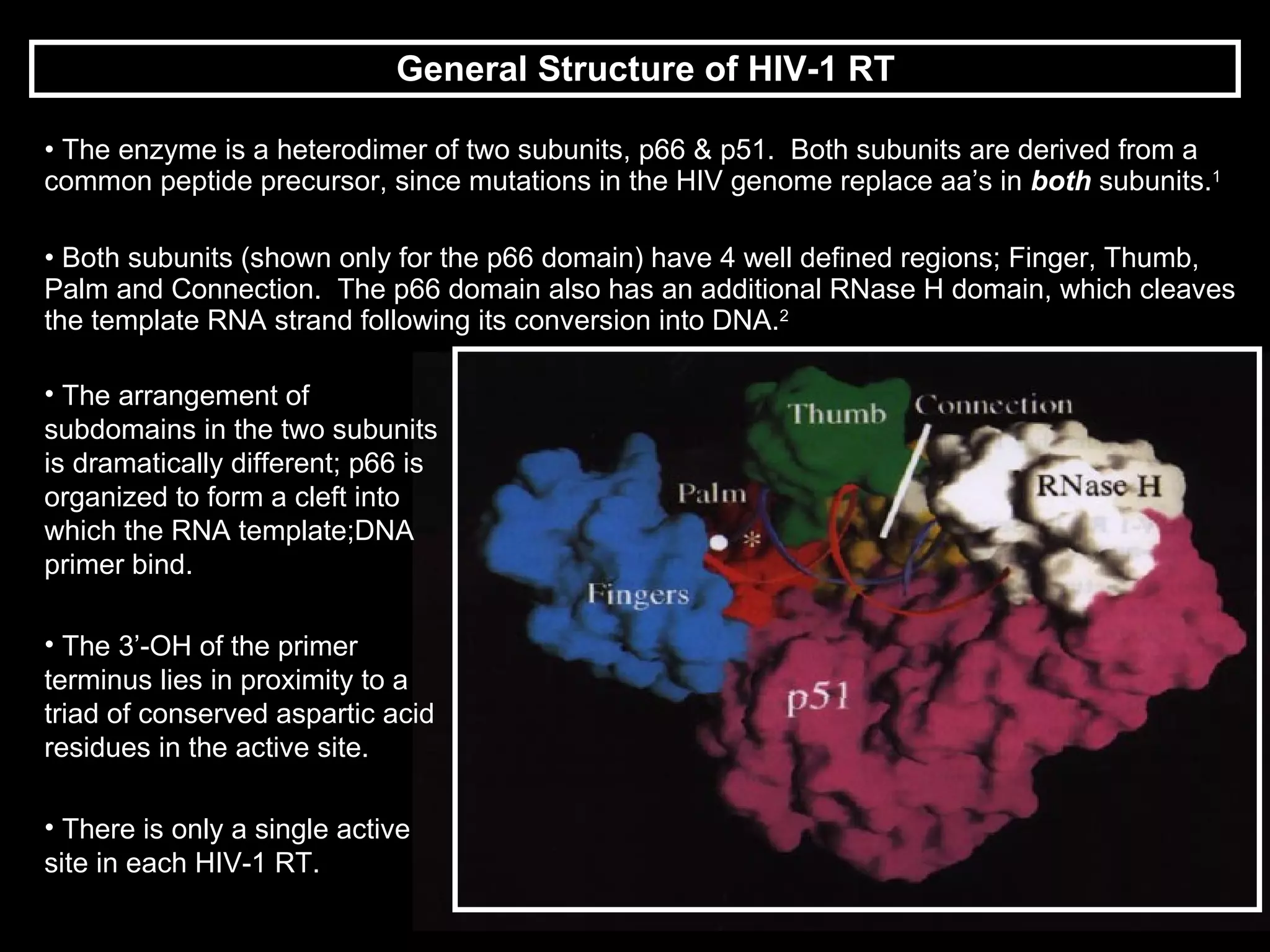
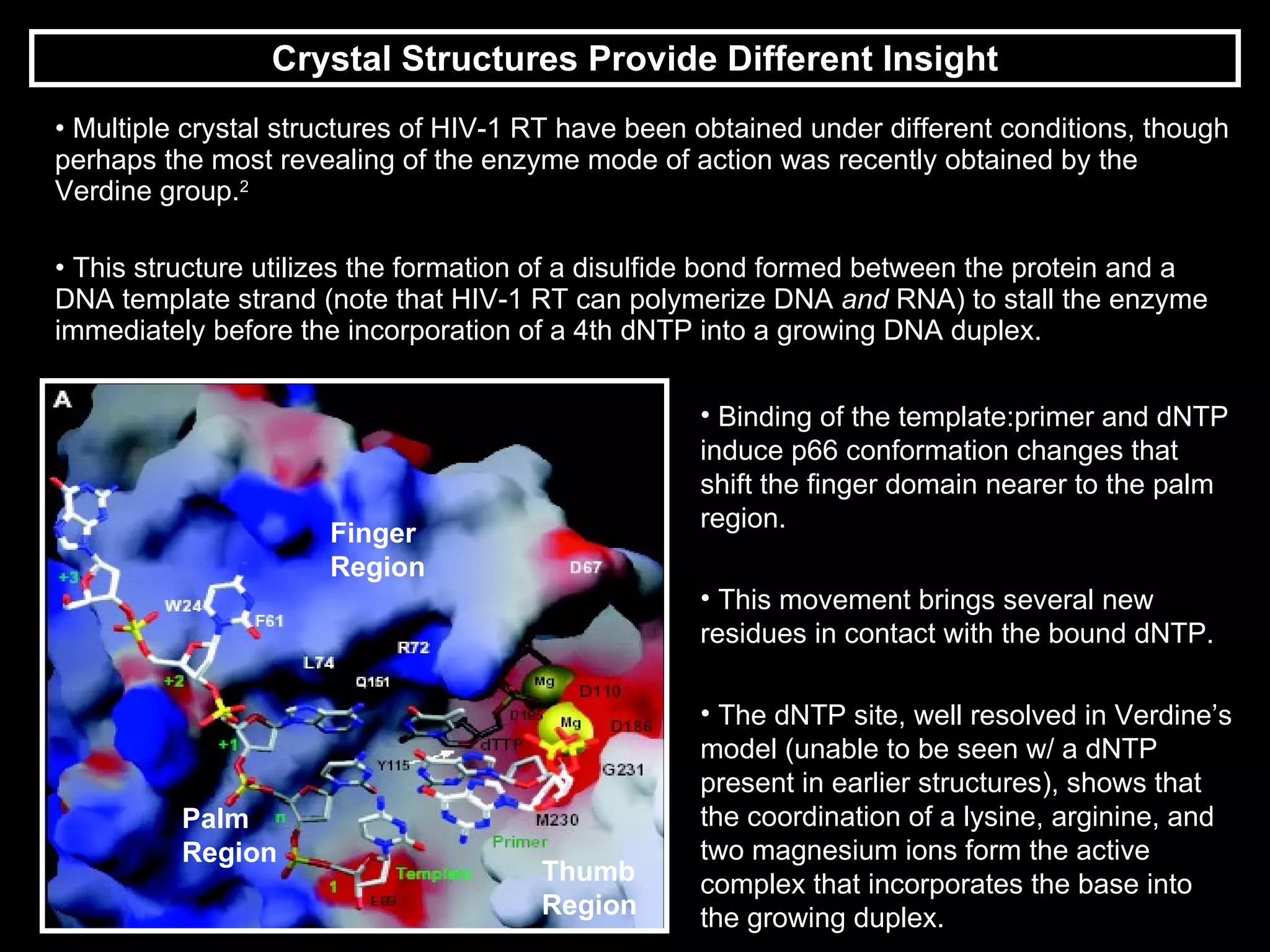
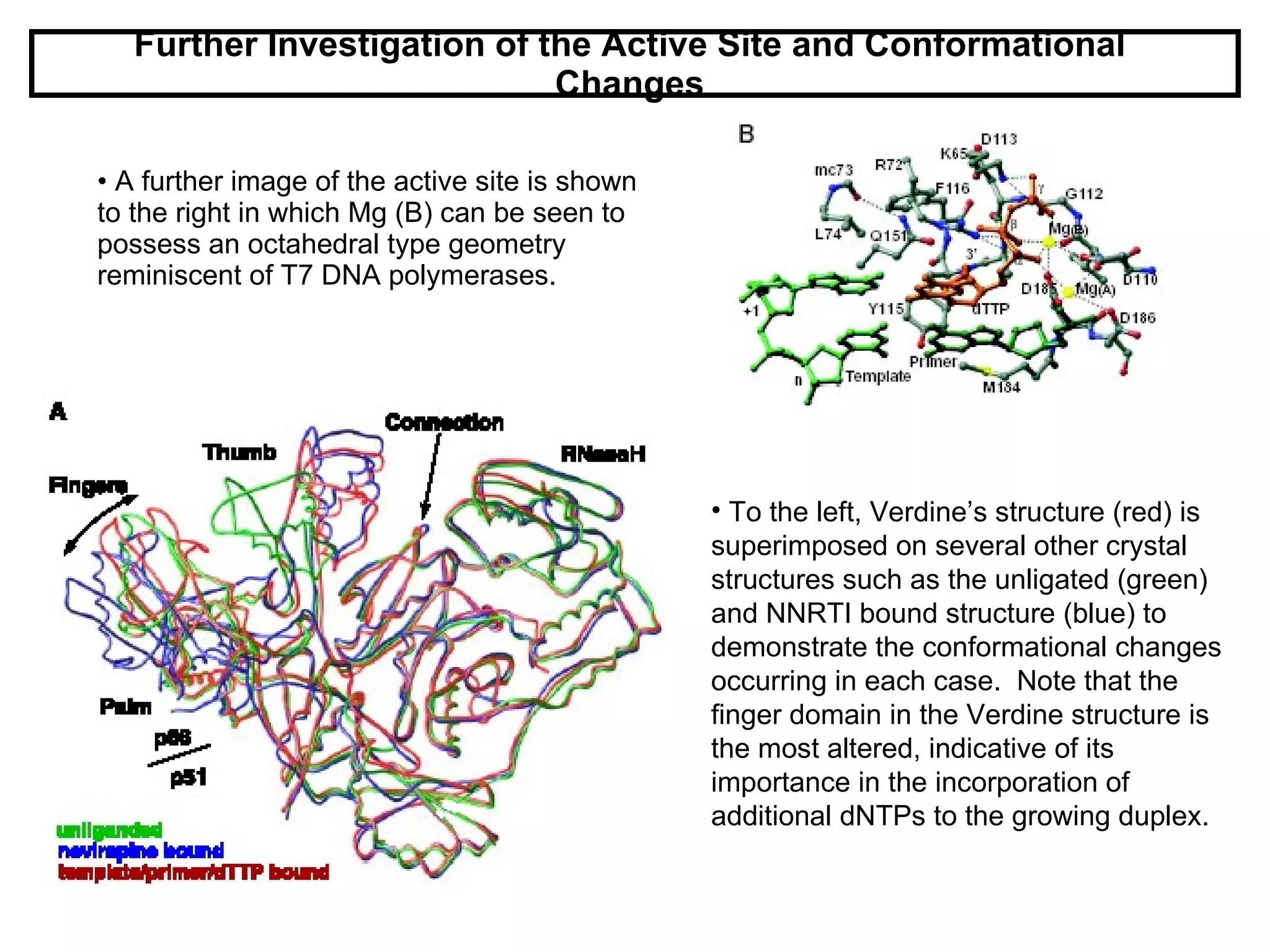
