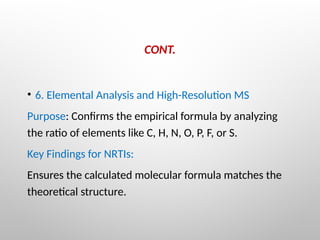
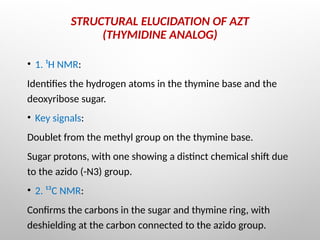
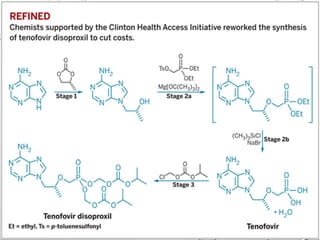
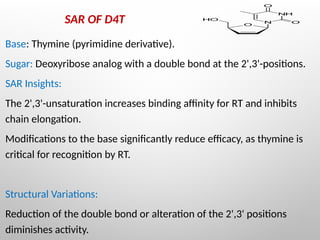
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) are classified based on their structural analogs and are key components in antiretroviral therapy for HIV and chronic hepatitis B infections. Their mechanism of action involves mimicking natural nucleotides, leading to chain termination in viral DNA synthesis. Various techniques, including NMR and mass spectrometry, are employed for structural elucidation and synthesis optimization of these compounds to enhance their efficacy and stability.









![CYTIDINE ANALOGS
Parent
cystidine
Lamivudine(2 ,3 -dideoxy-3 -
′ ′ ′
thiacytidine)
Emtricitabine (5-fluoro-1-[(2R,5S)-2-
(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-
yl]cytosine)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group8pharmacuetics2new-250125182632-f80ba7ab/85/Nucleoside-Reverse-transcriptase-inhibitors-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![GUANOSINE ANALOGS
Parent
Guanosine
Abacavir(ABC)
(4R)-4-[6-(cyclopropylamino)-2-
aminoguanin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-
1-methanol)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group8pharmacuetics2new-250125182632-f80ba7ab/85/Nucleoside-Reverse-transcriptase-inhibitors-pptx-11-320.jpg)