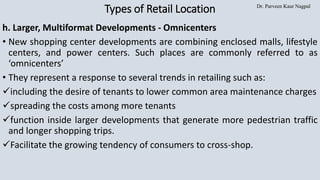
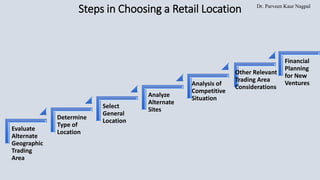
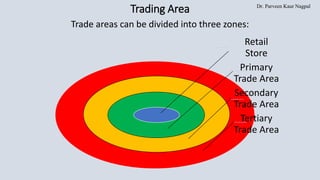
The document discusses the strategic importance of retail location planning, emphasizing that a well-chosen location provides a competitive advantage and significantly impacts customer traffic and revenue. Various types of retail locations are outlined, including freestanding stores, shopping centers, and non-traditional locations like pop-up shops and airport stores, each with unique benefits and challenges. The document also highlights the financial risks involved in location decisions, as retailers often commit to substantial investments or long-term leases.