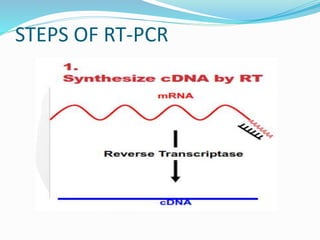
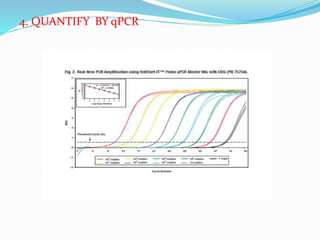
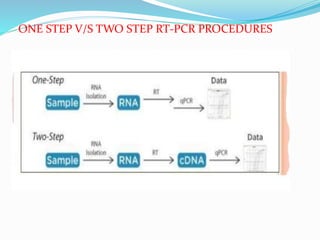
Reverse transcription is a technique used to generate cDNA from RNA. It involves using the enzyme reverse transcriptase to transcribe single-stranded RNA into cDNA. There are two common methods for reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR): one-step RT-PCR combines cDNA synthesis and PCR amplification in one reaction, while two-step RT-PCR performs cDNA synthesis and PCR amplification in separate reactions. The buffers and reagents used in RT-PCR, such as RT buffer, MgCl2, KCl, DTT, help stabilize the reaction and reduce RNA secondary structure.