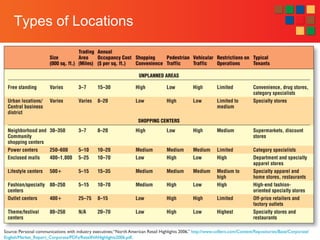
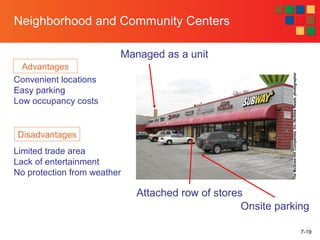
The document discusses various retail location strategies and types. It identifies location as one of the most important factors in retailing. It describes the advantages and disadvantages of different location types including free standing sites, shopping centers, malls, and other alternatives. Key considerations for retailers in selecting locations involve tradeoffs between factors like rent, traffic, size of customer base, and restrictions. Matching a location type to a retailer's strategy is important.