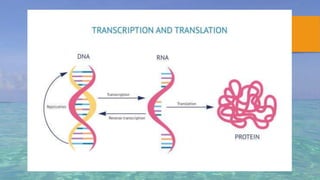
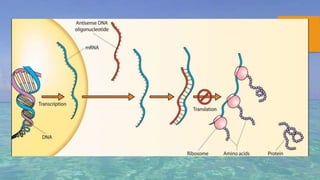
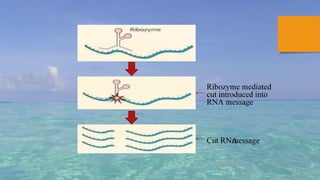
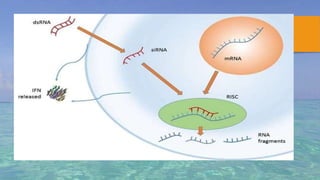
Gene silencing is a process where the expression of a gene is reduced or turned off. It occurs through transcriptional or post-transcriptional mechanisms. At the transcriptional level, gene expression is modified directly. At the post-transcriptional level, double stranded RNA suppresses gene expression by binding to mRNA and preventing protein production. There are three main gene silencing mechanisms - antisense oligonucleotides, ribozymes, and RNA interference. RNAi has become the most widely used mechanism due to its effectiveness and specificity. Gene silencing has many applications including developing treatments for diseases like cancer, HIV, and respiratory illnesses. It is also used to modify crop traits and study unknown gene functions.