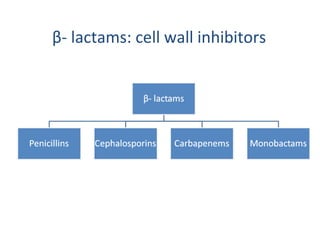
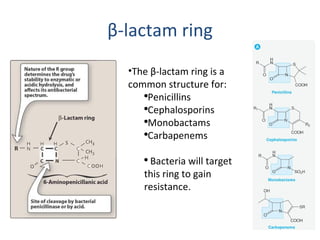
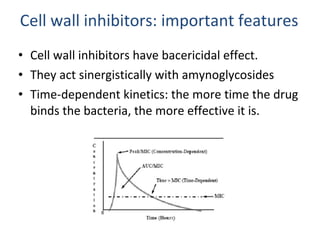
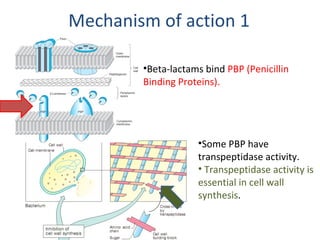
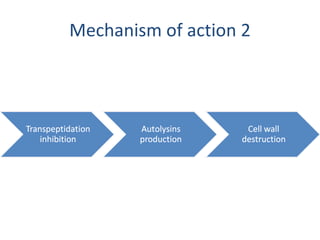
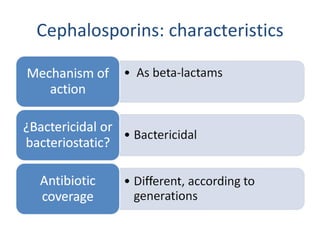
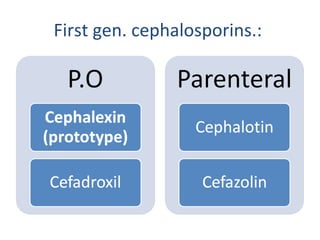
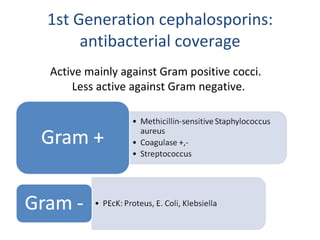
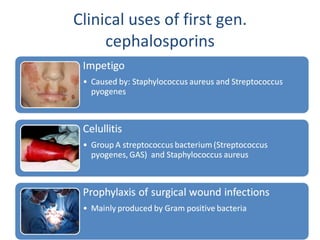
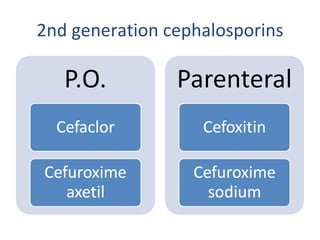
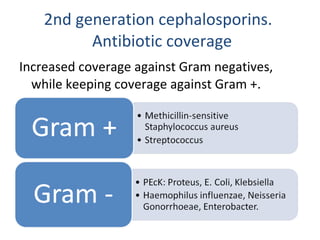
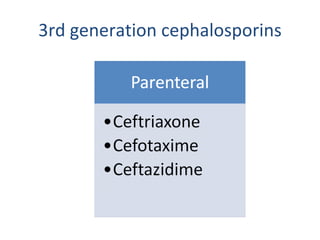
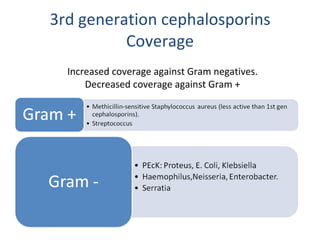
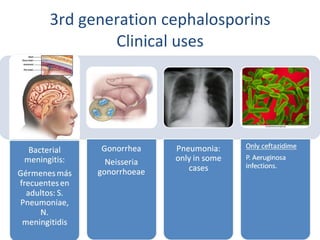
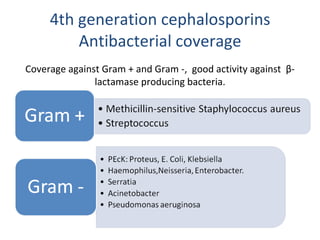
Cephalosporins are a class of beta-lactam antibiotics that share a beta-lactam ring structure with penicillins and other beta-lactams. They work by binding to penicillin-binding proteins in bacterial cell walls to inhibit cell wall synthesis. First generation cephalosporins are mainly active against gram-positive cocci, while later generations have increased gram-negative coverage. Each generation also has distinct and expanded clinical uses depending on their antimicrobial spectrum.