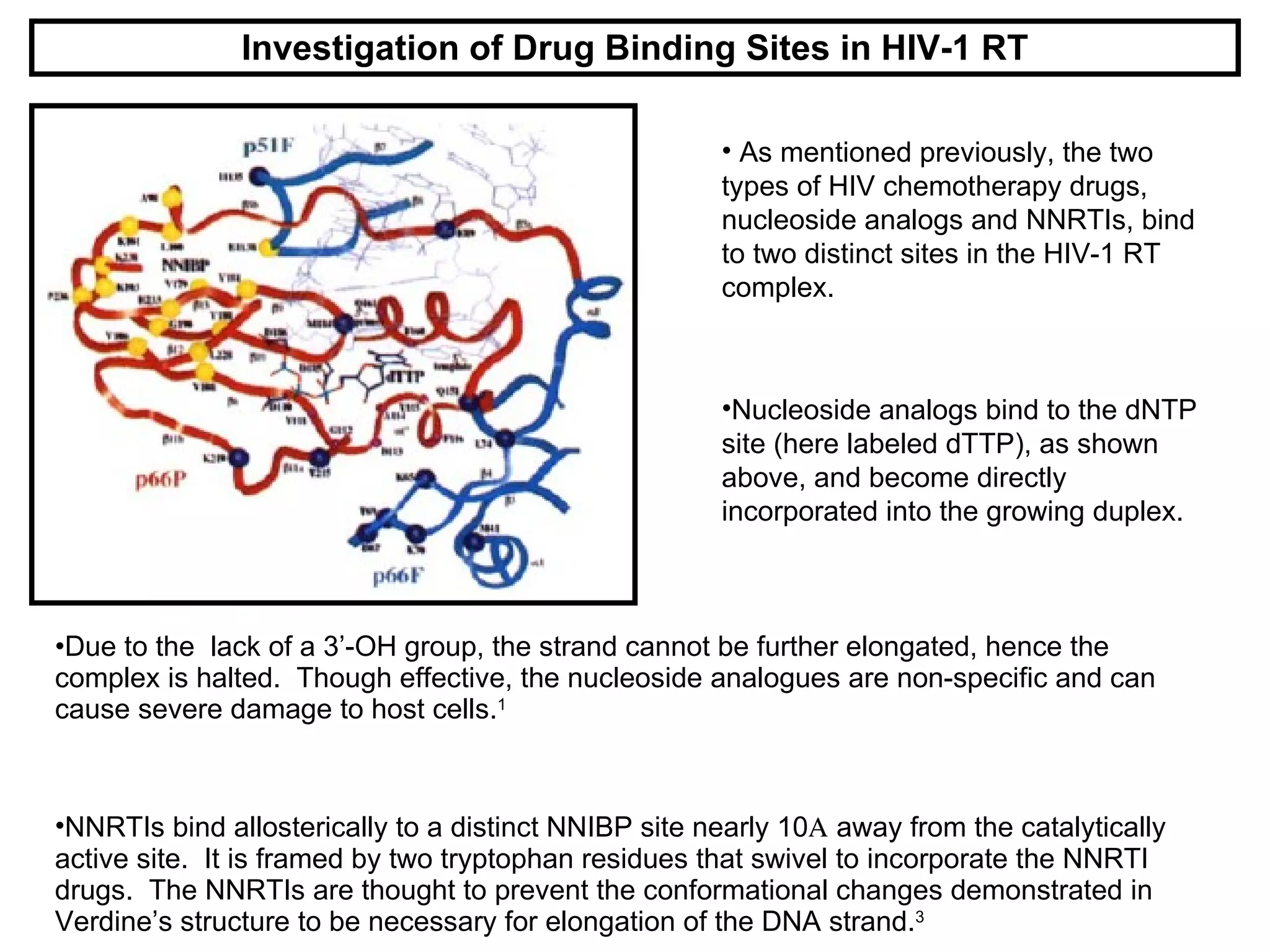
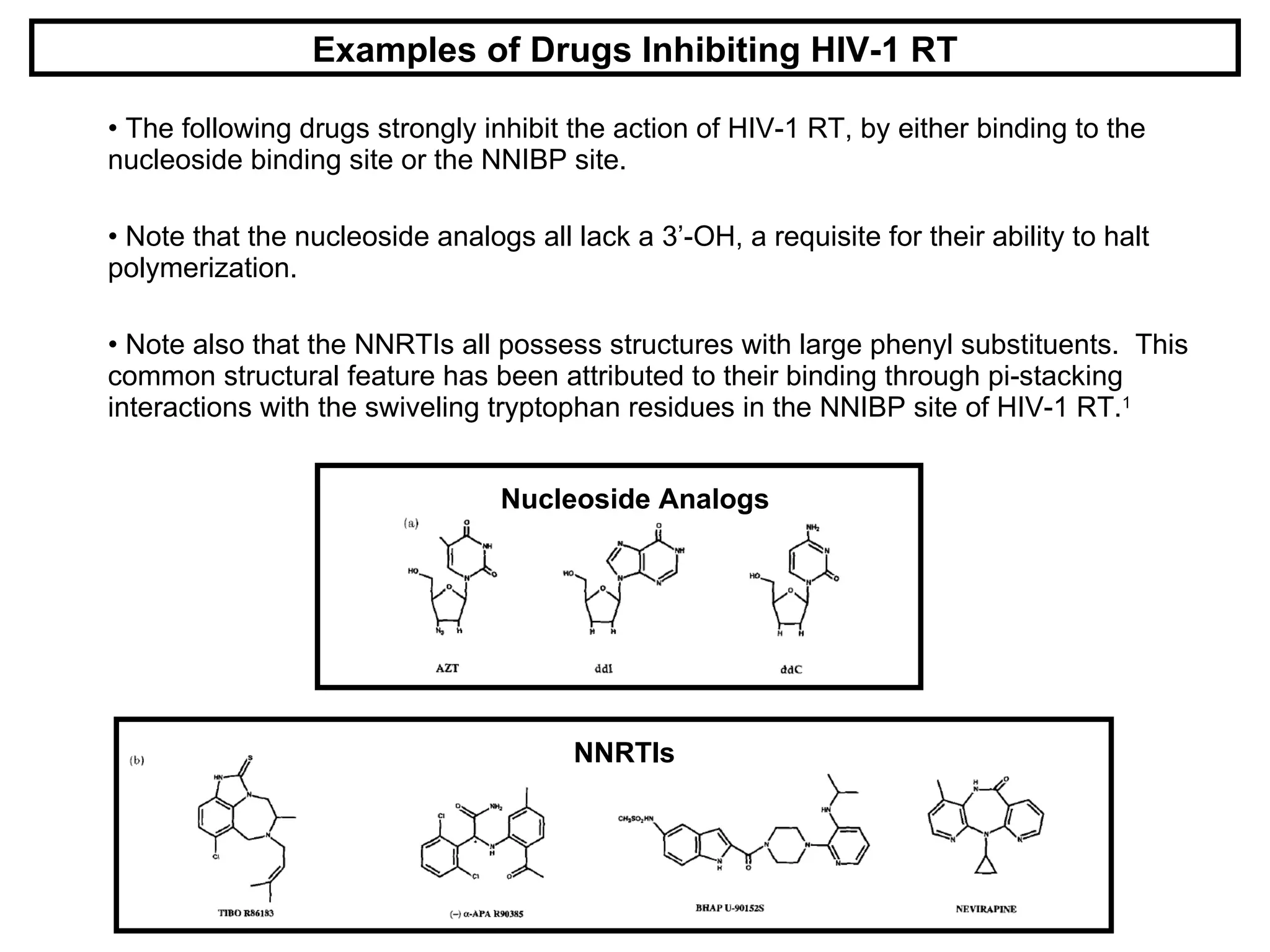
