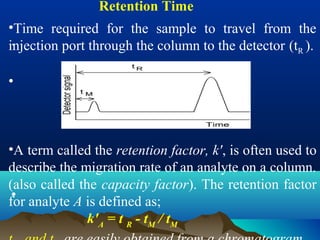
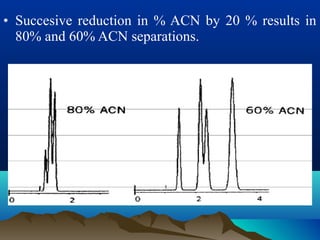
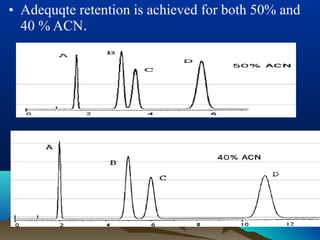
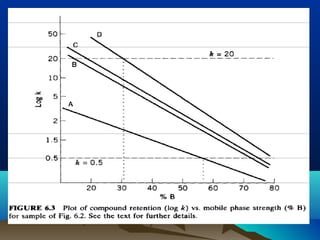
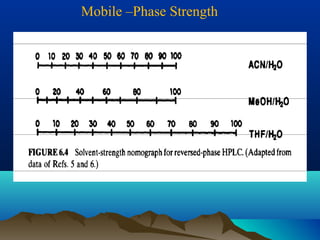
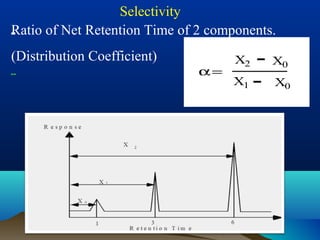
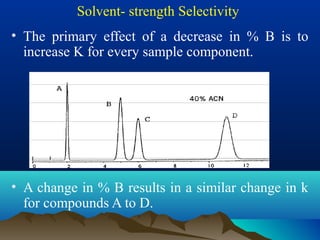
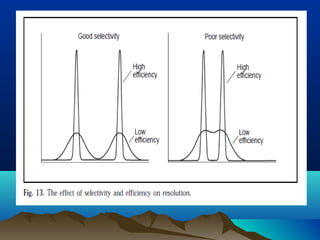
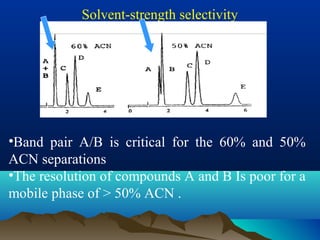
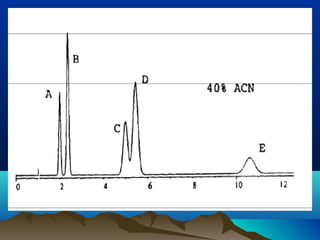
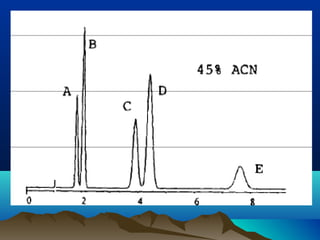
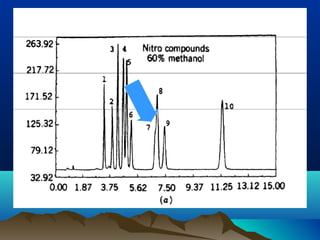
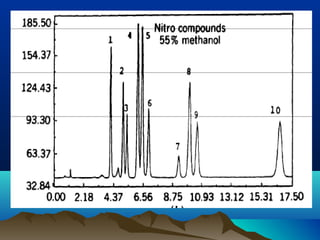
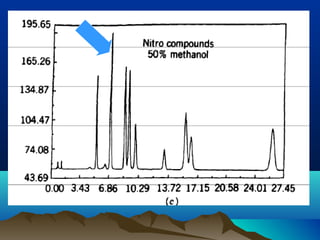
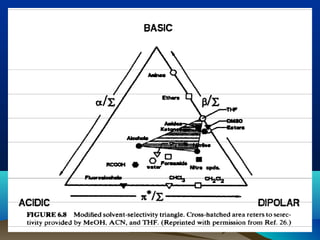
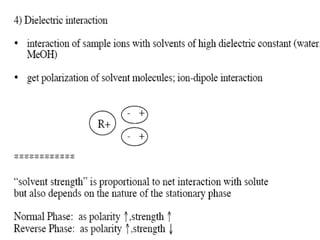
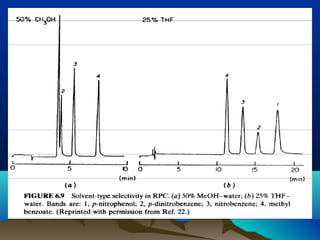
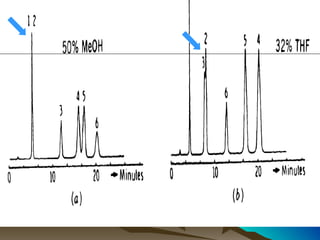
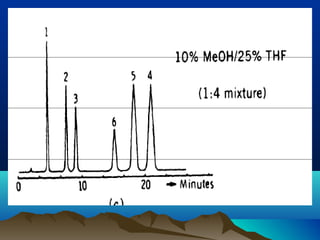
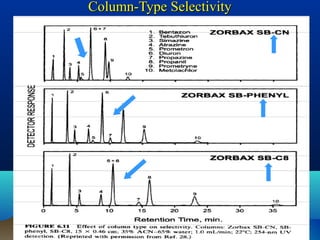
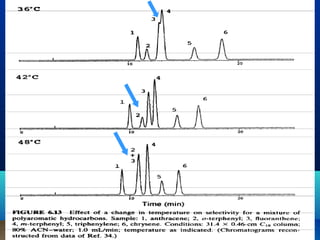
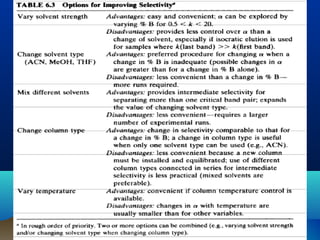
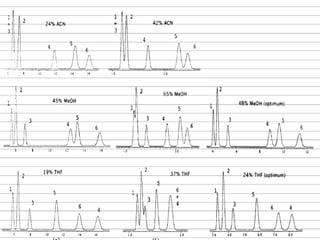
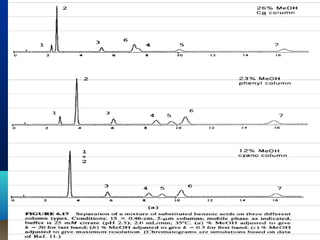
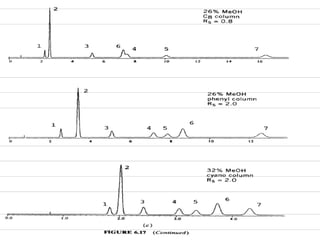
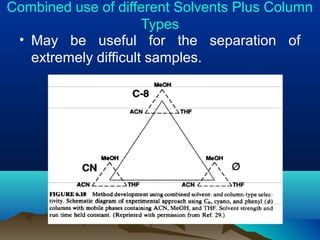
This document discusses reverse phase chromatography and factors that influence analyte retention times. It explains that analytes partition between the mobile and stationary phases, with more hydrophobic compounds retaining longer. Retention time is influenced by properties of both the analyte and experimental conditions like the mobile phase composition, column type, and temperature. Changing the mobile phase from more polar to less polar solvents decreases retention times.