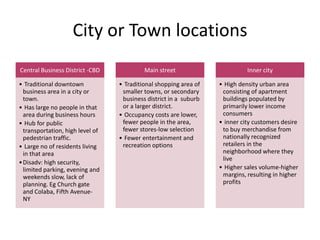
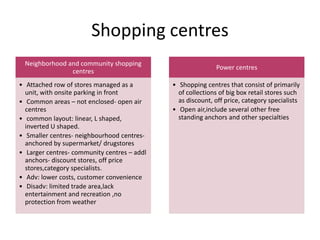
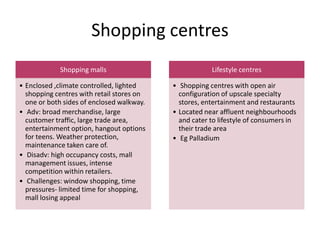
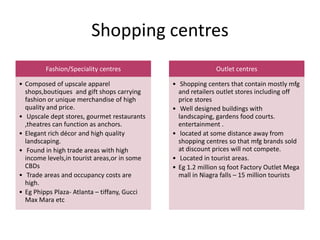
The document discusses the importance of location in retailing. Location is the prime consideration for customers and a strategic decision for competitive advantage, though it involves substantial investment and risk. There are three basic types of locations: free standing, city/town business districts, and shopping centres. Evaluation criteria for locations include trade area size, occupancy costs, traffic, and restrictions. Unplanned areas include free standing stores and urban locations, while shopping centres range from neighbourhood centres to enclosed malls to lifestyle centres. The type of location chosen must reinforce the retailer's strategy and target market's shopping behavior.