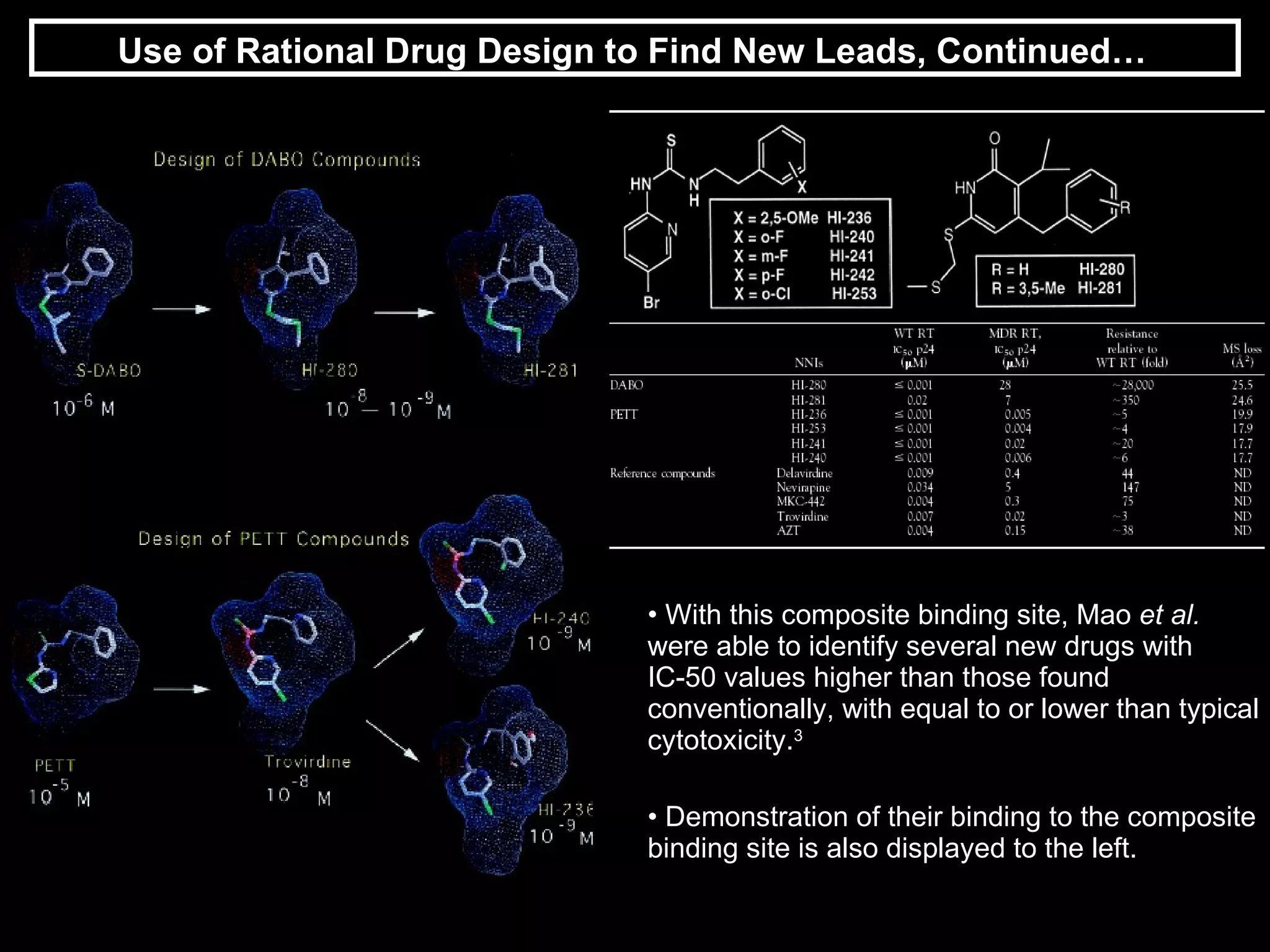
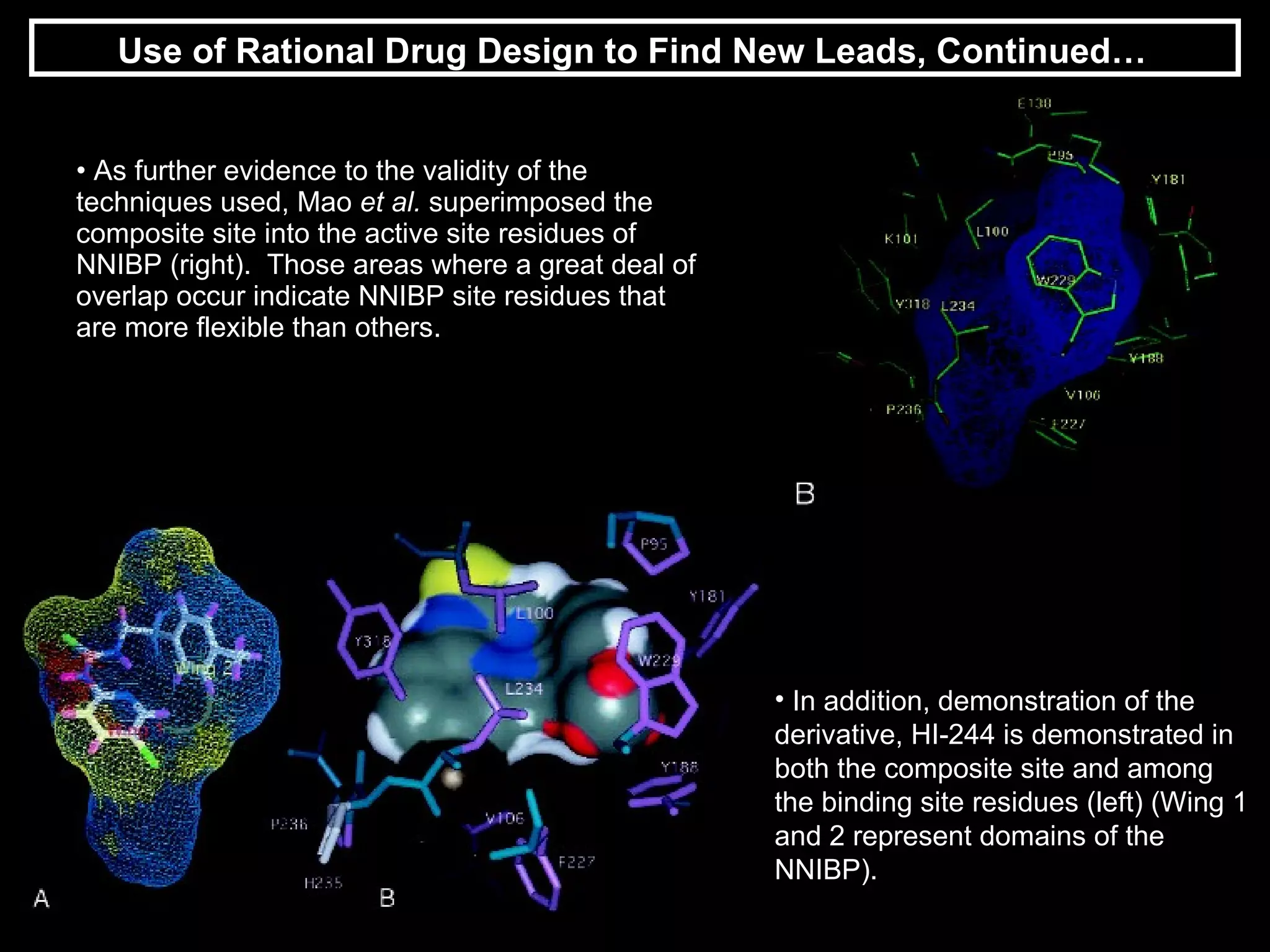
HIV reverse transcriptase is the primary target of AIDS drugs. It converts HIV's RNA code into DNA for viral replication. There are two classes of inhibitors: nucleoside analogs and non-nucleoside inhibitors (NNRTIs). NNRTIs bind to a site near the active site and prevent conformational changes needed for viral replication. Using composite binding sites from multiple structures allows rational drug design of new NNRTIs with higher inhibitory activity and lower toxicity than previous methods.